ASTM D3191-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Carbon Black in SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber)—Recipe and Evaluation Procedures
Standard Test Methods for Carbon Black in SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber)<span class='unicode'>—</span>Recipe and Evaluation Procedures
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The major portion of carbon black consumed by the rubber industry is used to improve the physical properties, life expectancy, and utility of rubber products. These test methods provide an SBR recipe and directions for evaluating all types of carbon black intended for use in rubber products. Other procedures are available elsewhere in the ASTM standards for the evaluation of carbon black itself.
These test methods may be used to characterize carbon black in terms of specific properties of the standard compound. These test methods are useful for the quality assurance of carbon black production. They may also be used for the preparation of reference compounds, to confirm the day-to-day reliability of testing operations used in the rubber industry, for the evaluation of experimental compounds, and quality control of production compounds.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the standard materials, test formula, mixing procedure, and test methods for the evaluation and production control of carbon blacks in styrene butadiene rubber (SBR).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3191 − 10
StandardTest Methods for
Carbon Black in SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber)—Recipe
1
and Evaluation Procedures
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3191; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D2084 Test Method for Rubber Property—Vulcanization
Using Oscillating Disk Cure Meter
1.1 These test methods cover the standard materials, test
D3182 PracticeforRubber—Materials,Equipment,andPro-
formula, mixing procedure, and test methods for the evaluation
cedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Preparing
and production control of carbon blacks in styrene butadiene
Standard Vulcanized Sheets
rubber (SBR).
D3674 Test Method for Carbon Black—Relative Extrusion
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the 3
Mass (Withdrawn 1999)
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
D4483 Practice for Evaluating Precision for Test Method
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Standards in the Rubber and Carbon Black Manufacturing
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the Industries
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
D5289 Test Method for Rubber Property—Vulcanization
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- Using Rotorless Cure Meters
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
E145 Specification for Gravity-Convection and Forced-
Ventilation Ovens
2. Referenced Documents
2
3. Significance and Use
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D412 Test Methods forVulcanized Rubber andThermoplas- 3.1 The major portion of carbon black consumed by the
tic Elastomers—Tension
rubber industry is used to improve the physical properties, life
D1646 Test Methods for Rubber—Viscosity, Stress expectancy, and utility of rubber products. These test methods
Relaxation, and Pre-Vulcanization Characteristics provideanSBRrecipeanddirectionsforevaluatingalltypesof
(Mooney Viscometer) carbon black intended for use in rubber products. Other
D1799 Practice for Carbon Black—Sampling Packaged procedures are available elsewhere in theASTM standards for
Shipments the evaluation of carbon black itself.
D1900 Practice for Carbon Black—Sampling Bulk Ship-
3.2 These test methods may be used to characterize carbon
ments
black in terms of specific properties of the standard compound.
These test methods are useful for the quality assurance of
1
carbon black production. They may also be used for the
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D24 on
Carbon Black and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D24.71 on Carbon
preparation of reference compounds, to confirm the day-to-day
Black Testing in Rubber.
reliability of testing operations used in the rubber industry, for
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2010. Published February 2010. Originally
´1 the evaluation of experimental compounds, and quality control
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D3191 – 09 . DOI:
10.1520/D3191-10. of production compounds.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3191 − 10
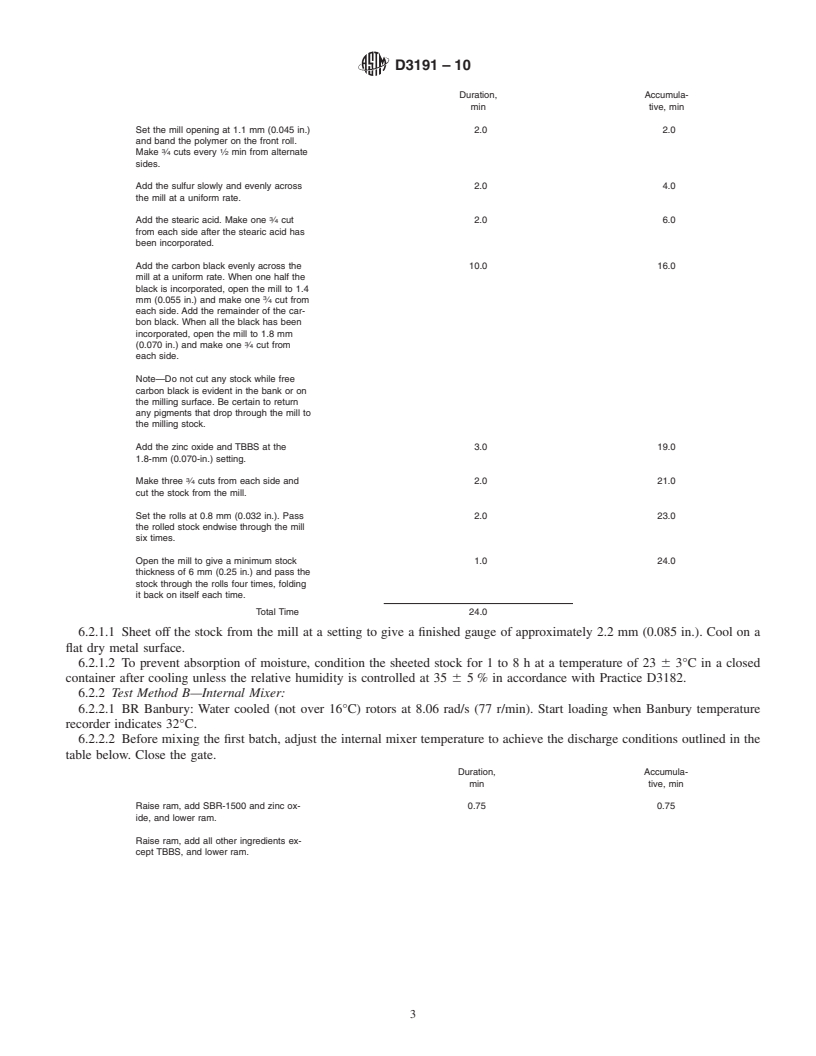
4. Standard Test Formula
Duration, Accumulative,
min min
4.1 Standard Formula:
Set the mill opening at 1.1 mm (0.045 in.) 2.0 2.0
A
Material IRM Quantity,
and band the polymer on the front roll.
