ASTM D3181-95(2002)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Conducting Wear Tests on Textiles
Standard Guide for Conducting Wear Tests on Textiles
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This guide may be used to evaluate textiles used in apparel, upholstered furniture, floor coverings, window treatments, and bed, bath and table linens.
This guide may be used for several purposes:
5.2.1 To determine the comparative performance of new or existing products,
5.2.2 To determine the suitability of current products in different end-uses, and
5.2.3 To evaluate and compare the effect of wear of construction details as well as specific fabrics, fibers, dyeings, finishing, fabrication techniques, etc.
This guide provides for flexibility in design and evaluation since the information sought from each wear test will vary (see Appendix X1).
This guide may be used to compare the wear performance of two or more textiles when these are included in the same test, or to compare a textile whose properties have not been evaluated with one having a known performance history.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide is designed to provide data on which a prediction can be based concerning the expected wear performance of a wide variety of textiles in end-use conditions.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D3181–95 (Reapproved 2002)
Standard Guide for
Conducting Wear Tests on Textiles
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3181; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 3514 Test Method for Resistance of Apparel Fabrics to
Pilling (Elastomeric Pad Method)
1.1 This guide is designed to provide data on which a
D 3597 Performance Specification for Woven Upholstery
prediction can be based concerning the expected wear perfor-
Fabrics—Plain, Tufted, or Flocked
mance of a wide variety of textiles in end-use conditions.
D 3884 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Textile
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Fabrics (Rotary Platform, Double-Head Method)
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
D 3885 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Textile
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Fabrics (Flexing and Abrasion Method)
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
D 3886 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Textile
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Fabrics (Inflated Diaphragm Method)
2. Referenced Documents
D 3936 Test Method for Delamination Strength of Second-
ary Backing of Pile Floor Coverings
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 3938 GuideforEvaluationofTextileProductsinRelation
D 123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
to Refurbishing Described on Care Labels
D 1335 Test Method for Tuft Bind of Pile Floor Coverings
D 3939 Test Method for Snagging Resistance of Fabrics
D 1683 Test Method for Failure in Sewn Seams of Woven
(Mace Test Method)
Fabrics
D 4157 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Textile
D 2051 Test Method for Durability of Finish of Zippers to
Fabrics (Oscillatory Cylinder Method)
Laundering
D 4158 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Textile
D 2052 Test Method for Colorfastness of Zippers to Dry-
Fabrics (Uniform Abrasion Method)
cleaning
D 4231 Practice for Evaluation of Men’s and Boy’s Home
D 2057 Test Method for Colorfastness of Zippers to Laun-
Launderable Woven Dress Shirts and Sport Shirts
dering
D 4390 Practice for Evaluating of the Performance of Terry
D 2058 Test Method for Durability of Finish of Zippers to
Bathroom Products for Household Use
Drycleaning
D 4720 Practice for Evaluation of the Performance of Soft
D 2062 Test Method for Operability of Zippers
Window Coverings
D 2401 Test Method for Service Change of Appearance of
D 4721 Practice for Evaluating the Performance of Woven
Pile Floor Coverings
and Knit Machine Washable and Drycleanable Bedcover-
D 2960 Test Method of Controlled Laundering Test Using
ings and Accessories
Naturally Soiled Fabrics and Household Appliances
D 4852 Practice for Evaluation of Attached Upholstery
D 3511 Test Method for Pilling Resistance and Other Re-
Fabrics
lated Surface Changes of Textile Fabrics: Brush Pilling
2.2 AATCC Standards:
Tester Method
5 Evaluation Procedure: Subjective Evaluation of Fabric
D 3512 Test Method for Pilling Resistance and Other Re-
Hand
lated Surface Changes of Textile Fabrics: Random Tumble
8 Colorfastness to Crocking: AATCC Crockmeter Method
Pilling Tester Method
88B Appearance of Seams in Wash-and-Wear Items After
Home Laundering
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles and
88C Appearance of Creases in Wash-and-Wear Items After
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.53 on Practices.
Home Laundering
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 2002. Published April 1995. Originally
96 Dimensional Changes in Laundering of Woven and
published as D 3181 – 73 T. Last previous edition D 3181 – 89.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.01.
Discontinued; see 1992 Annual Book of ASTM Standards , Vol 07.01.
4 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.04. Annual AATCC Technical Manual, available from American Association of
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.02. TextileChemistsandColorists,P.O.Box12215,ResearchTrianglePark,NC 27709.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D3181–95 (2002)
Knitted Textiles (Excluding Wool) 3.1.9 wear-refurbishing cycle, n—for a specific wear testing
119 Color Change Due to Flat Abrasion (Frosting): Screen program, one complete series of events that may be terminated
Wire Method by laundering or dry cleaning.
