ASTM D6784-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Elemental, Oxidized, Particle-Bound and Total Mercury in Flue Gas Generated from Coal-Fired Stationary Sources (Ontario Hydro Method)
Standard Test Method for Elemental, Oxidized, Particle-Bound and Total Mercury in Flue Gas Generated from Coal-Fired Stationary Sources (Ontario Hydro Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The measurement of particle-bound, oxidized, elemental, and total mercury in stationary-source flue gases provides data that can be used for emissions assessments and reporting, the certification of continuous mercury monitoring systems, regulatory compliance determinations and research programs associated with dispersion modeling, deposition evaluation, human health and environmental impact assessments. Particle-bound, oxidized, and elemental mercury measurements before and after control devices may be necessary for optimizing and evaluating the mercury removal efficiency of emission control technologies.
5.2 This test method was developed for the measurement of mercury in coal-fired power plants and has been extensively validated for that application. With additional procedures given in this standard, it is also applicable to sources having a flue gas composition with high levels of hydrochloric acid, and low levels of sulfur dioxide.
SCOPE
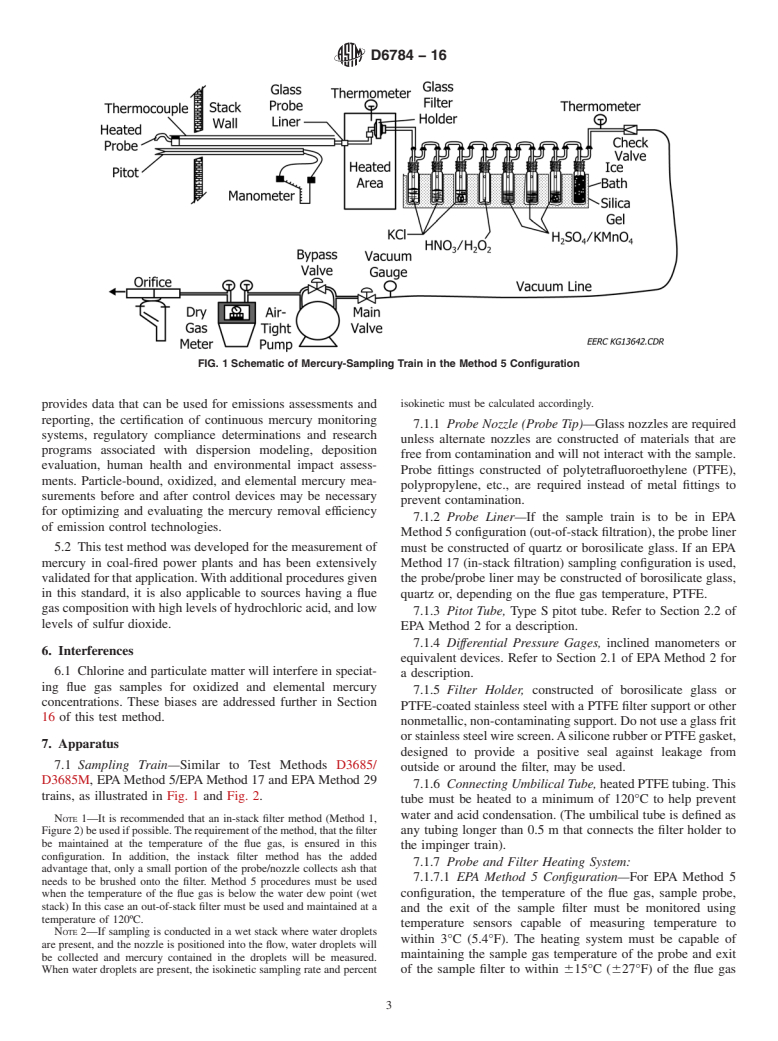
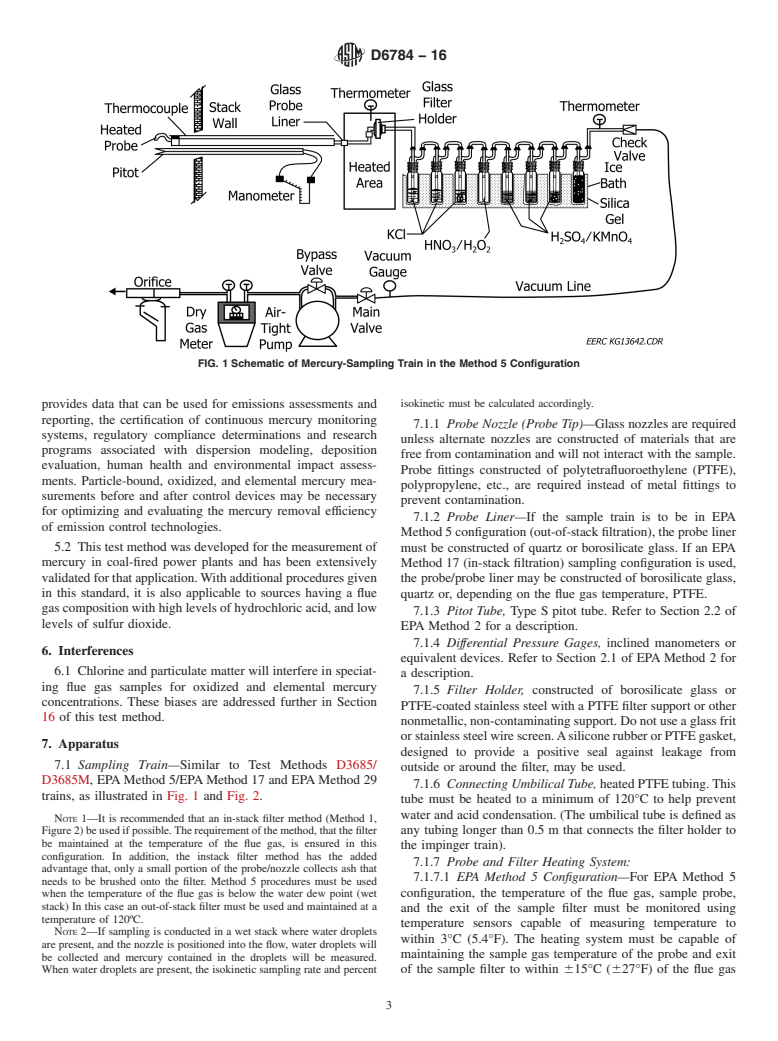
1.1 This test method applies to the determination of elemental, oxidized, particle-bound, and total mercury emissions from coal-fired stationary sources.
1.2 This test method is applicable to elemental, oxidized, particle-bound, and total mercury concentrations ranging from approximately 0.5 to 100 μg/Nm3.
1.3 This test method describes equipment and procedures for obtaining samples from effluent ducts and stacks, equipment and procedures for laboratory analysis, and procedures for calculating results.
