ASTM D4496-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive Materials
Standard Test Method for D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is useful for the comparison of materials, as a quality control test, and for specification purposes.
5.2 This test method is useful in the selection and use of materials in wires, cables, bushings, high-voltage rotating machinery, and other electrical apparatus in which shielding or the distribution of voltage stress is of value.
5.3 Commercially available “moderately conductive” materials frequently are comprised of both conductive and resistive components (that is, cellulose fibers with colloidal carbon black particles attached to portions of the surfaces of those fibers, or discrete conductive particles adhered to the surfaces of electrical insulating polymers). Such commercially available materials are often manufactured in a manner that results in anisotropy of electrical conduction. Hence, the significance of tests using this test method depends upon the orientation of the specimen tested to the direction of the electric field and the relationship between this orientation and the orientation of the material in the electrical apparatus, which uses these materials.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of electrical resistance and electrical resistivity of materials that are generally categorized as moderately conductive and are neither good electrical insulators nor good conductors.
1.2 This test method applies to the materials that exhibit volume resistivity in the range of 100 to 107 Ω-cm or surface resistivity in the range of 103 to 107 Ω (per square).
1.3 This test method is designed for measurements at standard conditions of 23 °C and 50 % relative humidity, but its principles of operation can be applied to specimens measured at lower or higher temperatures and relative humidities.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 8.3.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4496 − 21
Standard Test Method for
D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive
1
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4496; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
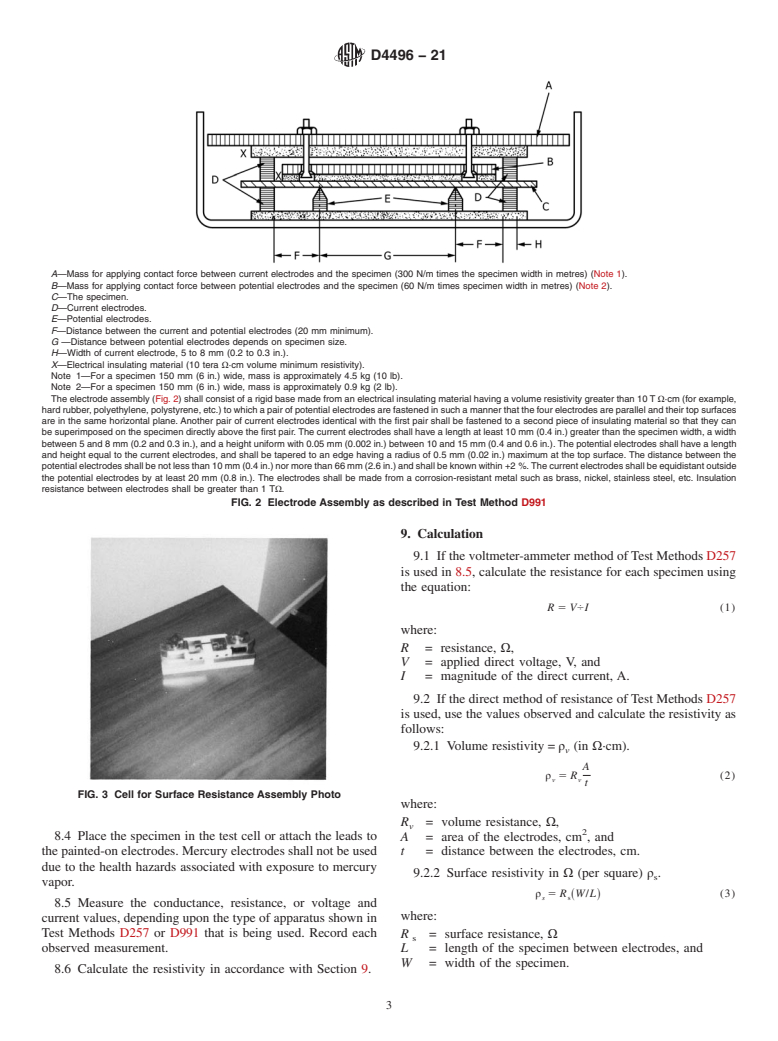
1. Scope D991Test Method for Rubber Property—Volume Resistiv-
ity Of Electrically Conductive and Antistatic Products
1.1 This test method covers the determination of electrical
D1711Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
resistance and electrical resistivity of materials that are gener-
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
allycategorizedasmoderatelyconductiveandareneithergood
3
Carbon black test cell (two drawings)
electrical insulators nor good conductors.
