ASTM F994-86(2001)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Design and Installation of Overboard Discharge Hull Penetration Connections
Standard Specification for Design and Installation of Overboard Discharge Hull Penetration Connections
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers carbon steel overboard discharge hull penetrations for system piping of NPS 1 through NPS 24 (see Note 1).
Note 1—The dimensionless designator NPS (nominal pipe size) has been substituted in this standard for such TRADITIONAL terms as nominal diameter, size, and nominal size.
1.2 The minimum pipe schedule and reinforcement dimensions presented in Tables 1-6 are based on specifications in 46 CFR, 56.50-95 and Navy Design Data Sheet 100-1.
1.3 This specification does not include sea chest penetrations.
1.4 This specification does not include penetrations in protective plating.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: F 994 – 86 (Reapproved 2001)
Standard Specification for
Design and Installation of Overboard Discharge Hull
Penetration Connections
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 994; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
TABLE 1 Pipe Schedule for Type 1 Penetrations, NPS 1 Through
1. Scope
A
NPS 24
1.1 This specification covers carbon steel overboard dis-
Pene-
charge hull penetrations for system piping of NPS 1 through
tration
Shell Plating Thickness (T), in.
NPS 24 (see Note 1).
Pipe Size,
NPS
NOTE 1—The dimensionless designator NPS (nominal pipe size) has
5 3 7 1 3
¼–½ ⁄8 ⁄4 ⁄8 11 ⁄8 1¼ 1 ⁄8 1½
been substituted in this standard for such TRADITIONAL terms as
1 80 80 160 160 160 160 XXS XXS XXS
nominal diameter, size, and nominal size.
1¼ 80 160 160 160 XXS XXS XXS XXS XXS
1.2 The minimum pipe schedule and reinforcement dimen-
1½ 80 160 160 160 160 XXS XXS XXS XXS
2 80 160 160 160 160 160 160 XXS XXS
sions presented in Tables 1-6 are based on specifications in 46
2½ 80 80 160 160 160 160 160 XXS XXS
CFR, 56.50-95 and Navy Design Data Sheet 100-1.
3 80 80 160 160 160 160 160 160 XXS
1.3 This specification does not include sea chest penetra-
4 80 80 120 120 120 120 160 160 160
5 80 80 80 120 120 120 120 160 160
tions.
6 80 80 80 120 120 120 120 120 160
1.4 This specification does not include penetrations in
8 80 80 80 80 100 100 100 120 120
protective plating. 10 60 60 60 80 80 100 100 100 120
12 60 60 60 80 80 80 100 100 100
14 60 60 60 80 80 80 80 100 100
2. Referenced Documents
16 40 60 60 60 80 80 80 80 100
2.1 ASTM Standards: 18 40 40 60 60 60 80 80 80 80
20 40 40 60 60 60 60 80 80 80
A 519 Specification for Seamless Carbon and Alloy Steel
22 40 40 60 60 60 60 80 80 80
Mechanical Tubing
24 40 40 60 60 60 60 60 60 80
2.2 ANSI Standard:
A
See Fig. 1.
B36.10 Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe
2.3 Military Document:
ABS Rules for Building and Classing Steel Vessels
MIL-STD-1689 Fabrication, Welding, and Inspection of
Ships Structure
3. Classification
2.4 Other Documents:
3.1 Type I—Nonreinforced penetrations. Table 1 provides
Title 46 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Subchapter F,
minimum schedules for the penetration pipe. See Fig. 1 for
Marine Engineering
details of the penetration.
Department of the Navy, Bureau of Ship Design Data Sheet
3.2 Type II—Doubler plate-reinforced penetrations. Table 2
100-1
provides minimum dimensions for doubler plates.
3.2.1 Class 1—Inboard doubler plates. (Fig. 2)
3.2.2 Class 2—Outboard doubler plates. (Fig. 3)
3.3 Type III—Insert plate-reinforced penetrations. Table 3
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships
provides minimum dimensions for insert plates.
and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on
3.3.1 Class 1—Single-bevel insert plates. (Fig. 4)
Machinery and Piping Systems.
3.3.2 Class 2—Double-bevel insert plates. (Fig. 5)
Current edition approved March 27, 1986. Published June 1986.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01.
