ASTM D2711-01a(2007)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Demulsibility Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
Standard Test Method for Demulsibility Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test provides a guide for determining the demulsibility characteristic of lubricating oils that are prone to water contamination and may encounter the turbulence of pumping and circulation capable of producing water-in-oil emulsions.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the ability of oil and water to separate from each other. It is intended for use in testing medium and high-viscosity lubricating oils.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D2711–01a (Reapproved 2007)
Standard Test Method for
Demulsibility Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2711; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the ability 4.1 This test provides a guide for determining the demulsi-
of oil and water to separate from each other. It is intended for bility characteristic of lubricating oils that are prone to water
use in testing medium and high-viscosity lubricating oils. contamination and may encounter the turbulence of pumping
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the and circulation capable of producing water-in-oil emulsions.
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
5. Apparatus
only.
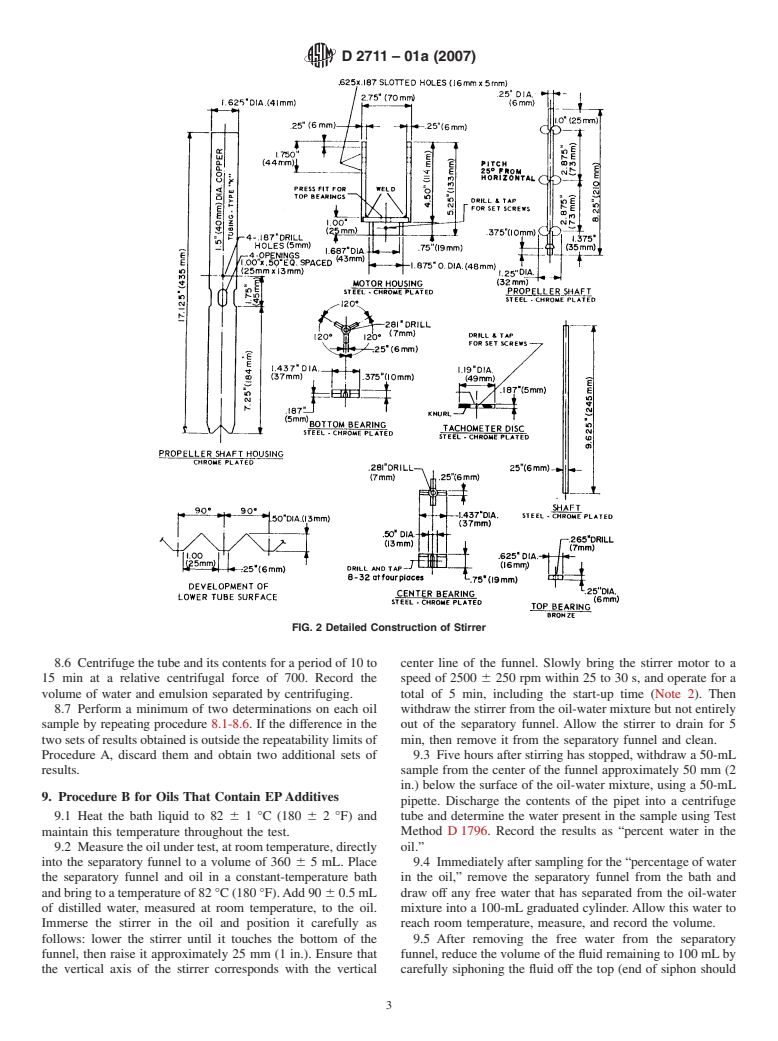
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 5.1 Stirrer, constructedfrompartsshowninFig.1andFig.
2.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 5.2 Special Graduated Separatory Funnel, as shown in
Fig. 3.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. 5.3 Heating Bath, sufficiently large and deep to permit the
immersion of at least two test separatory funnels in the bath
2. Referenced Documents
liquid up to their 500-mL graduation mark. The bath shall be
2.1 ASTM Standards: capable of maintaining a temperature of 82 6 1°C (180 6 2°F)
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water and shall be so equipped to hold the separatory funnels
D 1796 TestMethodforWaterandSedimentinFuelOilsby securely in a position so that the vertical axis of the stirrer
the Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure) corresponds to the center line of the separatory funnel during
the mixing of the oil and water.
3. Summary of Test Method
5.4 Centrifuge, as described in Test Method D 1796.
3.1 For Oils That Do Not Contain Extreme Pressure (EP) 5.5 Centrifuge Tubes, long-form, 195 to 203 mm (8 in.) as
Additives—A405-mL sample of the oil and 45 mL of distilled described in Fig. 1 of Test Method D 1796.
