ASTM F2736-13e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for 6 to 30 in. (152 To 762 mm) Polypropylene (PP) Corrugated Single Wall Pipe And Double Wall Pipe (Withdrawn 2018)
Standard Specification for 6 to 30 in. (152 To 762 mm) Polypropylene (PP) Corrugated Single Wall Pipe And Double Wall Pipe (Withdrawn 2018)
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions, workmanship, elongation, brittleness, pipe stiffness, and markings for single wall corrugated polypropylene (PP) pipe and double wall corrugated polypropylene (PP) pipe. It covers nominal sizes 6 in. through 30 in. (152 mm through 762 mm).
1.2 The corrugated polypropylene pipes governed by this standard are intended for use in non-pressure applications for sanitary sewers, storm sewers and drainage pipes. Single wall corrugated polypropylene pipe shall not be used for sanitary sewer applications.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This specification covers requirements and test methods for materials, dimensions, workmanship, elongation, brittleness, pipe stiffness, and markings for single wall corrugated polypropylene (PP) pipe and double wall corrugated polypropylene (PP) pipe. It covers nominal sizes 6 in. through 30 in. (152 mm through 762 mm).
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems, this specification was withdrawn in February 2018 and replaced by F3219 Specification for 3 to 30 in. (75 to 750 mm) Polypropylene (PP) Corrugated Single Wall Pipe and Fittings.1
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation:F2736 −13 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
6 to 30 in. (152 To 762 mm) Polypropylene (PP) Corrugated
Single Wall Pipe And Double Wall Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2736; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
ε NOTE—8.7 was editorially corrected in December 2014.
1. Scope* D792 Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Rela-
tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
1.1 This specification covers requirements and test methods
D1238 Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics
for materials, dimensions, workmanship, elongation,
by Extrusion Plastometer
brittleness, pipe stiffness, and markings for single wall corru-
D1505 Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-
gated polypropylene (PP) pipe and double wall corrugated
Gradient Technique
polypropylene (PP) pipe. It covers nominal sizes 6 in. through
D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
30 in. (152 mm through 762 mm).
tics
1.2 The corrugated polypropylene pipes governed by this
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
standard are intended for use in non-pressure applications for
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
sanitary sewers, storm sewers and drainage pipes. Single wall
D2321 PracticeforUndergroundInstallationofThermoplas-
corrugated polypropylene pipe shall not be used for sanitary
tic Pipe for Sewers and Other Gravity-Flow Applications
sewer applications.
D2412 Test Method for Determination of External Loading
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
D2444 Test Method for Determination of the Impact Resis-
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
tance of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings by Means of a
and are not considered standard.
Tup (Falling Weight)
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D2990 Test Methods for Tensile, Compressive, and Flexural
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Creep and Creep-Rupture of Plastics
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
D3212 Specification for Joints for Drain and Sewer Plastic
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Pipes Using Flexible Elastomeric Seals
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
D3895 Test Method for Oxidative-Induction Time of Poly-
olefins by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2. Referenced Documents
D4101 Specification for Polypropylene Injection and Extru-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
sion Materials
D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
D6992 Test Method for Accelerated Tensile Creep and
Impact Resistance of Plastics
Creep-Rupture of Geosynthetic Materials Based on Time-
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
Temperature Superposition Using the Stepped Isothermal
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
Method
D790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
F477 Specification for Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets) for Join-
als
ing Plastic Pipe
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
2.2 American Association of State Highway and transpor-
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.26 on Olefin
tation Offıcials (AASHTO) Standard:
Based Pipe.
AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2013. Published December 2013. Originally
approved in 2010. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F2736-12. DOI:
10.1520/F2736–13E01.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Suite 249, Washington, DC 2001,
the ASTM website. http://www.transportation.org
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
F2736−13
2.3 Transportation Research Record: least two years from the date of manufacture without degrada-
TRR No. 2028 , “Guidelines for Interpreting AASHTO tion of the stated properties.
Specifications to Design or Evaluate Buried Structures
4.3 Rework Material—Clean polypropylene rework
with Comprehensive Solution Methods,” 2007.
material, generated from the manufacturer’s own production of
the product and having the same minimum physical properties,
3. Terminology
may be used by the manufacturer, provided that the pipe
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
produced meets all the requirements of this specification.
nology F412 and abbreviations are accordance with Terminol-
4.4 Rubber Materials—Rubber compounds used in the
ogy D1600, unless otherwise specified.
manufacture of sealing rings or gaskets shall meet the require-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
ments of Specification F477.
