ASTM E384-11e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Knoop and Vickers Hardness of Materials
Standard Test Method for Knoop and Vickers Hardness of Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Hardness tests have been found to be very useful for materials evaluation, quality control of manufacturing processes and research and development efforts. Hardness, although empirical in nature, can be correlated to tensile strength for many metals, and is an indicator of wear resistance and ductility.
4.2 Microindentation hardness tests extend testing to materials that are too thin or too small for macroindentation hardness tests. Microindentation hardness tests also allow specific phases or constituents and regions or gradients too small for macroindentation hardness testing to be evaluated.
4.3 Because the Knoop and Vickers hardness will reveal hardness variations that may exist within a material, a single test value may not be representative of the bulk hardness.
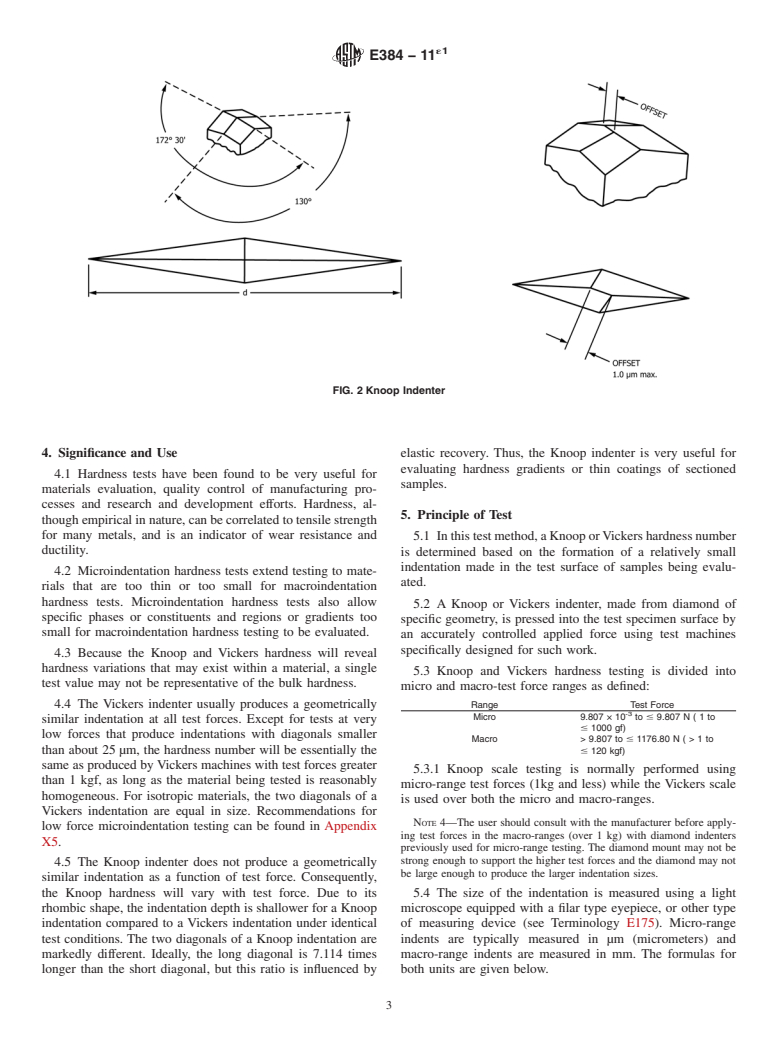
The Vickers indenter usually produces a geometrically similar indentation at all test forces. Except for tests at very low forces that produce indentations with diagonals smaller than about 25 μm, the hardness number will be essentially the same as produced by Vickers machines with test forces greater than 1 kgf, as long as the material being tested is reasonably homogeneous. For isotropic materials, the two diagonals of a Vickers indentation are equal in size. Recommendations for low force microindentation testing can be found in Appendix X5.
The Knoop indenter does not produce a geometrically similar indentation as a function of test force. Consequently, the Knoop hardness will vary with test force. Due to its rhombic shape, the indentation depth is shallower for a Knoop indentation compared to a Vickers indentation under identical test conditions. The two diagonals of a Knoop indentation are markedly different. Ideally, the long diagonal is 7.114 times longer than the short diagonal, but this ratio is influenced by elastic recovery. Thus, the Knoop indenter is very useful for evaluating hardness gradients or thin coatings of sectioned samples.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determination of the Knoop and Vickers hardness of materials, the verification of Knoop and Vickers hardness testing machines, and the calibration of standardized Knoop and Vickers test blocks.