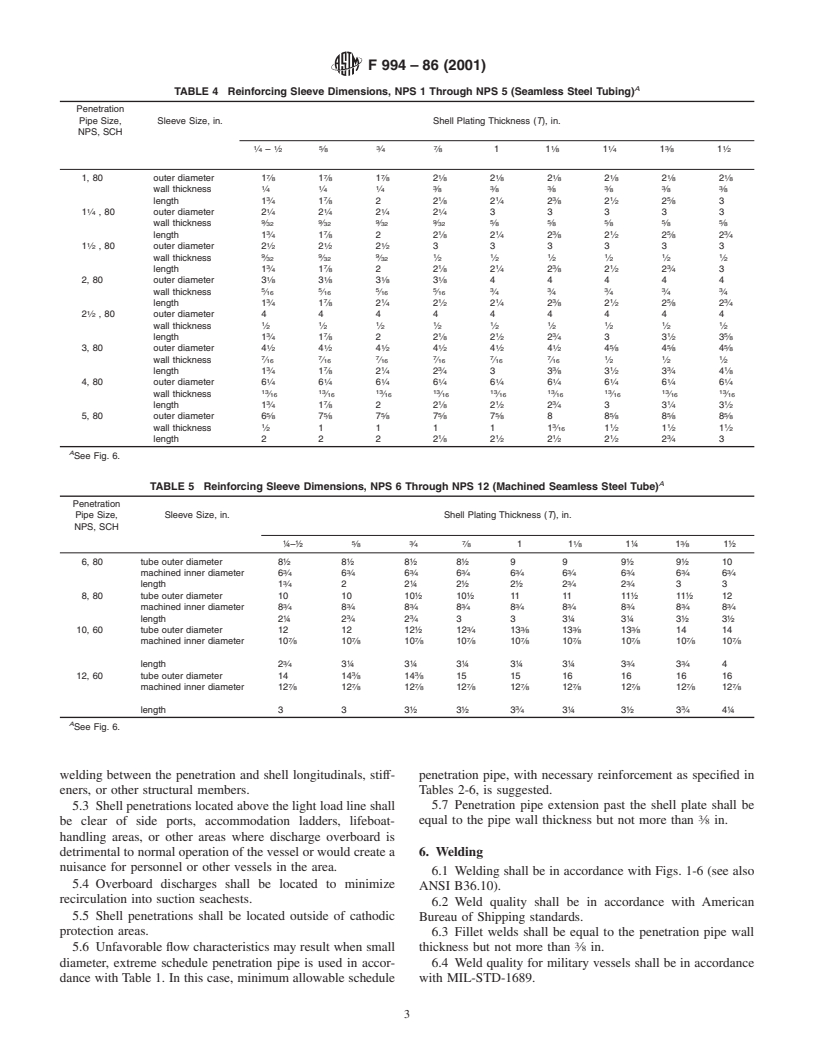
3.4 Type IV—Sleeve-reinforced penetrations. Fig. 6 details
Available from American National Standards Institute, 25 W. 43rd St., 4th
sleeve-reinforced penetrations.
Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing
Office, Washington, DC 20402.
5 6
Available from Department of the Navy, Naval Sea Systems Command, Available from American Bureau of Shipping, ABS Plaza, 16855 Northchase
Washington, DC 20362. Dr., Houston, TX 77060.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 994 – 86 (2001)
A
TABLE 2 Doubler Plate Dimensions (T 3 D) Type II Penetration, NPS 1 Through NPS 24 (in. 3 in.)
D
Penetrating
Pipe Size, Shell Plating Thickness (T), in.
NPS, SCH
5 3 7 1 3
¼to½ ⁄8 ⁄4 ⁄8 11 ⁄8 1¼ 1 ⁄8 1½
3 5 3 3
1, 80 ¼ 3 5 ⁄8 35½ 3 5 ⁄8 3 5 ⁄4 3 5 ⁄4 351 351 351¼ 3 5
3 5 3 3
1¼, 80 ¼ 3 6 ⁄8 36½ 3 6 ⁄8 3 6 ⁄4 3 6 ⁄4 361 361 361¼ 3 6
3 5 3 3
1½, 80 ¼ 3 6 ⁄8 36½ 3 6 ⁄8 3 6 ⁄4 3 6 ⁄4 361 361 361¼ 3 6
3 5 3 3
2, 80 ¼ 3 7 ⁄8 37½ 3 7 ⁄8 3 7 ⁄4 3 7 ⁄4 371 371 371¼ 3 7
3 5 3 3
2½, 80 ¼ 3 7 ⁄8 37½ 3 7 ⁄8 3 7 ⁄4 3 7 ⁄4 371 371 371¼ 3 7
3 5 3 3
3, 80 ¼ 3 8 ⁄8 38½ 3 8 ⁄8 3 8 ⁄4 3 8 ⁄4 381 381 381¼ 3 8
3 5 3 3
4, 80 ¼ 3 9 ⁄8 39½ 3 9 ⁄8 3 9 ⁄4 3 9 ⁄4 391 391 391¼ 3 9
3 5 3 3
5, 80 ¼ 3 10 ⁄8 3 10 ½ 3 10 ⁄8 3 10 ⁄4 3 10 ⁄4 3 10 1 3 10 1 3 10 1¼ 3 10
3 5 3 3
6, 80 ¼ 3 12 ⁄8 3 12 ½ 3 12 ⁄8 3 12 ⁄4 3 12 ⁄4 3 12 1 3 12 1 3 12 1¼ 3 12
3 5 3 3
8, 80 ¼ 3 14 ⁄8 3 14 ½ 3 14 ⁄8 3 14 ⁄4 3 14 ⁄4 3 14 1 3 14 1 3 14 1¼ 3 14
3 5 3 3
10, 60 ¼ 3 16 ⁄8 3 16 ½ 3 16 ⁄8 3 16 ⁄4 3 16 ⁄4 3 16 1 3 16 1 3 16 1¼ 3 16
3 5 3 3
12, 60 ¼ 3 18 ⁄8 3 18 ½ 3 18 ⁄8 3 18 ⁄4 3 18 ⁄4 3 18 1 3 18 1 3 18 1¼ 3 18
3 5 3 3
14, 60 ¼ 3 20 ⁄8 3 20 ½ 3 20 ⁄8 3 20 ⁄4 3 20 ⁄4 3 20 1 3 20 1 3 20 1¼ 3 20
3 5 3 3
16, 40 ¼ 3 22 ⁄8 3 22 ½ 3 22 ⁄8 3 22 ⁄4 3 22 ⁄4 3 23 1 3 22 1 3 23 1¼ 3 24
3 5 3 3