1.4 This test method is applicable for sampling elemental, oxidized, and particle-bound mercury in flue gases of coal-fired stationary sources. It may not be suitable at all measurement locations, particularly those with high particulate loadings, as explained in Section 16.
1.5 Method applicability is limited to flue gas stream temperatures within the thermal stability range of the sampling probe and filter components.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard requires users to be familiar with EPA stack-gas sampling procedures as stated in EPA Methods 1–4, Method 5, and Method 17.
1.8 The method requires a high level of experience and quality control both in the field testing and analytical procedures in order to obtain high quality data.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6784 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Elemental, Oxidized, Particle-Bound and Total Mercury in
Flue Gas Generated from Coal-Fired Stationary Sources
1
(Ontario Hydro Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6784; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.10 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This test method applies to the determination of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
elemental, oxidized, particle-bound, and total mercury emis-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
sions from coal-fired stationary sources.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.2 This test method is applicable to elemental, oxidized,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
particle-bound, and total mercury concentrations ranging from
3
approximately 0.5 to 100 µg/Nm .
2. Referenced Documents
2
1.3 This test method describes equipment and procedures
2.1 ASTM Standards:
for obtaining samples from effluent ducts and stacks, equip-
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
ment and procedures for laboratory analysis, and procedures
D1356Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
for calculating results.
