ASTM D4446-05
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Anti-Swelling Effectiveness of Water-Repellent Formulations and Differential Swelling of Untreated Wood When Exposed to Liquid Water Environments
Standard Test Method for Anti-Swelling Effectiveness of Water-Repellent Formulations and Differential Swelling of Untreated Wood When Exposed to Liquid Water Environments
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is useful in determining the relative anti-swelling efficiency of various water-repellent formulations when applied to wood. It is the initial means of estimating the ability of water-repellent treated wood to perform satisfactorily when exposed to liquid water environments.
The swelling differences of untreated wood species when subjected to water immersion can also be determined by this test method.
This method is a basic screening test and thus provides an initial determination of the anti-swelling efficiency of water repellents. It is a qualitative method designed to provide a reproducible means of establishing: (1) the anti-swelling efficiency of water-repellent formulations, and (2) the relative swelling of untreated wood species when both are exposed to liquid water environments.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is designed to evaluate the effectiveness of water-repellent compositions for retarding dimensional changes in coated wood submerged in water. It can also be used to measure the differential swelling of untreated wood when exposed to liquid water environments. The compositions tested are designed to be mixed until uniform and applied by brush, roller, dip or spray to an exterior wood surface.
1.2The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D4446–05
Standard Test Method for
Anti-Swelling Effectiveness of Water-Repellent Formulations
and Differential Swelling of Untreated Wood When Exposed
1
to Liquid Water Environments
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4446; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ability of water-repellent treated wood to perform satisfactorily
when exposed to liquid water environments.
1.1 This test method is designed to evaluate the effective-
3.2 The swelling differences of untreated wood species
ness of water-repellent compositions for retarding dimensional
when subjected to water immersion can also be determined by
changesincoatedwoodsubmergedinwater.Itcanalsobeused
this test method.
to measure the differential swelling of untreated wood when
3.3 This method is a basic screening test and thus provides
exposed to liquid water environments. The compositions tested
an initial determination of the anti-swelling efficiency of water
are designed to be mixed until uniform and applied by brush,
repellents. It is a qualitative method designed to provide a
roller, dip or spray to an exterior wood surface.
reproducible means of establishing: (1) the anti-swelling effi-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
ciency of water-repellent formulations, and (2) the relative
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
swelling of untreated wood species when both are exposed to
only.
liquid water environments.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Apparatus
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 Conditioning Room or Chamber, having a controlled
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
temperature of 23 6 2°C (73.5 6 3.5°F), and a controlled
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
relative humidity of 50 6 5 %. This room is used to establish
2. Summary of Method a uniform moisture content in the test specimens. In all studies
the temperature and relative humidity selected by the investi-
2.1 Wood samples in the form of elongated slats that
gator must be stated and must remain constant throughout a
represent the timber species or product/treatment combination
given conditioning and test period.
to be evaluated are exposed in soak containers. The elongated
4.2 Balance, sensitive to at least 0.01 g.
slats are immersed in the water-repellent formulation, condi-
4.3 Treating Tank (Fig. 1).
tioned with appropriate weighing, then subjected to immersion
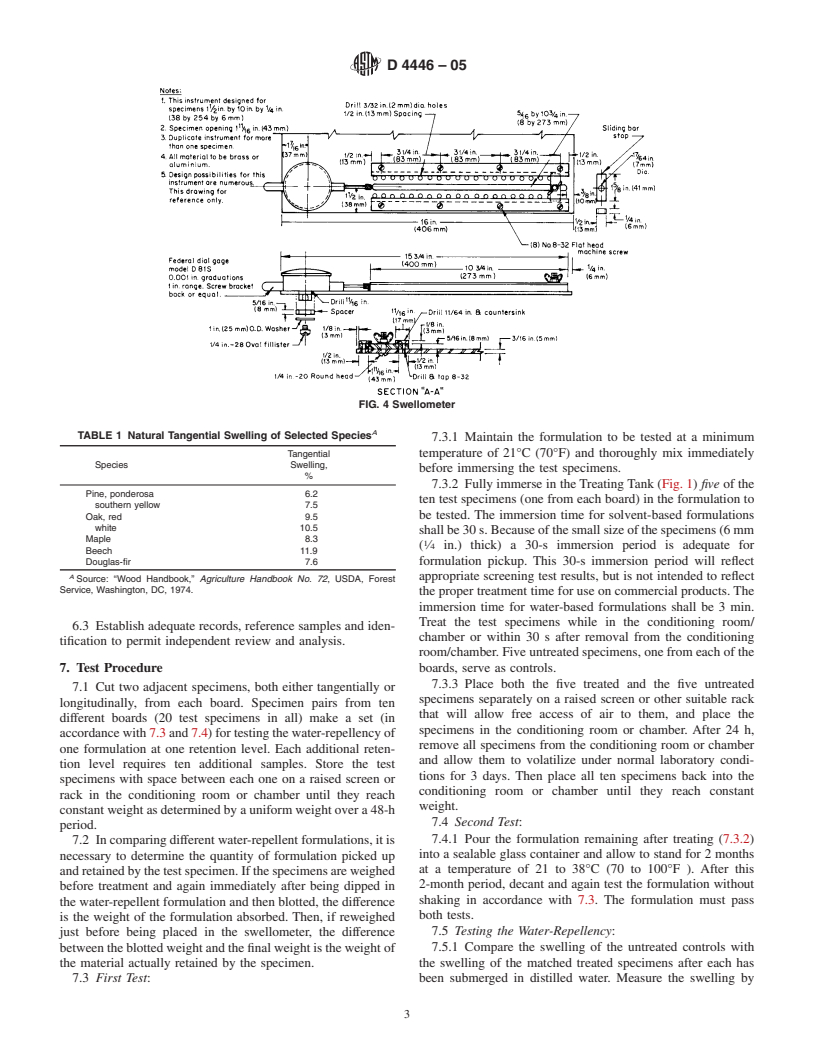
4.4 Swellometer, as illustrated in Fig. 2, Fig. 3, and Fig. 4.
in distilled water for a prescribed period. The untreated slats
omit the immersion in the water-repellent formulation. The
5. Test Specimens
swelling resulting from immersion for the selected time period
5.1 Wood used for these tests must be straight-grained,
is determined by reading a dial gage calibrated in increments of
flat-sawn, clear, kiln-dried Ponderosa pine sapwood or other
0.025 mm (0.001 in.).
suitable species. Cut the parent boards in a manner to give
2.2 A water repellent efficiency of 60 % is required to pass
1 1
specimens 6 mm ( ⁄4 in.) in the longitudinal dimension, 1 ⁄2 in.
this test.
(38 mm) in the radial dimension, and 254 mm (10 in.) in the
3. Significance and Use tangential dimension. Cut with a sharp, fine-toothed saw to
obtain as smooth a surface as possible without sanding.
3.1 This test method is useful in determining the relative
Number each specimen for identification and reference.
anti-swelling efficiency of various water-repellent formulations
5.1.1 Selection of Ponderosa pine sapwood can be assured
when applied to wood. It is the initial means of estimating the
by the following quick chemical test: (1) prepare a solution of
5 g of benzidine in 25 g of hydrochloric acid and 970 g of
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
water, and (2) prepare a second solution consisting of a 10 %
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
concentration of sodium nitrite in water. When the test is to be
Subcommittee D01.42 on Architectural Coatings.
made, pour equal amounts of the two solutions together and
Current edition approved May 15, 2005. Published June 2005. Originally
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D 4446 – 02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ---------------------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.