120 Color Change Due to Flat Abrasion (Frosting): Emery 3.1.9.1 Discussion—A description of a wear-refurbishing
Method cycle usually includes the number of hours worn or used and
121 Carpet Soiling: Visual Rating Method the number of wearing or uses an item receives prior to
122 Carpet Soiling: Service Soiling Method refurbishing (that is, laundering or drycleaning), or both.
123 Carpet Soiling: Accelerated Soiling Method 3.1.10 wear-service condition, n—the specific conditions
124 Appearance of Fabrics After Repeated Home Launder- under which a textile is used.
ings 3.1.11 wear test, n—a test in which textiles are subjected to
128 Wrinkle Recovery of Fabrics: Appearance Method wear-service conditions and evaluated for performance.
130 Soil Release: Oily Stain Release Method 3.1.12 For definitions of other textile terms used in this
150 Dimensional Changes in Automatic Home Laundering practice, refer to Terminology D 123.
of Woven Garments
4. Summary of Guide
158 Dimensional Changes on Drycleaning in Perchloroeth-
ylene: Machine Method 4.1 Textiles are subjected to actual wear under service
163 Color Fastness: Dye Transfer in Storage: Fabric-to- conditions. This practice recommends a control textile having
Fabric a known wear performance history to be included with other
2.3 Other Documents: items being tested. Statistical methods for design of test and
Knit Upholstery Fabric Standards and Guidelines analysis of data are included that are applicable to all wear
Woven Upholstery Fabric Standards and Guidelines tests. Standard procedures for evaluation of textiles are pro-
vided.
3. Terminology
5. Significance and Use
3.1 Definitions:
5.1 This guide may be used to evaluate textiles used in
3.1.1 control textile, n—a textile having a known history,
apparel, upholstered furniture, floor coverings, window treat-
the performance of which in a specific end-use has been
ments, and bed, bath and table linens.
established previously, and which is used as a standard of
5.2 This guide may be used for several purposes:
comparison.
5.2.1 To determine the comparative performance of new or
3.1.2 end-use, n—in wear testing,theuseforwhichatextile
existing products,
is intended.
5.2.2 To determine the suitability of current products in
3.1.3 evaluation period, n—the period of time an item is
different end-uses, and
used before being evaluated on the specific performance
5.2.3 To evaluate and compare the effect of wear of con-
properties.
struction details as well as specific fabrics, fibers, dyeings,
3.1.4 grade, n—in textile testing, the symbol for any step of
finishing, fabrication techniques, etc.
a multistep standard reference scale, for a quality characteris-
5.3 This guide provides for flexibility in design and evalu-
tic.
ation since the information sought from each wear test will
3.1.4.1 Discussion—The grade is assigned to test specimen
vary (see Appendix X1).
exhibitingadegreeofthequalitycomparabletothatstepofthe
5.4 This guide may be used to compare the wear perfor-
standard. Numerical grades assigned to different specimens
mance of two or more textiles when these are included in the
from a sample, or by different observers are commonly
same test, or to compare a textile whose properties have not
averaged (AATCC).
been evaluated with one having a known performance history.
3.1.5 participant, n— in wear testing, any individual that
uses a test or control textile during a wear test.
6. Apparatus
3.1.5.1 Discussion—The term does not include additional
6.1 Viewing Board, with standard lighting, as specified in
personnel contributing other services needed to carry out a test.
AATCC 124.
3.1.6 performance property, n— in wear testing,anychemi-
6.2 Smoothness Appearance Replicas, as specified in
cal or physical property of a fiber, yarn, or fabric that is
AATCC 124.
evaluated during the wear-refurbishing cycles.
6.3 Gray Scale for Color Change, as specified in AATCC
3.1.7 rating, n—in textile testing, the process for determin-
Evaluation Procedure 1.
ing or assigning a grade to a material by comparing it to a
6.4 Soil Release Replicas, as specified inAATCC 130-1981.
standard reference scale.
6.5 Pilling Standards, as specified in Test Method D 3512.
3.1.8 wear level, n—thenumberofwear-refurbishingcycles
6.6 Seam Puckering Standards, as specified in AATCC
to which an item has been subjected.
88B-1984.
6.7 Crease Retention Standards, as specified in AATCC
88C.
Issued in 1982 by the Joint-Industry Fabric Standards Committee. Available
from the American Furniture Mfrs. Assc., P. O. Box Hp-7, High Point, NC 27261.
Re-issued in 1986 by the Joint-Industry Fabric Standards Committee.Available
from the American Furniture Mfrs. Assc., P. O. Box Hp-7, High Point, NC 27261. This is the same as ISO R105/1, Part 2.
D3181–95 (2002)
6.8 Photographic Standards for Evaluating Shirt Compo- 8.4 Selecttheperformancepropertiesthatmustbeevaluated
nents (collar, pocket, placket), as specified in Practice D 4231. to obtain the necessary information. See Table 1.
