ASTM D6549-06(2015)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Cooling Characteristics of Quenchants by Cooling Curve Analysis with Agitation (Drayton Unit)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Cooling Characteristics of Quenchants by Cooling Curve Analysis with Agitation (Drayton Unit)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method provides a cooling time versus temperature curve (profile) that can be related to physical properties, such as the hardness obtainable upon quenching of a metal. The results obtained by this test method may be used as a guide in quenchant selection or as a comparison of quench severities of different quenchants, new or used.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the equipment and the procedure for evaluation of quenching characteristics of a quenching fluid by cooling rate determination.
1.2 This test method is designed to evaluate quenching fluids with agitation, using the Drayton Agitation Unit.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6549 − 06 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Cooling Characteristics of Quenchants by
1
Cooling Curve Analysis with Agitation (Drayton Unit)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6549; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
5
1. Scope 2.4 ASTM Adjuncts:
ADJD6300 D2PP, Determination of Precision and Bias
1.1 This test method covers the equipment and the proce-
Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and
dure for evaluation of quenching characteristics of a quenching
Lubricants
fluid by cooling rate determination.
1.2 This test method is designed to evaluate quenching 3. Terminology
fluids with agitation, using the Drayton Agitation Unit.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as 3.1.1 aqueous polymer quenchant—an aqueous polymer