1.2 This test method applies to the materials that exhibit
3. Terminology
0 7
volume resistivity in the range of 10 to 10 Ω-cm or surface
3.1 Definitions:
3 7
resistivity in the range of 10 to 10 Ω (per square).
3.1.1 moderately conductive—a solid material having vol-
0 7
1.3 This test method is designed for measurements at
ume resistivity between 10 and 10 Ω·cm.
standardconditionsof23°Cand50%relativehumidity,butits
3.1.2 For definitions of the terms used, but not defined in
principles of operation can be applied to specimens measured
this standard, refer to Terminology D1711.
at lower or higher temperatures and relative humidities.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.1 steady state—for the purpose of this test method,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
steady-state is attained if any rate of change in the observed
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
resistance (or conductance) averages less than 0.25%⁄s.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 4. Summary of Test Method
Specific precautionary statements are given in 8.3.
4.1 Specimens of the test material are conditioned at pre-
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
scribed conditions and subjected to direct-voltage stress. Re-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
sistance or conductance is measured and used with the dimen-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
sional aspects of the specimen to compute the resistivity of the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
material.Theapparatusandtechniquesusedinthistestmethod
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
are selected in accordance with the general principles set forth
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
in Test Methods D257 and D991.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Significance and Use
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 This test method is useful for the comparison of
D257Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of
materials, as a quality control test, and for specification
Insulating Materials
purposes.
D374/D374MTest Methods for Thickness of Solid Electri-
5.2 This test method is useful in the selection and use of
cal Insulation
materials in wires, cables, bushings, high-voltage rotating
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
machinery, and other electrical apparatus in which shielding or
the distribution of voltage stress is of value.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
5.3 Commercially available “moderately conductive” mate-
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D09.12 on Electrical Tests.
rials frequently are comprised of both conductive and resistive
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2021. Published February 2021. Originally
components (that is, cellulose fibers with colloidal carbon
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D4496 – 13. DOI:
black particles attached to portions of the surfaces of those
10.1520/D4496-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct
the ASTM website. No.ADJD4496. Original adjunct produced in 2015. Adjunct last revised in 2015.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4496 − 21
fibers, or discrete conductive particles adhered to the surfaces the same specimen agree within 61%. The two consecutive
ofelectricalinsulat
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4496 − 13 D4496 − 21
Standard Test Method for
D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive
1
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4496; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of electrical resistance and electrical resistivity of materials that are generally
categorized as moderately conductive and are neither good electrical insulators nor good conductors.
0 7
1.2 This test method applies to the materials that exhibit volume resistivity in the range of 10 to 10 Ω-cm or surface resistivity
3 7
in the range of 10 to 10 Ω (per square).
1.3 This test method is designed for measurements at standard conditions of 23°C 23 °C and 50 % relative humidity, but its
principles of operation can be applied to specimens measured at lower or higher temperatures and relative humidities.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 8.3.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D257 Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
D374D374/D374M Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insulation (Metric) D0374_D0374M
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D991 Test Method for Rubber Property—Volume Resistivity Of Electrically Conductive and Antistatic Products
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
3
D6054 Practice for Conditioning Electrical Insulating Materials for Testing (Withdrawn 2012)
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
3
Carbon black test cell (two drawings)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D09.12 on Electrical Tests.
Current edition approved May 1, 2013Jan. 1, 2021. Published July 2013February 2021. Originally approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 20042013 as D4496
ε1
– 0413. , which was withdrawn in January 2013 and reinstated in May 2013. DOI: 10.1520/D4496-13. DOI: 10.1520/D4496-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No. No. ADJD4496. Original adjunct produced in 2015. Adjunct last revised in 2015.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4496 − 21
0 7
3.1.1 moderately conductive—a solid material having volume resistivity between 10 and 10 Ω·cm.
3.1.2 For definitions of the terms used, but not defined in this standard, refer to Terminology D1711.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 steady state—for the purpose of this test method, steady-state is attained if any rate of change in the observed resistance (or
conductance) averages less than 0.25 % ⁄s.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Specimens of the test material are conditioned at prescribed conditions and subjected to direct-voltage stress. Resistance or
conductance is measured and used with the dimensional aspects of the specimen to compute the resistivity of the material. The
apparatus and techniques used in this test method are selected in accordance with the general principles set forth in Test Methods
D257 and D991.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is useful for the comparison of materials, as a quality control test, and for specification purposes.
5.2 This test method is useful in the selectio
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.