18, 40 ¼ 3 24 ⁄8 3 24 ½ 3 24 ⁄8 3 24 ⁄4 3 24 ⁄4 3 25 1 3 24 1 3 25 1¼ 3 28
3 5 3 3
20, 40 ¼ 3 26 ⁄8 3 26 ½ 3 26 ⁄8 3 26 ⁄4 3 26 ⁄4 3 27 1 3 26 1 3 27 1¼ 3 30
3 5 3 3
22, 60 ¼ 3 28 ⁄8 3 28 ½ 3 28 ⁄8 3 28 ⁄4 3 28 ⁄4 3 29 1 3 28 1 3 29 1¼ 3 32
3 5 3 3
24, 40 ¼ 3 30 ⁄8 3 30 ½ 3 30 ⁄8 3 30 ⁄4 3 30 ⁄4 3 31 1 3 30 1 3 31 1¼ 3 33
A
See Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.
A
TABLE 3 Insert Plate Dimensions (T 3 D), NPS 1 Through NPS 24 (in. 3 in.)
I
Penetrating
Pipe Size, Shell Plating Thickness (T), in.
NPS, SCH
5 3 7 1 3
¼to½ ⁄8 ⁄4 ⁄8 11 ⁄8 1¼ 1 ⁄8 1½
1 3 3 5 3 7 3
1, 80 1 381 ⁄8 3 8¼ 1¼ 3 8½ 1 ⁄8 3 8 ⁄4 1½ 391 ⁄8 3 9¼ 1 ⁄4 3 9½ 1 ⁄8 3 9 ⁄4 2 3 10
1 3 3 5 3 7
1¼, 80 1 3 8¼ 1 ⁄8 3 8½ 1¼ 3 8 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 391½ 3 9¼ 1 ⁄8 3 9½ 1 ⁄4 3 10 1 ⁄8 3 10¼ 2 3 10½
3 1 3 3 5 3 7 3
1½, 80 1 3 8 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 3 8 ⁄4 1¼ 391 ⁄8 3 9¼ 1½ 3 9½ 1 ⁄8 3 10 1 ⁄4 3 10 1 ⁄8 3 10½ 2 3 10 ⁄4
1 3 3 5 3 7
2, 80 1 391 ⁄8 3 9¼ 1¼ 3 9½ 1 ⁄8 3 9 ⁄4 1½ 3 10 1 ⁄8 3 10¼ 1 ⁄4 3 10½ 1 ⁄8 3 11 2 3 11
1 3 5 3 3 7
2½, 80 1 3 10 1 ⁄8 3 10 1¼ 3 10 1 ⁄8 3 10¼ 1½ 3 10½ 1 ⁄8 3 10 ⁄4 1 ⁄4 3 11 1 ⁄8 3 11¼ 2 3 11½
1 3 3 3 5 3 3 7
3, 80 1 3 10½ 1 ⁄8 3 10 ⁄4 1¼ 3 10 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 3 11 1½ 3 11¼ 1 ⁄8 3 11½ 1 ⁄4 3 11 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 3 12 2 3 12¼
1 3 3 5 3 3 7
4, 80 1 3 11 1 ⁄8 3 11½ 1¼ 3 11 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 3 12 1½ 3 12¼ 1 ⁄8 3 12½ 1 ⁄4 3 12 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 3 13 2 3 13¼
1 3 5 3 3 7 1
5, 80 1 3 12 1 ⁄8 3 12½ 1¼ 3 13 1 ⁄8 3 13 1½ 3 13¼ 1 ⁄8 3 13½ 1 ⁄4 3 13 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 3 14 2 ⁄8 3 15
1 3 5 3 3 7 1
6, 80 1 3 13 1 ⁄8 3 13½ 1¼ 3 14 1 ⁄8 3 14 1½ 3 14¼ 1 ⁄8 3 14½ 1 ⁄4 3 14 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 3 15 2 ⁄8 3 16¼