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information quenchant is an aqueous solution containing a water soluble
only. polymer, typically including poly(alkylene glycol), poly(ethyl
oxazoline), poly(sodium acrylate), and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
6
(1, 2, 3). The quenchant solution also typically contains
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
additives for corrosion and foam control, if needed. Quench
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
severity of aqueous polymer quenchants is dependent on
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
concentration and molecular weight of the specific polymer
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
being evaluated, quenchant temperature, and agitation rate as
shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2, and Fig. 3, respectively.
2. Referenced Documents
2
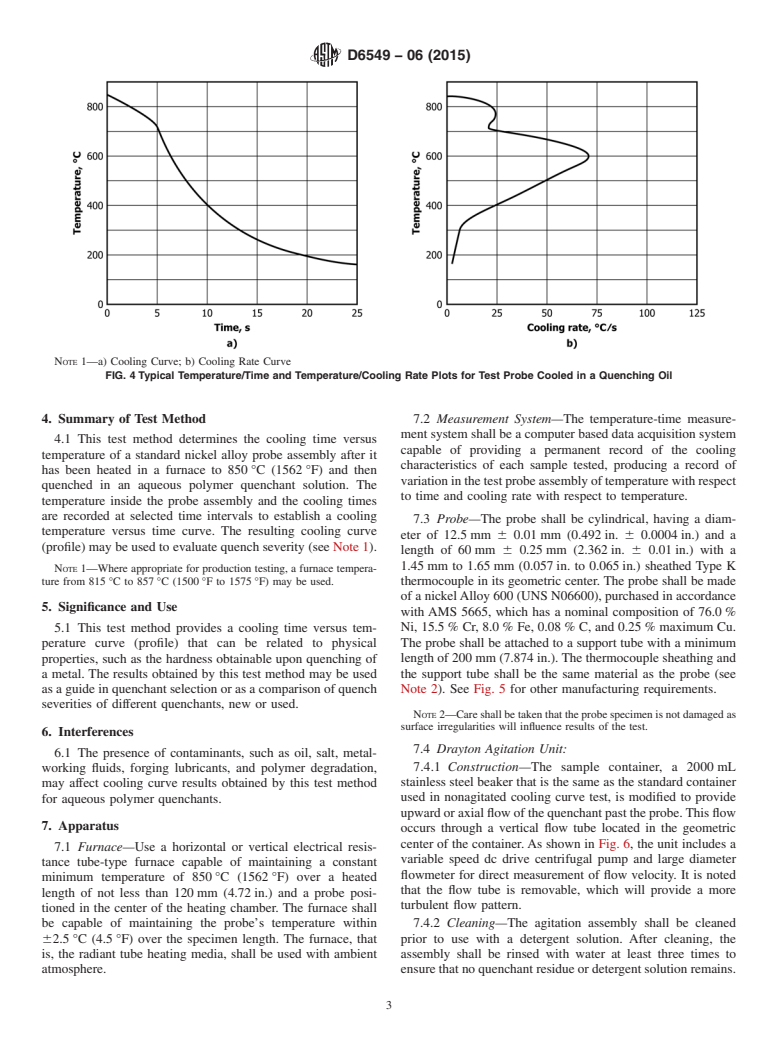
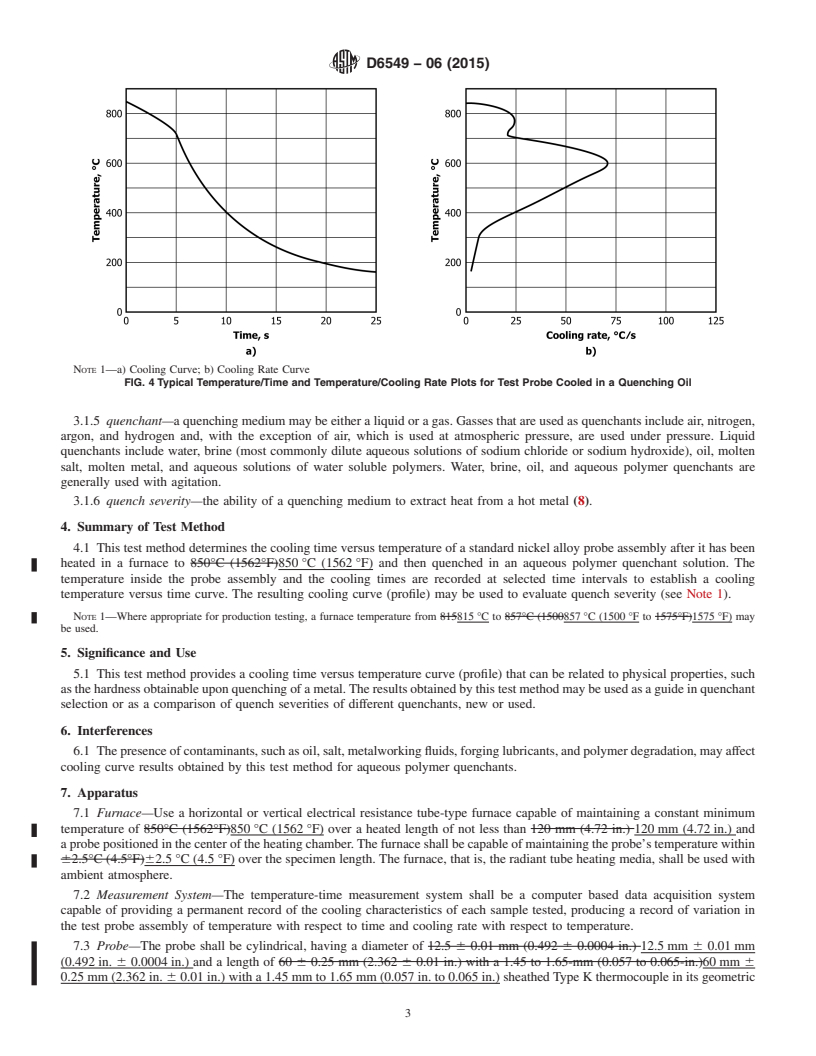
3.1.2 cooling curve—the cooling curve is a graphical repre-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
sentation of the cooling time (t) versus temperature (T)
E220 Test Method for Calibration of Thermocouples By
response of the probe (see 7.3). An example is illustrated in
Comparison Techniques
Fig. 4.
E230 Specification and Temperature-Electromotive Force
(EMF) Tables for Standardized Thermocouples 3.1.3 cooling curve analysis—the process of quantifying the
3
coolingcharacteristicsofaquenchantbasedonthetemperature
2.2 SAE Standards:
versustimeprofileobtainedbycoolingapreheatedmetalprobe
AMS 5665 NickelAlloy Corrosion and Heat Resistant Bars,
assembly (see Fig. 4) under standard conditions (1-7).