No.
parts by
3 1
Make ⁄4 cuts every ⁄2 min from alternate
mass
sides.
SBR-1500 . 100.00
Add the sulfur slowly and evenly across 2.0 4.0
B,C
Zinc oxide 91 3.00
the mill at a uniform rate.
B,C
Sulfur 31 1.75
B,C
Stearic acid 21 1.00
3
Add the stearic acid. Make one ⁄4 cut 2.0 6.0
Carbon black . 50.00
from each side after the stearic acid has
C,D
TBBS . 1.00
been incorporated.
Total 156.75
E
Batch factor:
Add the carbon black evenly across the 10.0 16.0
mill at a uniform rate. When one half the
A
IRM 91 is available from G. H. Chemicals, Ltd., 1550 Brouillette St., P.O. Box
black is incorporated, open the mill to 1.4
456, St. Hyacinthe Quebec Canada, J2S 7B8. IRM 21 and IRM 31 are available 3
mm (0.055 in.) and make one ⁄4 cut from
from Akron Rubber Development Lab, 2887 Gilchrist Road, Akron, OH 44305.
each side. Add the remainder of the
B
FortheMIMproc
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation:D3191–09 Designation:D3191–10
Standard Test Methods for
Carbon Black in SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber)—Recipe
1
and Evaluation Procedures
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3191; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Note A in 4.1 and Table2 were editorially corrected in July 2009.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover the standard materials, test formula, mixing procedure, and test methods for the evaluation and
production control of carbon blacks in styrene butadiene rubber (SBR).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D412 Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic ElastomersTension
D1646 Test Methods for RubberViscosity, Stress Relaxation, and Pre-Vulcanization Characteristics (Mooney Viscometer)
D1799 Practice for Carbon BlackSampling Packaged Shipments
D1900 Practice for Carbon BlackSampling Bulk Shipments
D2084 Test Method for Rubber PropertyVulcanization Using Oscillating Disk Cure Meter
D3182 Practice for RubberMaterials, Equipment, and Procedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Preparing Standard
Vulcanized Sheets
3
D3674 Test Method for Carbon Black Relative Extrucion Mass
D4483 Practice for Evaluating Precision for Test Method Standards in the Rubber and Carbon Black Manufacturing Industries
D5289 Test Method for Rubber PropertyVulcanization Using Rotorless Cure Meters
E145 Specification for Gravity-Convection and Forced-Ventilation Ovens
3. Significance and Use
3.1 The major portion of carbon black consumed by the rubber industry is used to improve the physical properties, life
expectancy, and utility of rubber products. These test methods provide an SBR recipe and directions for evaluating all types of
carbon black intended for use in rubber products. Other procedures are available elsewhere in the ASTM standards for the
evaluation of carbon black itself.
3.2 Thesetestmethodsmaybeusedtocharacterizecarbonblackintermsofspecificpropertiesofthestandardcompound.These
testmethodsareusefulforthequalityassuranceofcarbonblackproduction.Theymayalsobeusedforthepreparationofreference
compounds, to confirm the day-to-day reliability of testing operations used in the rubber industry, for the evaluation of
experimental compounds, and quality control of production compounds.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D24 on Carbon Black and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D24.71 on Carbon Black
Testing in Rubber.
Current edition approved MayJan. 1, 2009.2010. Published May 2009.February 2010. Originally approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 20062009 as
´1
D3191 – 069 . DOI: 10.1520/D3191-09E01. DOI: 10.1520/D3191-10.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Withdrawn.
3
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3191–10
4. Standard Test Formula
4.1 Standard Formula:
A
Material IRM Quantity,
No. parts by
mass
SBR-1500 . 100.00
B,C
Zinc oxide 91 3.00
B,C
Sulfur 31 1.75
B,C
Stearic acid 21 1.00
Carbon black . 50.00
C,D
TBBS . 1.00
Total 156.75
E
Batch factor:
A
IRM 91 is available from G. H. Chemicals, Ltd., 1550 Brouillette St., P.O. Box 456, St. Hyacinthe Quebec Canada, J2S 7B8. IRM 21 and IRM 31 are available from
Akron Rubber Development Lab, 2887 Gilchrist Road, Akron, OH 44305.
B
For the MIM procedure, it is recommended that a blend of compounding materials be prepared to improve accuracy of the weighing of these materials. This material
blend is prepared by blending a proportional
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.