3.2.1 double wall pipe, n—corrugated pipe with a coex-
4.5 Lubricant—The lubricant used for assembly of gasketed
truded interior liner.
joints shall have no detrimental effect on the gasket or on the
3.2.2 single wall pipe, n—corrugated pipe without an inte-
pipe.
rior liner.
3.2.3 waterway wall, n—the pipe wall in single wall pipe
5. Joining System
and the interior wall in double wall pipe.
5.1 Bell and Spigot Joint:
5.1.1 The pipe ends shall consist of integrally formed bell
4. Materials
and spigot designed to accommodate a gasket, which when
4.1 Polypropylene—Polypropylene compounds used in the
assembled forms a watertight seal by the radial compression of
manufacture of corrugated single wall and double wall pipe
the gasket between the spigot and the bell ends.
shall have the minimum properties as shown in Table 1.
5.1.2 The joint shall be designed to avoid displacement of
Polypropylene compounds shall be comprised of the base
the gasket when it is assembled in accordance with the
polypropylene virgin material and all additives, colorants, UV
manufacturer’s recommendations.
inhibitors, and stabilizers. Polypropylene compounds can be
5.1.3 The assembly of the joint shall be in accordance with
pre-compounded or made in-situ during pipe extrusion by
the manufacturer’s recommendations.
combining natural polypropylene material with a color master-
5.2 Other Joining Systems—Where these connections are
batch or other additives, or both. Conditioning, sampling,
not practical or undesirable because of space, layout, or other
preparation and testing of molded specimens shall be in
requirements, joining methods such as external snap couplers,
accordance with the requirements in Specification D4101.
split couplers, or other joining methods that are equally
Material for preparation of molded specimens shall be taken
effective are to be used in accordance with the manufacturer’s
from the pipe.
recommendations.
4.2 Color and Ultraviolet (UV) Stabilization— The pipe
shall be colored or black. Black polypropylene compounds
6. Requirements
shall have between 2.0 and 3.0 percent carbon black. Colored
polypropylene compounds shall be protected from Ultraviolet 6.1 Workmanship—The pipe and fittings shall be homoge-
(UV) degradation with UV stabilizers. Colored polypropylene neous throughout and be as uniform as commercially practical
compoundsshallcontainsufficientUVprotectiontoallowpipe in color, opacity, and density. The pipe wall shall be free of
made according to this standard to be stored outdoors for at cracks,holes,blisters,voids,foreigninclusionsorotherdefects
Note-This figure is included for informational purposes only.
FIG. 1Typical Annular Corrugated Profile Wall Polypropylene Pipe with Interior Liner
´1
F2736−13
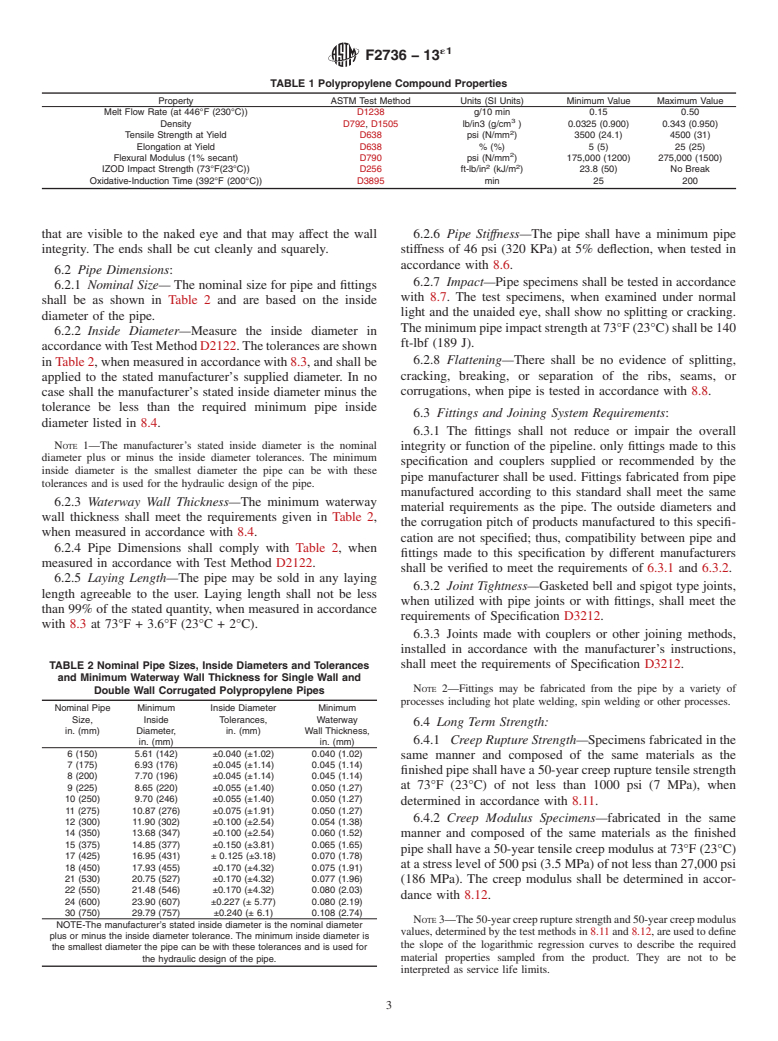
TABLE 1 Polypropylene Compound Properties
