ASTM A914/A914M-92(1999)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Steel Bars Subject to Restricted End-Quench Hardenability Requirements
Standard Specification for Steel Bars Subject to Restricted End-Quench Hardenability Requirements
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers hot-worked alloy and carbon-boron steels designed to attain restricted depth of hardening in the end-quench test. These steel compositions are identified by the suffix letter "RH" added to the conventional grade number.
1.2 In general, steels with restricted hardenability (RH steels) will exhibit a hardness range not greater than 5 HRC at the initial position on the end-quench hardenability bar and not greater than 65% of the hardness range for standard H-band steels (Specification A304) in the inflection region. Generally the restricted hardenability band follows the middle of the corresponding standard H-band. An example of the RH band compared with the H band is given for Grade 4140 in Fig. 1.
1.3 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and SI units. However, the material will be supplied to inch-pound units unless the purchase order specifies the "M" specification designation.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: A 914/A 914M – 92 (Reapproved 1999) An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
Steel Bars Subject to Restricted End-Quench Hardenability
Requirements
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 914/A 914M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This specification covers hot-worked alloy and carbon- 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
boron steels designed to attain restricted depth of hardening in 3.1.1 hardenability—the relative ability of a steel to harden
the end-quench test. These steel compositions are identified by under heat treatment becomes apparent in the degree to which
the suffix letter “RH” added to the conventional grade number. the material hardens when quenched at different cooling rates.
1.2 In general, steels with restricted hardenability (RH 3.1.1.1 Discussion— Hardenability is measured quantita-
steels) will exhibit a hardness range not greater than 5 HRC at tively, usually by noting the extent or depth of hardening of a
the initial position on the end-quench hardenability bar and not standard size and shape test specimen in a standardized
greater than 65 % of the hardness range for standard H-band quench. In the end-quench test the depth of hardening is the
steels (Specification A 304) in the inflection region. Generally distance along the specimen from the quenched end to a given
the restricted hardenability band follows the middle of the hardness.
corresponding standard H-band. An example of the RH band
4. Ordering Information
compared with the H band is given for Grade 4140 in Fig. 1.
1.3 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units 4.1 Orders for material under this specification should
include the following information, in proper sequence:
and SI units. However, the material will be supplied to
inch-pound units unless the purchase order specifies the “M” 4.1.1 Quantity (weight),
4.1.2 Name of material (alloy or carbon-boron steel),
specification designation.
4.1.3 Cross-sectional shape,
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.4 Size,
2.1 ASTM Standards: 4.1.5 Length,
A 29/A 29M Specification for Steel Bars, Carbon and Alloy, 4.1.6 Grade,
Hot-Wrought and Cold Finished, General Requirements 4.1.7 End-quenched hardenability (see Section 9),
for 4.1.8 Report of heat analysis, if desired (see Section 7),
A 255 Test Methods for Determining Hardenability of 4.1.9 Special straightness, if required,
Steel 4.1.10 ASTM designation and date of issue, and
A 304 Specification for Steel Bars, Alloy, Subject to End- 4.1.11 End use or special requirements.
Quench Hardenability Requirements
NOTE 1—A typical ordering description is as follows: 10 000 lb, alloy
E 112 Test Method for Determining Average Grain Size
bars, round, 4.0-in. diameter by 10 ft, Grade 4140RH, heat analysis
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
required, complete hardenability data required, ASTM AXXX, [AXXXM]
2.2 SAE Standards:
dated _____ worm gear.
J 406 Methods of Determining Hardenability of Steels
4.2 The purchaser shall specify the desired grade, including
J 1268 Hardenability Bands for Carbon and Alloy H Steels
the suffix letters “RH”, in accordance with Table 1.
J 1868 Restricted Hardenability Bands for Selected Alloy
4.3 Band limits are shown graphically and as tabulations in
Steels
Figs. 2-23, inclusive. For specification purposes, one must use
tabulated values of Rockwell hardness (HRC) as a function of
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel,
distance from the quenched end of the hardenability bar, either
Stainless Steel, and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
in inch-pound units (sixteenths of an inch) or in SI units
A01.15 on Bars.
(millimetres). Values below 20 HRC are not specified because
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 1992. Published February 1993.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05. such values are not accurate.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
4.3.1 Band limits shown graphically are so depicted for
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01.
convenience in estimating the hardness values at various
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Dr.,
intermediate locations on the end quench test bar for quick
Warrendale, PA 15096.
A 914/A 914M
comparisons of the various RH grades. The values of “Ap- 6. General Requirements
proximate Diameter of Rounds with Same As-Quenched Hard-
6.1 Material furnished under this specification shall con-
ness” shown above each RH-band, were selected from ranges
form to the applicable requirements of the current edition of
appearing in Fig. 7 of SAE J406. The RH-bands are presented
Specification A 29/A 29M, unless otherwise provided for
graphically, with distances from the quenched end in both
herein.
inch-pound units and also SI units.
