ASTM D7043-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Non-Petroleum and Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a Constant Volume Vane Pump
Standard Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Non-Petroleum and Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a Constant Volume Vane Pump
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is an indicator of the wear characteristics of non-petroleum and petroleum hydraulic fluids operating in a constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in critical applications.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume vane pump test procedure operated at 1200 r/min and 13.8 MPa.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Exception—There are no SI equivalents for the inch fasteners and inch O-rings that are used in the apparatus in this test method.
1.2.2 Exception—In some cases English pressure values are given in parentheses as a safety measure.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7043 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Indicating Wear Characteristics of Non-Petroleum and
Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a Constant Volume Vane
1
Pump
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7043; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and
Lubricants
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume vane pump
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
test procedure operated at 1200r⁄min and 13.8MPa.
ASTM Test Methods
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
standard.
1.2.1 Exception—There are no SI equivalents for the inch
3. Terminology
fastenersandinchO-ringsthatareusedintheapparatusinthis
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
test method.
3.1.1 flushing, v—process of cleaning the test system before
1.2.2 Exception—In some cases English pressure values are
testing to prevent cross-contamination.
given in parentheses as a safety measure.
3.1.2 torquing, v—processoftighteningthepumpheadbolts
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
to achieve a uniform clamping force.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Summary of Test Method
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 An amount of 18.9L 6 0.5L of a hydraulic fluid are
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
circulated through a rotary vane pump system for 100h at a
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
pump speed of 1200r⁄min 6 60r⁄min and a pump outlet
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
pressure of 13.8MPa 6 0.3MPa (2000psi 6 40psi). Fluid
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
temperature at the pump inlet is 66°C 6 3°C for all water
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
glycols, emulsions, and other water containing fluids and for
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
petroleum and synthetic fluids of ISO Grade 46 or lighter. A
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
temperature of 80°C 6 3°C is used for all other synthetic and
petroleum fluids.
2. Referenced Documents
2
4.2 The result obtained is the total mass loss from the cam
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ringandthetwelvevanesduringthetest.Otherreportedvalues
D2882Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of
are initial flow rate and final flow rate.
Petroleum and Non-Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in Con-
3
stant Volume Vane Pump (Withdrawn 2003)
4.3 Thetotalquantityoftestoilrequiredforarunis26.5L.
D6300Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is an indicator of the wear character-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
istics of non-petroleum and petroleum hydraulic fluids operat-
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
ing in a constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane
Subcommittee D02.N0 on Hydraulic Fluids.