Forgings and Rings
4
3.1.4 cooling rate curve—the cooling rate curve is a graphi-
2.3 Other Standards:
Wolfson Engineering Group Specification Laboratory Tests cal representation of first derivative of the cooling curve, the
rate of temperature change (dT/dt) versus temperature. An
forAssessing the Cooling Curve Characteristics of Indus-
trial Quenching Media example is illustrated in Fig. 4.
3.1.5 quenchant—a quenching medium may be either a
liquid or a gas. Gasses that are used as quenchants include air,
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
nitrogen, argon, and hydrogen and, with the exception of air,
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
which is used at atmospheric pressure, are used under pressure.
Subcommittee D02.L0.06 on Non-Lubricating Process Fluids.
Current edition approved July 1, 2015. Published July 2015. Originally approved Liquid quenchants include water, brine (most commonly dilute
in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D6549 – 06 (2011). DOI:
aqueous solutions of sodium chloride or sodium hydroxide),
10.1520/D6549-06R15.
oil, molten salt, molten metal, and aqueous solutions of water
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
soluble polymers. Water, brine, oil, and aqueous polymer
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
quenchants are generally used with agitation.
the ASTM website.
3
Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr.,Warrendale,
5
PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org. No longer available from ASTM International Headquarters.
4
6
Available from Wolfson Heat Treatment Centre, Federation House, Vyse St., The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of
Birmingham, B18 6LT, UK. http://www.sea.org.uk/whtc. this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ---
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6549 − 06 (Reapproved 2011) D6549 − 06 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Cooling Characteristics of Quenchants by
1
Cooling Curve Analysis with Agitation (Drayton Unit)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6549; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the equipment and the procedure for evaluation of quenching characteristics of a quenching fluid
by cooling rate determination.
1.2 This test method is designed to evaluate quenching fluids with agitation, using the Drayton Agitation Unit.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E220 Test Method for Calibration of Thermocouples By Comparison Techniques
E230 Specification and Temperature-Electromotive Force (EMF) Tables for Standardized Thermocouples
3
2.2 SAE Standards:
AMS 5665 Nickel Alloy Corrosion and Heat Resistant Bars, Forgings and Rings
4
2.3 Other Standards:
Wolfson Engineering Group Specification Laboratory Tests for Assessing the Cooling Curve Characteristics of Industrial
Quenching Media
5
2.4 ASTM Adjuncts:
ADJD6300 D2PP, Determination of Precision and Bias Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and Lubricants
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 aqueous polymer quenchant—an aqueous polymer quenchant is an aqueous solution containing a water soluble polymer,
6
typically including poly(alkylene glycol), poly(ethyl oxazoline), poly(sodium acrylate), and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (1, 2, 3). The
quenchant solution also typically contains additives for corrosion and foam control, if needed. Quench severity of aqueous polymer
quenchants is dependent on concentration and molecular weight of the specific polymer being evaluated, quenchant temperature,
and agitation rate as shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2, and Fig. 3, respectively.
3.1.2 cooling curve—the cooling curve is a graphical representation of the cooling time (t) versus temperature (T) response of
the probe (see 7.3). An example is illustrated in Fig. 4.
3.1.3 cooling curve analysis—the process of quantifying the cooling characteristics of a quenchant based on the temperature
versus time profile obtained by cooling a preheated metal probe assembly (see Fig. 4) under standard conditions (1-7).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.L0.06 on Non-Lubricating Process Fluids.
Current edition approved May 1, 2011July 1, 2015. Published August 2011July 2015. Originally approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 20062011 as
D6549D6549 – 06 (2011).–06. DOI: 10.1520/D6549-06R11.10.1520/D6549-06R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001, http://www.sae.org.
4
Available from Wolfson Heat Treatment Centre, Federation House, Vyse St., Birmingham, B18 6LT, UK. http://www.sea.org.uk/whtc.
5
No longer available from ASTM International Headquarters.
6
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6549 − 06 (2015)
FIG. 1 Effect of Quenchant Concentration on Cooling Curve Performance for a Poly(Alkylene Glycol) Quenchant at 30°C and 0.5 m/s
FIG. 2 Effect of Bath Temperature Variation on Cooling Curve Performance for 15 % Aqueous Solution of Poly(Alkylene Glycol) Quen-
chant at 0.5 m/s
FIG. 3 Effect of Agitation Rate Variation on Cool
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.