ASTM C755-02
(Practice)Standard Practice for Selection of Vapor Retarders for Thermal Insulation
Standard Practice for Selection of Vapor Retarders for Thermal Insulation
SCOPE
1.1 This practice outlines factors to be considered, describes design principles and procedures for water vapor retarder selection, and defines water vapor transmission values appropriate for established criteria. It is intended for the guidance of design engineers in preparing vapor retarder application specifications for control of water vapor flow through thermal insulation. It covers commercial and residential building construction and industrial applications in the service temperature range from -40 to +80°F (-40 to +27°C). Emphasis is placed on the control of moisture penetration by choice of the most suitable components of the system.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C 755 – 02
Standard Practice for
1
Selection of Water Vapor Retarders for Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 755; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
1.1 This practice outlines factors to be considered, describes 4.1 Experience has shown that uncontrolled water entry into
design principles and procedures for water vapor retarder thermal insulation is the most serious factor causing impaired
selection, and defines water vapor transmission values appro- performance. Water entry into an insulation system may be
priate for established criteria. It is intended for the guidance of through diffusion of water vapor, air leakage carrying water
design engineers in preparing vapor retarder application speci- vapor, and leakage of surface water. Application specifications
fications for control of water vapor flow through thermal for insulation systems that operate below ambient dew-point
insulation. It covers commercial and residential building con- temperatures should include an adequate vapor retarder sys-
struction and industrial applications in the service temperature tem. This may be separate and distinct from the insulation
range from −40 to +80°F (−40 to +27°C). Emphasis is placed system or may be an integral part of it. For selection of
on the control of moisture penetration by choice of the most adequate retarder systems to control vapor diffusion, it is
suitable components of the system. necessary to establish acceptable practices and standards.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the 4.2 Vapor Retarder Function—Water entry into an insula-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the tion system may be through diffusion of water vapor, air
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- leakage carrying water vapor, and leakage of surface water.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- The primary function of a vapor retarder is to control move-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. ment of diffusing water vapor into or through a permeable
insulation system. The vapor retarder system alone is seldom
2. Referenced Documents
intended to prevent either entry of surface water or air leakage,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
but it may be considered as a second line of defense.
2
C 168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation 4.3 Vapor Retarder Performance—Design choice of retard-
C 1136 Specification for Flexible, Low Permeance Vapor
ers will be affected by thickness of retarder materials, substrate
2
Retarders for Thermal Insulation to which applied, the number of joints, available length and
E 96 Test Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of Mate-
width of sheet materials, useful life of the system, and
2
rials inspection procedures. Each of these factors will have an effect
F 372 Test Method for Water Vapor Transmission Rate of
on the retarder system performance and each must be consid-
Flexible Barrier Materials Using an Infrared Detection
ered and evaluated by the designer.
3
Technique 4.3.1 Although this practice properly places major emphasis
F 1249 Test Method for Water Vapor Transmission Rate
on selecting the best vapor retarders, it must be recognized that
through Plastic Film and Sheeting Using a Modulated faulty installation techniques can impair vapor retarder perfor-
3
Infrared Sensor
mance. The effectiveness of installation or application tech-
niques in obtaining design water vapor transmission (WVT)
3. Terminology
performance must be considered in the selection of retarder
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this practice, refer to
materials.
Terminology C 168.
4.3.2 As an example of the evaluation required, it may be
impractical to specify a lower “as installed” value, because
difficulties of field application often will preclude “as installed”
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal
attainment of the inherent WVT values of the vapor retarder
Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.33 on Insulation
materials used. The designer could approach this requirement
Finishes and Moisture.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 2002. Published February 2003. Originally by selecting a membrane retarder material that has a lower
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved 1997 published as C 755 – 97.
permeance manufactured in 5-ft (1.5-m) width or a sheet
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.06.
material 20 ft (6.1 m) wide having a higher permeance. These
3
Annual Book of ASTM
...







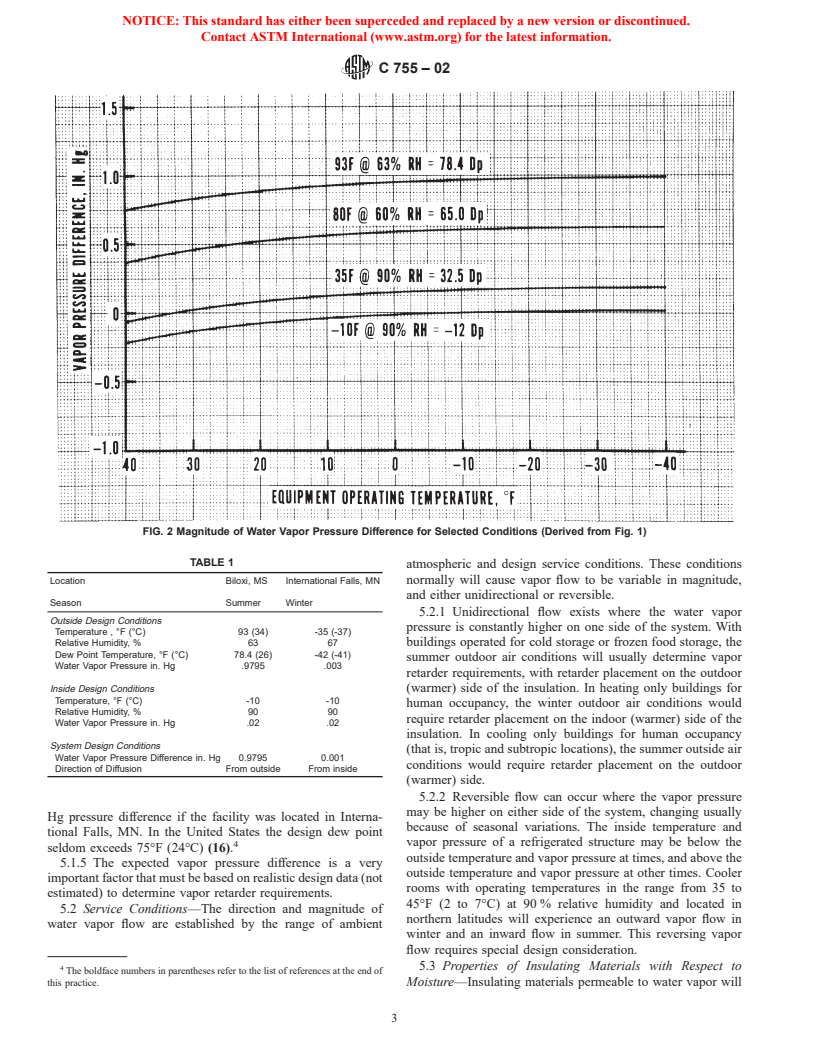
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.