CurrenteditionapprovedJuly1,2017.PublishedJuly2017.Originallyapproved
pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in
in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D7043–12. DOI: 10.1520/
critical applications.
D7043-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6. Apparatus
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
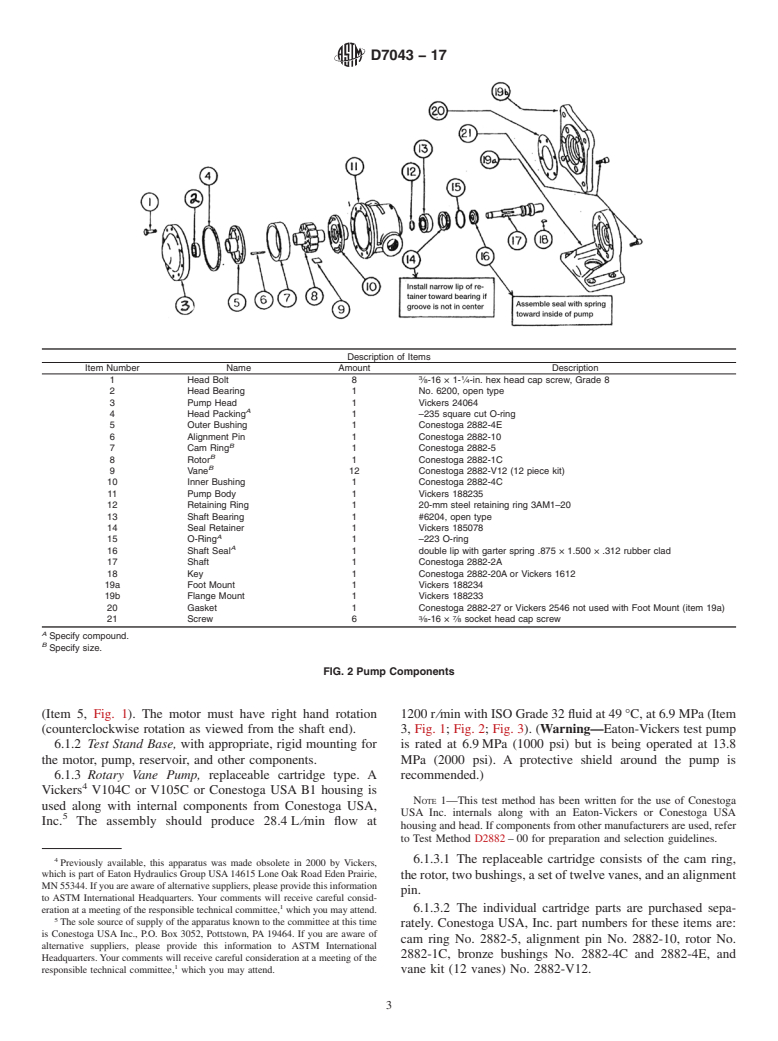
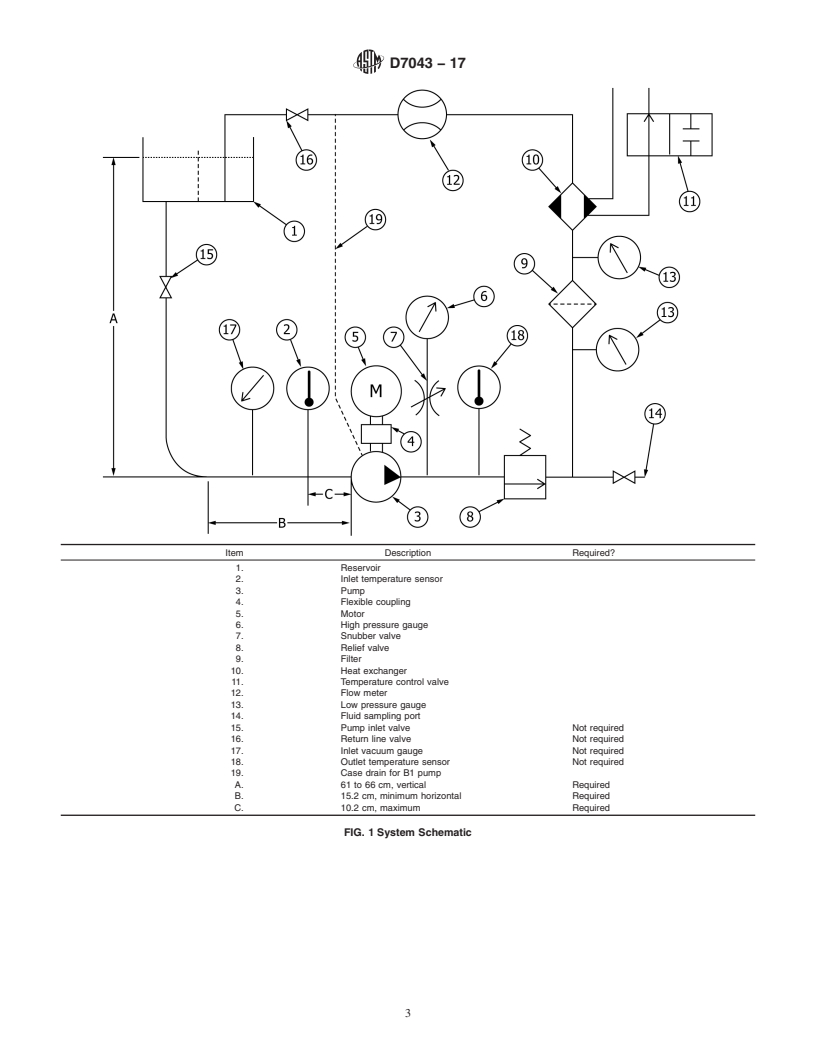
6.1 The basic system consists of the following (see Fig. 1):
the ASTM website.
3
6.1.1 AC Motor, 1200r⁄min, or other suitable drive, with
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. 11kW (15hp) as suggested minimum power requirement
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7043 − 17
Item Description Required?
1. Reservoir
2. Inlet temperature sensor
3. Pump
4. Flexible coupling
5. Motor
6. High pressure gauge
7. Snubber valve
8. Relief valve
9. Filter
10. Heat exchanger
11. Temperature control valve
12. Flow meter
13. Low pressure gauge
14. Fluid sampling port
15. Pump inlet valve Not required
16. Return line valve Not required
17. Inlet vacuum gau
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7043 − 12 D7043 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Indicating Wear Characteristics of Non-Petroleum and
Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a Constant Volume Vane
1
Pump
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7043; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume vane pump test procedure operated at 1200 r ⁄min and 13.8 MPa.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Exception—There are no SI equivalents for the inch fasteners and inch O-rings that are used in the apparatus in this test
method.
1.2.2 Exception—In some cases English pressure values are given in parentheses as a safety measure.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2882 Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum and Non-Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in Constant Volume
3
Vane Pump (Withdrawn 2003)
D6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and Lubricants
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 flushing, v—process of cleaning the test system before testing to prevent cross-contamination.
3.1.2 torquing, v—process of tightening the pump head bolts to achieve a uniform clamping force.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 An amount of 18.9 L 6 0.5 L of a hydraulic fluid are circulated through a rotary vane pump system for 100 h at a pump
speed of 1200 r ⁄min 6 60 r ⁄min and a pump outlet pressure of 13.8 MPa 6 0.3 MPa (2000 psi 6 40 psi). Fluid temperature at
the pump inlet is 66 °C 6 3 °C for all water glycols, emulsions, and other water containing fluids and for petroleum and synthetic
fluids of ISO Grade 46 or lighter. A temperature of 80 °C 6 3 °C is used for all other synthetic and petroleum fluids.
4.2 The result obtained is the total mass loss from the cam ring and the twelve vanes during the test. Other reported values are
initial flow rate and final flow rate.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.N0 on Hydraulic Fluids.
Current edition approved June 1, 2012July 1, 2017. Published October 2012July 2017. Originally approved in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 20102012 as
D7043D7043 – 12.–10. DOI: 10.1520/D7043-12.10.1520/D7043-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7043 − 17
4.3 The total quantity of test oil required for a run is 26.5 L.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is an indicator of the wear characteristics of non-petroleum and petroleum hydraulic fluids operating in a
constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in critical applications.
6. Apparatus
6.1 The basic system consists of the following (see Fig. 1):
6.1.1 AC Motor, 1200 r ⁄min, or other suitable drive, with 11 kw11 kW (15 hp)
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.