waterarestirredtogetherfor5minat82°C(180°F)inaspecial
6. Materials
graduated separatory funnel.After a 5-h settling period follow-
ing the stirring, a percentage of the water in the oil and the 6.1 Cleaning Solvent—Any suitable solvent capable of
volumes of water and emulsion separating from the oil are cleaning and effectively removing any oil or fluid from the
measured and recorded. stirrer and graduated cylinder. 1,1,1-Trichloroethane has been
3.2 For Oils That Contain Extreme Pressure (EP) found suitable for use in this test method. (Warning—
Additives—A360-mL sample of the oil and 90 mL of distilled 1,1,1–Trichloroethane, Harmful if inhaled or swallowed. Eye
waterarestirredtogetherfor5minat82°C(180°F)inaspecial irritant. High concentration can cause unconsciousness or
graduated separatory funnel.After a 5-h settling period follow- death.)
ing the stirring, percentage of water in the oil and the volumes
NOTE 1—In cases in which the use of 1,1,1 trichloroethane is unac-
ofwaterandemulsionseparatingfromtheoilaremeasuredand
ceptable, some laboratories are using heptane or mineral spirits as
recorded.
alternative solvents. The effect on the precision of this test method when
using an alternate solvent has not been determined.
1 6.2 Water—Type II reagent grade water conforming to
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Specification D 1193.
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.L0.01 on Metal Removal Fluids and Lubricants.
Current edition approved July 15, 2007. Published September 2007. Originally
approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D 2711–01a. The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or is Research Appliance Co., Moose Lodge Rd., Dept. T, Cambridge, MD 21613. If
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a
the ASTM website. meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D2711–01a (2007)
FIG. 1 Stirrer
7. Preparation of Apparatus total of 5 min, including the start-up time. Then withdraw the
stirrer from the oil-water mixture but not entirely out of the
7.1 Clean the graduated separatory funnel by removing any
separatory funnel. Allow the stirrer to drain for 5 min, then
film of oil with cleaning solvent followed by a wash first with
remove from the separatory funnel and clean.
acetone (Warning—Extremely flammable vapors may cause
flash fires.) and then with tap water. Rinse thoroughly with tap
8.3 Five hours after stirring has stopped, withdraw a 50-mL
water and then with reagent grade water.
sample from the center of the funnel and approximately 50 mm
7.2 Clean the stirrer by appropriate means, using the clean-
(2 in.) below the surface of the oil-water mixture, using a
ing solvent (6.1). Allow the stirrer to air dry completely prior
50-mL pipet. Discharge the contents of the pipet into a
to use in the test.
centrifuge tube and determine the water present in the sample
using Test Method D 1796. Record the results as “percent
8. Procedure A for Oils That Do Not Contain EP
water in the oil.”
Additives
8.4 Withminimumdelay,aftersamplingforthe“percentage
8.1 Heat the bath liquid to 82 6 1°C (180 6 2°F) and
ofwaterintheoil,”removetheseparatoryfunnelfromthebath
maintain this temperature throughout the test.
and draw off any free water that has separated from the
8.2 Measure the oil under test, at room temperature, directly
oil-water mixture into a 50-mL graduated cylinder. Allow this
into the separatory funnel to a volume of 405 6 5 mL. Place
water to reach room temperature, measure, and record the
the separatory funnel and oil in the constant-temperature bath
volume.
and bring it to a temperature of 82°C (180°F). Add 45 6 0.5
8.5 After removing the free water from the separatory
mLof distilled water, measured at room temperature, to the oil.
funnel, reduce the volume of the fluid remaining to 100 mLby
Immerse the stirrer in the oil and position it carefully as
carefully siphoning the fluid off the top (end of siphon should
follows: lower the stirrer until it touches the bottom of the
not be more than 20 mm below the surface of the fluid at any
funnel, then raise it approximately 25 mm (1 in.). Ensure that
time) down to the 100-mL graduation mark on the separatory
the vertical axis of the stirrer corresponds with the vertical
funnel. Drain the remaining 100 mL of fluid (oil, water, and
center line of the funnel. Slowly bring the stirrer motor to a
speed of 4500 6 500 rpm within 25 to 30 s, and operate for a emulsion) directly into a centrifuge tube.
D2711–01a (2007)
FIG. 2 Detailed Construction of Stirrer
8.6 Centrifuge the tube and its contents for a period of 10 to center line of the funnel. Slowly bring the stirrer motor to a
15 min at a relative centrifugal force of 700. Record the speed of 2500 6 250 rpm within 25 to 30 s, and operate for a
volume of water and emulsion separated by centrifuging. total of 5 min, including the start-up time (Note 2). Then
8.7 Perform a minimum of two determinations on each oil withdraw the stirrer from the oil-water mixture but not entirely
sample by repeating procedure 8.1-8.6. If the difference in the out of the separatory funnel. Allow the stirrer to drain for 5
two sets of results obtained is outside the repeatability limits of min, then remove it from the separatory funnel and clean.
Procedure A, discard them and obtain two additional sets of 9.3 Five hours after stirring has stopped, withdraw a 50-mL
results. sample from the center of the funnel approximately 50 mm (2
in.) below the surface of the oil-water mixture, using a 50-mL
9. Procedure B for Oils That Contain EPAdditives
pipette. Discharge the contents of the pipet into a centrifuge
9.1 Heat the bath liquid to 82 6 1 °C (180 6 2
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.