1.2 This test method covers Knoop and Vickers hardness tests made utilizing test forces in micro (9.807 × 10-3 to 9.807 N ) ( 1 to 1000 gf ) and macro (>9.807 to 1176.80 N) ( >1kg to 120 kgf ) ranges.
Note 1—Previous versions of this standard limited test forces to 9.807 N (1 kgf).
1.3 This test method includes all of the requirements to perform macro Vickers hardness tests as previously defined in Test Method E92, Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness Testing.
1.4 This test method includes an analysis of the possible sources of errors that can occur during Knoop and Vickers testing and how these factors affect the accuracy, repeatability, and reproducibility of test results.
Note 2—While Committee E04 is primarily concerned with metals, the test procedures described are applicable to other materials.
1.5 Units—When Knoop and Vickers hardness tests were developed, the force levels were specified in units of grams-force (gf) and kilograms-force (kgf). This standard specifies the units of force and length in the International System of Units (SI); that is, force in Newtons (N) and length in mm or μm. However, because of the historical precedent and continued common usage, force values in gf and kgf units are provided for information and much of the discussion in this standard as well as the method of reporting the test results refers to these units.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: E384 − 11
StandardTest Method for
1
Knoop and Vickers Hardness of Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E384; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—Sections 8.3 and A1.1.4 were editorially corrected in March 2012.
1. Scope* 1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 ThistestmethodcoversdeterminationoftheKnoopand
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Vickers hardness of materials, the verification of Knoop and
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Vickers hardness testing machines, and the calibration of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
standardized Knoop and Vickers test blocks.
1.2 This test method covers Knoop and Vickers hardness
2. Referenced Documents
-3
tests made utilizing test forces in micro (9.807 × 10 to 9.807
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
N)(1to 1000 gf ) and macro (>9.807 to 1176.80 N) ( >1kg
C1326Test Method for Knoop Indentation Hardness of
to 120 kgf ) ranges.
Advanced Ceramics
NOTE 1—Previous versions of this standard limited test forces to 9.807
C1327Test Method for Vickers Indentation Hardness of
N (1 kgf).
Advanced Ceramics
1.3 This test method includes all of the requirements to
E3Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
perform macro Vickers hardness tests as previously defined in
E7Terminology Relating to Metallography
Test Method E92, Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness
E29Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Testing.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
E74Practice of Calibration of Force-Measuring Instruments
1.4 This test method includes an analysis of the possible
for Verifying the Force Indication of Testing Machines
sources of errors that can occur during Knoop and Vickers
E92TestMethodforVickersHardnessofMetallicMaterials
testing and how these factors affect the accuracy, repeatability,
3
(Withdrawn 2010)
and reproducibility of test results.
E122PracticeforCalculatingSampleSizetoEstimate,With
NOTE2—WhileCommitteeE04isprimarilyconcernedwithmetals,the
Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a
test procedures described are applicable to other materials.
Lot or Process
1.5 Units—When Knoop and Vickers hardness tests were
E140Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals Relationship
developed, the force levels were specified in units of grams-
Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell
force (gf) and kilograms-force (kgf). This standard specifies
Hardness, Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hardness, Sclero-
the units of force and length in the International System of
scope Hardness, and Leeb Hardness
Units (SI); that is, force in Newtons (N) and length in mm or
E175Terminology of Microscopy
µm. However, because of the historical precedent and contin-
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ued common usage, force values in gf and kgf units are
ASTM Test Methods
provided for information and much of the discussion in this
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
standard as well as the method of reporting the test results
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
refers to these units.
E766Practice for Calibrating the Magnification of a Scan-
ning Electron Microscope
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E04 on
Metallography and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E04.05 on Micro-
indentation Hardness Testing.With this revision the test method was expanded to
2
include the requirements previously defined in E28.92, Standard Test Method for For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Vickers Hardness Testing of Metallic Material that was under the jurisdiction of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
E28.06 Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2011. Published August 2011. Originally the ASTM website.
ε2 3
approved in 1969. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as E384–10 . DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/E0384-11E01. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
E384 − 11
4
2.2 ISO Standards: recovery aft
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.