ASTM D2670-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Wear Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Block Method)
Standard Test Method for Measuring Wear Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Block Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
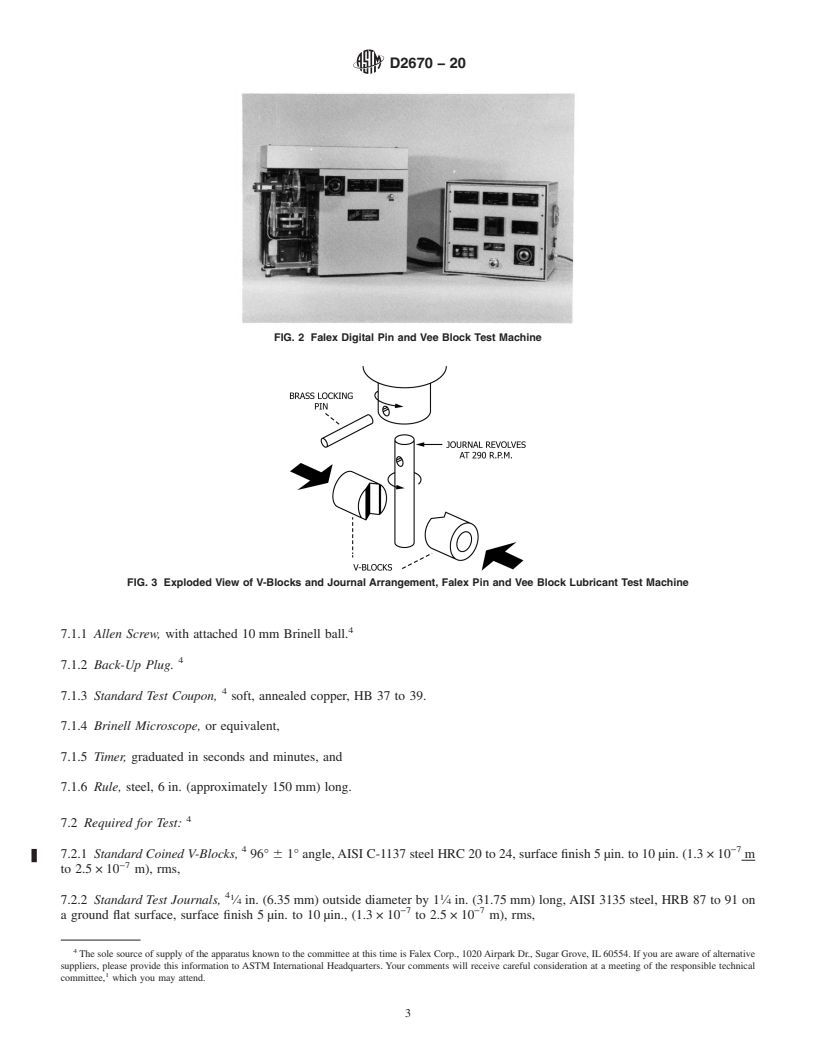
5.1 This test method may be used to determine wear obtained with fluid lubricants under the prescribed test conditions. The user of this test method should determine to his or her own satisfaction whether results of this test procedure correlate with field performance or other bench test machines. If the test conditions are changed, wear values may change and relative ratings of fluids may be different.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for making a preliminary evaluation of the wear properties of fluid lubricants by means of the Falex Pin and Vee Block Lubricant Test Machine.
Note 1: Certain fluid lubricants may require different test parameters depending upon their performance characteristics.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D2670 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Measuring Wear Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin
1
and Vee Block Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2670; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for making a 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
preliminaryevaluationofthewearpropertiesoffluidlubricants 3.1.1 actual gauge load, n—the value obtained from the
by means of the Falex Pin and Vee Block Lubricant Test gauge while running the test and before any corrections are
Machine. made.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Thegaugereadingisirrespectiveofthe
NOTE 1—Certain fluid lubricants may require different test parameters
particulargaugeused,andcorrectionsaremadebycomparison
depending upon their performance characteristics.
to a standard reference.