1 3 5 3
8, 80 1 3 14 1 ⁄8 3 14½ 1¼ 3 15 1 ⁄8 3 16 1½ 3 16¼ 1 ⁄8 3 16½ 1 ⁄4 3 17 2 3 18 2½ 3 19¼
1 3 5 3 3 3 3
10, 60 1 3 16 1 ⁄8 3 17 1¼ 3 18 1 ⁄8 3 18¼ 1½ 3 18½ 1 ⁄8 3 18 ⁄4 2 3 20 ⁄4 2 ⁄8 3 22 ⁄4 2¼ 3 23
1 3 5 3 3 3 3
12, 60 1 3 18 1 ⁄8 3 18½ 1¼ 3 19 1 ⁄8 3 20 1½ 3 20½ 1 ⁄8 3 20 ⁄4 2 3 22 ⁄4 2 ⁄8 3 24 ⁄4 2½ 3 25
1 3 3 5 3 5 3
14, 60 1 3 21 1 ⁄8 3 21 1¼ 3 21 1 ⁄8 3 21½ 1½ 3 21 ⁄4 1 ⁄8 3 22 2 3 24 2 ⁄8 3 26 2 ⁄8 3 25 ⁄4
1 3 3 1 3 5 3 7
16, 40 1 3 23 1 ⁄8 3 23 1¼ 3 23¼ 1 ⁄8 3 24¼ 1 ⁄4 3 26½ 2 ⁄8 3 27½ 2 ⁄8 3 28½ 2 ⁄8 3 29 ⁄4 2 ⁄8 3 31
1 3 3 1 3 5 3 7
18, 40 1 3 25 1 ⁄8 3 25 1¼ 3 25¼ 1 ⁄8 3 25½ 1 ⁄4 3 27½ 2 ⁄8 3 29½ 2 ⁄8 3 30½ 2 ⁄8 3 31 ⁄4 2 ⁄8 3 33
1 3 7 1 3 5 3 7
20, 40 1 3 27 1 ⁄8 3 27¼ 1¼ 3 27¼ 1 ⁄8 3 28¼ 1 ⁄8 3 30½ 2 ⁄8 3 31½ 2 ⁄8 3 32½ 2 ⁄8 3 33 ⁄4 2 ⁄8 3 35
1 3 7 1 3 5 7
22, 60 1 3 29 1 ⁄8 3 29 1¼ 3 29 1 ⁄8 3 30 1 ⁄8 3 30 2 ⁄8 3 30 2 ⁄8 3 33½ 2 ⁄8 3 34½ 2 ⁄8 3 36
1 3 7 1 3 5 7
24, 40 1 3 31 1 ⁄8 3 31 1¼ 3 31¼ 1 ⁄8 3 31½ 1 ⁄8 3 34½ 2 ⁄8 3 35½ 2 ⁄8 3 36½ 2 ⁄8 3 38 2 ⁄8 3 39
A
See Fig. 4 and Fig. 5.
3.4.1 Class 1—Sleeves of nonmachined steel tube. Table 4
Penetration Pipe Size Sleeve Material
provides minimum dimensions for nonmachined sleeves.
NPS 1 through NPS 10 Seamless Steel Tubing, Specification
3.4.2 Class 2—Sleeves of machined steel tube or pipe.
A 519.
NPS 12 through NPS 18 Machined seamless steel pipe of same
Table 5 provides minimum dimensions for machined sleeves.
material as penetration pipe.
3.4.3 Class 3—Sleeves of rolled steel flatbar or plate. Table
NPS 20 through NPS 24 Steel flatbar or plate of same or
superior material as hull plate,
6 provides minimum dimensions for rolled sleeves.
manufactured with a full pene-
tration, longitudinal butt weld.
4. M
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.