Property ASTM Test Method Units (SI Units) Minimum Value Maximum Value
Melt Flow Rate (at 446°F (230°C)) D1238 g/10 min 0.15 0.50
Density D792, D1505 lb/in3 (g/cm ) 0.0325 (0.900) 0.343 (0.950)
Tensile Strength at Yield D638 psi (N/mm ) 3500 (24.1) 4500 (31)
Elongation at Yield D638 % (%) 5 (5) 25 (25)
Flexural Modulus (1% secant) D790 psi (N/mm ) 175,000 (1200) 275,000 (1500)
2 2
IZOD Impact Strength (73°F(23°C)) D256 ft-lb/in (kJ/m ) 23.8 (50) No Break
Oxidative-Induction Time (392°F (200°C)) D3895 min 25 200
that are visible to the naked eye and that may affect the wall 6.2.6 Pipe Stiffness—The pipe shall have a minimum pipe
integrity. The ends shall be cut cleanly and squarely. stiffness of 46 psi (320 KPa) at 5% deflection, when tested in
accordance with 8.6.
6.2 Pipe Dimensions:
6.2.7 Impact—Pipe specimens shall be tested in accordance
6.2.1 Nominal Size— The nominal size for pipe and fittings
with 8.7. The test specimens, when examined under normal
shall be as shown in Table 2 and are based on the inside
light and the unaided eye, shall show no splitting or cracking.
diameter of the pipe.
Theminimumpipeimpactstrengthat73°F(23°C)shallbe140
6.2.2 Inside Diameter—Measure the inside diameter in
ft-lbf (189 J).
accordancewithTestMethodD2122.Thetolerancesareshown
6.2.8 Flattening—There shall be no evidence of splitting,
in Table 2, when measured in accordance with 8.3, and shall be
cracking, breaking, or separation of the ribs, seams, or
applied to the stated manufacturer’s supplied diameter. In no
corrugations, when pipe is tested in accordance with 8.8.
case shall the manufacturer’s stated inside diameter minus the
tolerance be less than the required minimum pipe inside
6.3 Fittings and Joining System Requirements:
diameter listed in 8.4.
6.3.1 The fittings shall not reduce or impair the overall
NOTE 1—The manufacturer’s stated inside diameter is the nominal
integrity or function of the pipeline. only fittings made to this
diameter plus or minus the inside diameter tolerances. The minimum
specification and couplers supplied or recommended by the
inside diameter is the smallest diameter the pipe can be with these
pipe manufacturer shall be used. Fittings fabricated from pipe
tolerances and is used for the hydraulic design of the pipe.
manufactured according to this standard shall meet the same
6.2.3 Waterway Wall Thickness—The minimum waterway
material requirements as the pipe. The outside diameters and
wall thickness shall meet the requirements given in Table 2,
the corrugation pitch of products manufactured to this specifi-
when measured in accordance with 8.4.
cation are not specified; thus, compatibility between pipe and
6.2.4 Pipe Dimensions shall comply with Table 2, when
fittings made to this specification by different manufacturers
measured in accordance with Test Method D2122.
shall be verified to meet the requirements of 6.3.1 and 6.3.2.