4.4 For specification purposes, RH-band steels shall exhibit
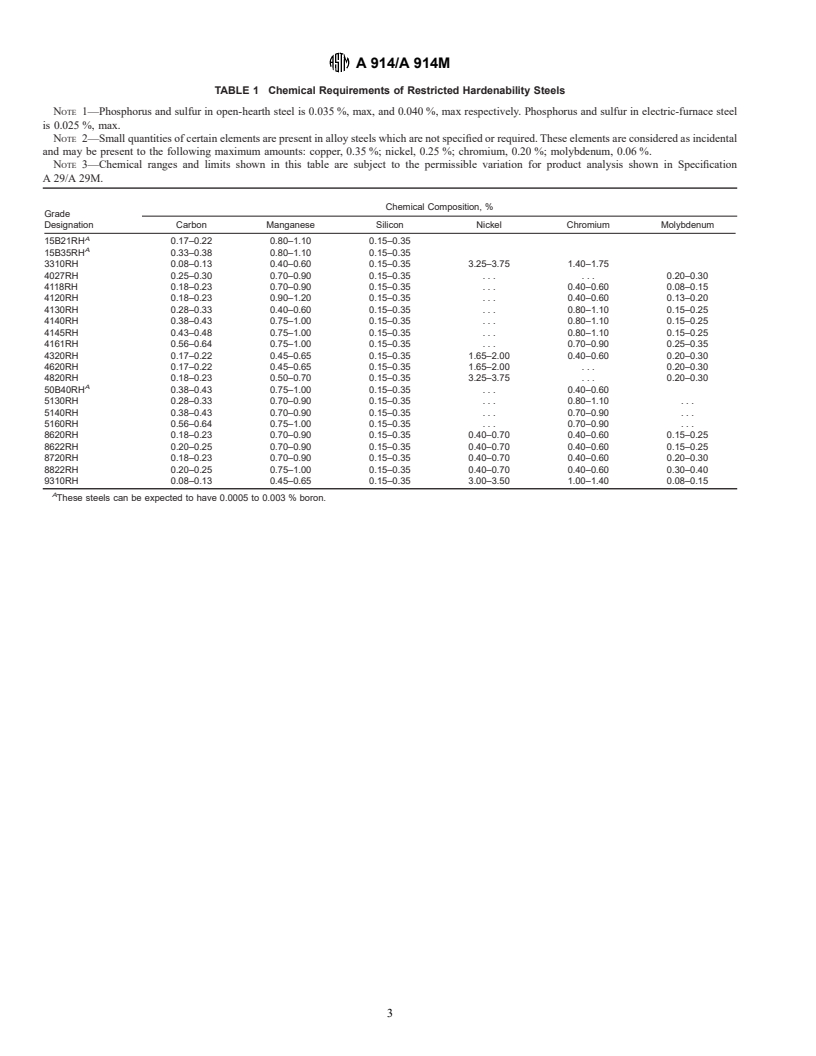
7. Chemical Requirements
hardness within the minimum and maximum HRC range
7.1 The heat analysis shall conform to the requirements as
specified at the J1 (J1.5-mm) position and shall meet one
to chemical composition prescribed in Table 1 for the grade
additional minimum and one additional maximum value. In
specified by the purchaser.
this specification, the two additional hardness values shall
represent the approximate hardness for 50 % martensite for the
8. Grain Size Requirements
minimum and maximum specified carbon content, respectively
8.1 The steel shall have an austenitic grain size of five to
(except where hardenability is too high; then the two additional
eight. The grain structure shall be considered satisfactory when
hardness control values shall be five HRC points below the
a minimum of 70 % of the rated grains are within the specified
maximum hardness value specified at the J1 (J1.5-mm) posi-
size limits.
tion).
4.4.1 In general, these points define the critical locations of 8.2 Hardenability values specified are based on fine-grain
the Jominy hardenability band for purposes of characterizing steels and are not applicable to coarse-grain steel.
heat treatment response. The four specification points are
9. End-Quench Hardenability Requirements
circled in the tables of hardness versus Jominy distance and on
the RH-bands. For all other Jominy positions, a tolerance of
9.1 The end-quench hardenability shall conform to the
two points HRC is permitted for a maximum consecutive
requirements specified on the purchase order.
⁄16-in. or 5-mm Jominy distance on the restricted hardenability
9.2 Hardenability values shall be specified in accordance
band.
with the applicable values in Figs. 2-23, inclusive, for the grade
4.4.2 For example, referring to Fig. 9, a hardenability test
specified.
bar of a steel meeting the requirements for 4140RH must
exhibit a hardness at J1 not less than 54 HRC, nor more than
10. Test Specimens
59 HRC. At J12, the test bar must exhibit hardness not less than
10.1 Number and Location—The number and location of
43 HRC, but the maximum hardness can be as high as 52 HRC
test specimens shall be in accordance with the manufacturer’s
(or even 54 HRC if the region of the test bar is chosen as the
standard practice and shall adequately represent the harden-
exception). At J20, the bar must exhibit hardness not greater
ability of each heat.
than 47 HRC, but
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.