1.2 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
3.1.2 direct load, n—theloadthatisappliedlinearly,bisect-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
ing the angle of the vee block corrected to either the 800lbf or
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3000lbf gauge reference.
and are not considered standard.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—This load is equivalent to the true load
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
times the cos 42°.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.3 true load, n—the sum of the applied forces normal to
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the tangents of contact between the faces of one vee block and
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
the journal pin corrected to the 4500lbf gauge reference line.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor- 3.1.4 wear teeth, n—a measurement of wear, which in this
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- test, is based on the number of ratchet wheel teeth advanced
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the during the test while maintaining load.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- 3.1.4.1 Discussion—The number of teeth is directly related
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical to the total wear (inches).
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4. Summary of Test Method
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 The test consists of running a rotating steel journal
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: againsttwostationarysteelV-blocksimmersedinthelubricant
B16/B16MSpecification for Free-Cutting Brass Rod, Bar sample. Load is applied to the V-blocks and maintained by a
and Shapes for Use in Screw Machines ratchet mechanism. Wear is determined and recorded as the
numberofteethoftheratchetmechanismadvancedtomaintain
load constant during the prescribed testing time.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum
Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
5. Significance and Use
mittee D02.L0.11 on Tribological Properties of Industrial Fluids and Lubricates.
This test method was prepared under the joint sponsorship of the American
5.1 This test method may be used to determine wear
Society of Lubrication Engineers. Accepted by ASLE in May 1967.
obtained with fluid lubricants under the prescribed test condi-
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2020. Published September 2020. Originally
tions. The user of this test method should determine to his or
approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as D2670–19. DOI:
10.1520/D2670-20.
her own satisfaction whether results of this test procedure
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
correlate with field performance or other bench test machines.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Ifthetestconditionsarechanged,wearvaluesmaychangeand
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. relative ratings of fluids may be different.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2670 − 20
6. Apparatus
3
6.1 F
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2670 − 19 D2670 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Measuring Wear Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin
1
and Vee Block Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2670; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for making a preliminary evaluation of the wear properties of fluid lubricants by means
of the Falex Pin and Vee Block Lubricant Test Machine.
NOTE 1—Certain fluid lubricants may require different test parameters depending upon their performance characteristics.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B16/B16M Specification for Free-Cutting Brass Rod, Bar and Shapes for Use in Screw Machines
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 actual gauge load, n—the value obtained from the gauge while running the test and before any corrections are made.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
The gauge reading is irrespective of the particular gauge used, and corrections are made by comparison to a standard reference.
3.1.2 direct load, n—the load that is applied linearly, bisecting the angle of the vee block corrected to either the 800 lbf or 3000 lbf
gauge reference.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.L0.11 on Tribological Properties of Industrial Fluids and Lubricates.
This test method was prepared under the joint sponsorship of the American Society of Lubrication Engineers. Accepted by ASLE in May 1967.
Current edition approved May 1, 2019Sept. 1, 2020. Published August 2019September 2020. Originally approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 20162019
as D2670 – 95 (2016).D2670 – 19. DOI: 10.1520/D2670-19.10.1520/D2670-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2670 − 20
3.1.2.1 Discussion—
This load is equivalent to the true load times the cos 42°.
3.1.3 true load, n—the sum of the applied forces normal to the tangents of contact between the faces of one vee block and the
journal pin corrected to the 4500 lbf gauge reference line.
3.1.4 wear teeth, n—a measurement of wear, which in this test, is based on the number of ratchet wheel teeth advanced during
the test while maintaining load.
3.1.4.1 Discussion—
The number of teeth is directly related to the total wear (inches).
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The test consists of running a rotating steel journal against two stationary steel V-blocks immersed in the lubricant sample.
Load is applied to the V-blocks and maintained by a ratchet mechanism. Wear is determined and recorded as the number of teeth
of the ratchet mechanism advanced to maintain load constant during the prescribed testing time.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method may be used to determine wear obtained with fluid lubricants under the prescribed test conditions. The user
of this test method should determine to hi
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.