Atmospheres
D3154Test Method for Average Velocity in a Duct (Pitot
1.4 This test method is applicable for sampling elemental,
Tube Method)
oxidized,andparticle-boundmercuryinfluegasesofcoal-fired
D3685/D3685MTestMethodsforSamplingandDetermina-
stationary sources. It may not be suitable at all measurement
tion of Particulate Matter in Stack Gases
locations, particularly those with high particulate loadings, as
D3796Practice for Calibration of Type S Pitot Tubes
explained in Section 16.
D4840Guide for Sample Chain-of-Custody Procedures
1.5 Method applicability is limited to flue gas stream
D7036Practice for Competence of Air Emission Testing
temperatureswithinthethermalstabilityrangeofthesampling
Bodies
probe and filter components.
E2251Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
3
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
2.2 Other Standards:
EPAMethod1SampleandVelocityTraversesforStationary
1.7 This standard requires users to be familiar with EPA
Sources
stack-gas sampling procedures as stated in EPAMethods 1–4,
EPA Method 2Determination of Stack Gas Velocity and
Method 5, and Method 17.
Volumetric Flow Rate (Type S Pitot Tube)
1.8 The method requires a high level of experience and
EPA Method 3Gas Analysis for the Determination of Dry
quality control both in the field testing and analytical proce-
Molecular Weight
dures in order to obtain high quality data.
EPA Method 4Determination of Moisture Content in Stack
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Gases
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
EPAMethod 5Determination of Particulate Emissions from
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Stationary Sources
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.03 on Ambient the ASTM website.
3
Atmospheres and Source Emissions. EPA Methods1–29 available from the U.S. Environmental Protection
Current edition approved March 1, 2016. Published June 2016. Originally Agency’s Emission Measurement Technical Information Center or Code of Federal
approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D6784–02 (2008). Regulations (40 CFR Part 60, Appendix A), Method 101A in 40 CFR Part 61,
DOI: 10.1520/D6784-16. Appendix B, Method 301 in 40 CFR 63AppendixA40 CFR Part 61,Appendix B.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6784 − 16
tp 3
EPAMethod 12Determination of Inorganic Lead Emissions Hg =concentration of particle-bound mercury, µg/Nm
0 3
from Stationary Sou
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6784 − 02 (Reapproved 2008) D6784 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Elemental, Oxidized, Particle-Bound and Total Mercury in
Flue Gas Generated from Coal-Fired Stationary Sources
1
(Ontario Hydro Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6784; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method applies to the determination of elemental, oxidized, particle-bound, and total mercury emissions from
coal-fired stationary sources.
1.2 This test method is applicable to elemental, oxidized, particle-bound, and total mercury concentrations ranging from
3
approximately 0.5 to 100 μg/Nm .
1.3 This test method describes equipment and procedures for obtaining samples from effluent ducts and stacks, equipment and
procedures for laboratory analysis, and procedures for calculating results.
1.4 This test method is applicable for sampling elemental, oxidized, and particle-bound mercury in flue gases of coal-fired
stationary sources. It may not be suitable at all measurement locations, particularly those with high particulate loadings, as
explained in Section 16.
1.5 Method applicability is limited to flue gas stream temperatures within the thermal stability range of the sampling probe and
filter components.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard assumesrequires users are to be familiar with EPA stack-gas sampling procedures as stated in EPA Methods
1–4, Method 5, and Method 17.
1.8 The method requires a high level of experience and quality control both in the field testing and analytical procedures in order
to obtain high quality data.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of Atmospheres
D2986 Practice for Evaluation of Air Assay Media by the Monodisperse DOP (Dioctyl Phthalate) Smoke Test (Withdrawn
3
2004)
D3154 Test Method for Average Velocity in a Duct (Pitot Tube Method)
D3685/D3685M Test Methods for Sampling and Determination of Particulate Matter in Stack Gases
D3796 Practice for Calibration of Type S Pitot Tubes
D4840 Guide for Sample Chain-of-Custody Procedures
D7036 Practice for Competence of Air Emission Testing Bodies
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.03 on Ambient Atmospheres
and Source Emissions.