6.2.5 Laying Length—The pipe may be sold in any laying
6.3.2 Joint Tightness—Gasketed bell and spigot type joints,
length agreeable to the user. Laying length shall not be less
when utilized with pipe joints or with fittings, shall meet the
than 99% of the stated quantity, when measured in accordance
requirements of Specification D3212.
with 8.3 at 73°F + 3.6°F (23°C + 2°C).
6.3.3 Joints made with couplers or other joining methods,
installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions,
shall meet the requirements of Specification D3212.
TABLE 2 Nominal Pipe Sizes, Inside Diameters and Tolerances
and Minimum Waterway Wall Thickness for Single Wall and
NOTE 2—Fittings may be fabricated from the pipe by a variety of
Double Wall Corrugated Polypropylene Pipes
processes including hot plate welding, spin welding or other processes.
Nominal Pipe Minimum Inside Diameter Minimum
Size, Inside Tolerances, Waterway
6.4 Long Term Strength:
in. (mm) Diameter, in. (mm) Wall Thickness,
6.4.1 Creep Rupture Strength—Specimens fabricated in the
in. (mm) in. (mm)
6 (150) 5.61 (142) ±0.040 (±1.02) 0.040 (1.02)
same manner and composed of the same materials as the
7 (175) 6.93 (176) ±0.045 (±1.14) 0.045 (1.14)
finished pipe shall have a 50-year creep rupture tensile strength
8 (200) 7.70 (196) ±0.045 (±1.14) 0.045 (1.14)
at 73°F (23°C) of not less than 1000 psi (7 MPa), when
9 (225) 8.65 (220) ±0.055 (±1.40) 0.050 (1.27)
10 (250) 9.70 (246) ±0.055 (±1.40) 0.050 (1.27)
determined in accordance with 8.11.
11 (275) 10.87 (276) ±0.075 (±1.91) 0.050 (1.27)
6.4.2 Creep Modulus Specimens—fabricated in the same
12 (300) 11.90 (302) ±0.100 (±2.54) 0.054 (1.38)
14 (350) 13.68 (347) ±0.100 (±2.54) 0.060 (1.52)
manner and composed of the same materials as the finished
15 (375) 14.85 (377) ±0.150 (±3.81) 0.065 (1.65)
pipe shall have a 50-year tensile creep modulus at 73°F (23°C)
17 (425) 16.95 (431) ± 0.125 (±3.18) 0.070 (1.78)
atastresslevelof500psi(3.5MPa)ofnotlessthan27,000psi
18 (450) 17.93 (455) ±0.170 (±4.32) 0.075 (1.91)
21 (530) 20.75 (527) ±0.170 (±4.32) 0.077 (1.96)
(186 MPa). The creep modulus shall be determined in accor-
22 (550) 21.48 (546) ±0.170 (±4.32) 0.080 (2.03)
dance with 8.12.
24 (600) 23.90 (607) ±0.227 (± 5.77) 0.080 (2.19)
30 (750) 29.79 (757) ±0.240 (± 6.1) 0.108 (2.74)
NOTE3—The50-yearcreeprupturestrengthand50-yearcreepmodulus
NOTE-The manufacturer’s stated inside diameter is the nominal diameter
values, determined by the test methods in 8.11 and 8.12, are used to define
plus or minus the inside diameter tolerance. The minimum inside diameter is
the slope of the logarithmic regression curves to describe the required
the smallest diameter the pipe can be with these tolerances and is used for
the hydraulic design of the pipe. material properties sampled from the product. They are not to be
interpreted as service life limits.
´1
F2736−13
6.5 Installation Requirements—The pipe manufacturer shall pitch; (2) Locate the first specimen in the loading machine
provide the purchaser with the requirements for the proper eitheralongamoldlineorwiththeimaginarylinebetweentwo
installation of the pipe and the minimum and maximum corrugations described by the mold line and parallel to the
allowable cover height for specific traffic and non-traffic loading plates. The specimen must lay flat on the plate within
loading conditions. The installation requirements shall be ⁄8 in. (3 mm) and may be straightened by hand bending at
based
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.