Current edition approved April 1, 2008March 1, 2016. Published July 2008June 2016. Originally approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 20022008 as
D6784 – 02.D6784 – 02 (2008). DOI: 10.1520/D6784-02R08.10.1520/D6784-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6784 − 16
E1E2251 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass ThermometersLiquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermometers with Low-Hazard
Precision Liquids
3
2.2 Other Standards:
EPA Method 1 Sample and Velocity Traverses for Stationary Sources
EPA Method 2 Determination of Stack Gas Velocity and Volumetric Flow Rate (Type S Pitot Tube)
EPA Method 3 Gas Analysis for the Determination of Dry Molecular Weight
EPA Method 4 Determination of Moisture Content in Stack Gases
EPA Method 5 Determination of Particulate Emissions from Stationary Sources
EPA Method 12 Determination of Inorganic Lead Emissions from Stationary Sources
EPA Method 17 Determination of Particulate Emissions from Stationary Sources (In-Stack Filtration Method)
EPA Method 29 Determination of Metals Emissions from Stationary Sources
EPA Method 101A Determination of Particle-Bound and Gaseous Mercury Emissions from Sewage Sludge In
...
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6784 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Elemental, Oxidized, Particle-Bound and Total Mercury in
Flue Gas Generated from Coal-Fired Stationary Sources
1
(Ontario Hydro Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6784; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.10 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This test method applies to the determination of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
elemental, oxidized, particle-bound, and total mercury emis-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
sions from coal-fired stationary sources.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.2 This test method is applicable to elemental, oxidized,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
particle-bound, and total mercury concentrations ranging from
3
approximately 0.5 to 100 µg/Nm .
2. Referenced Documents
2
1.3 This test method describes equipment and procedures
2.1 ASTM Standards:
for obtaining samples from effluent ducts and stacks, equip-
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
ment and procedures for laboratory analysis, and procedures
D1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
for calculating results.
Atmospheres
D3154 Test Method for Average Velocity in a Duct (Pitot
1.4 This test method is applicable for sampling elemental,
Tube Method)
oxidized, and particle-bound mercury in flue gases of coal-fired
D3685/D3685M Test Methods for Sampling and Determina-
stationary sources. It may not be suitable at all measurement
tion of Particulate Matter in Stack Gases
locations, particularly those with high particulate loadings, as
D3796 Practice for Calibration of Type S Pitot Tubes
explained in Section 16.
D4840 Guide for Sample Chain-of-Custody Procedures
1.5 Method applicability is limited to flue gas stream
D7036 Practice for Competence of Air Emission Testing
temperatures within the thermal stability range of the sampling
Bodies
probe and filter components.
E2251 Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
3
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
2.2 Other Standards:
EPA Method 1 Sample and Velocity Traverses for Stationary
1.7 This standard requires users to be familiar with EPA
Sources
stack-gas sampling procedures as stated in EPA Methods 1–4,
EPA Method 2 Determination of Stack Gas Velocity and
Method 5, and Method 17.
Volumetric Flow Rate (Type S Pitot Tube)
1.8 The method requires a high level of experience and
EPA Method 3 Gas Analysis for the Determination of Dry
quality control both in the field testing and analytical proce-
Molecular Weight
dures in order to obtain high quality data.
EPA Method 4 Determination of Moisture Content in Stack
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Gases
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
EPA Method 5 Determination of Particulate Emissions from
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Stationary Sources
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.03 on Ambient the ASTM website.
3
Atmospheres and Source Emissions. EPA Methods 1 – 29 available from the U.S. Environmental Protection
Current edition approved March 1, 2016. Published June 2016. Originally Agency’s Emission Measurement Technical Information Center or Code of Federal
approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D6784 – 02 (2008). Regulations (40 CFR Part 60, Appendix A), Method 101A in 40 CFR Part 61,
DOI: 10.1520/D6784-16. Appendix B, Method 301 in 40 CFR 63 Appendix A40 CFR Part 61, Appendix B.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6784 − 16
tp 3
EPA Method 12 Determination of Inorganic Lead Emissions Hg = concentration of particle-bound mercury, µg/Nm
0 3
from Stationary Sources Hg = concentration of elemental mercury, µg/Nm
2+ 3
EPA Method 17 Determination of Par
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.