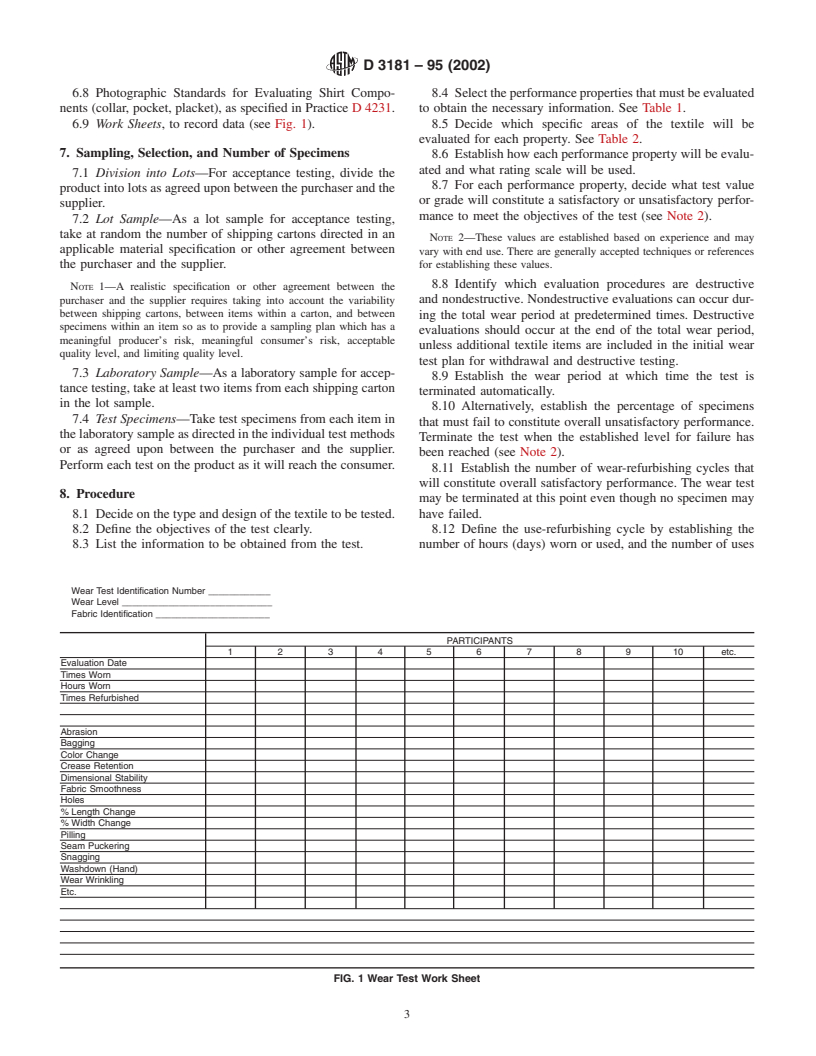
6.9 Work Sheets, to record data (see Fig. 1). 8.5 Decide which specific areas of the textile will be
evaluated for each property. See Table 2.
7. Sampling, Selection, and Number of Specimens 8.6 Establish how each performance property will be evalu-
ated and what rating scale will be used.
7.1 Division into Lots—For acceptance testing, divide the
8.7 For each performance property, decide what test value
product into lots as agreed upon between the purchaser and the
or grade will constitute a satisfactory or unsatisfactory perfor-
supplier.
mance to meet the objectives of the test (see Note 2).
7.2 Lot Sample—As a lot sample for acceptance testing,
take at random the number of shipping cartons directed in an
NOTE 2—These values are established based on experience and may
applicable material specification or other agreement between
vary with end use. There are generally accepted techniques or references
the purchaser and the supplier. for establishing these values.
8.8 Identify which evaluation procedures are destructive
NOTE 1—A realistic specification or other agreement between the
purchaser and the supplier requires taking into account the variability and nondestructive. Nondestructive evaluations can occur dur-
between shipping cartons, between items within a carton, and between
ing the total wear period at predetermined times. Destructive
specimens within an item so as to provide a sampling plan which has a
evaluations should occur at the end of the total wear period,
meaningful producer’s risk, meaningful consumer’s risk, acceptable
unless additional textile items are included in the initial wear
quality level, and limiting quality level.
test plan for withdrawal and destructive testing.
7.3 Laboratory Sample—As a laboratory sample for accep-
8.9 Establish the wear period at which time the test is
tance testing, take at least two items from each shipping carton
terminated automatically.
in the lot sample.
8.10 Alternatively, establish the percentage of specimens
7.4 Test Specimens—Take test specimens from each item in
that must fail to constitute overall unsatisfactory performance.
the laboratory sample as directed in the individual test methods
Terminate the test when the established level for failure has
or as agreed upon between the purchaser and the supplier.
been reached (see Note 2).
Perform each test on the product as it will reach the consumer.
8.11 Establish the number of wear-refurbishing cycles that
will constitute overall satisfactory performance. The wear test
8. Procedure
may be terminated at this point even though no specimen may
8.1 Decide on the type and design of the textile to be tested. have failed.
8.2 Define the objectives of the test clearly. 8.12 Define the use-refurbishing cycle by establishing the
8.3 List the information to be obtained from the test. number of hours (days) worn or used, and the number of uses
Wear Test Identification Number ____________
Wear Level _____________________________
Fabric Identification ______________________
PARTICIPANTS
12 34 56 78 9 10 etc.
Evaluation Date
Times Worn
Hours Worn
Times Refurbished
Abrasion
Bagging
Color Change
Crease Retention
Dimensional Stability
Fabric Smoothness
Holes
% Length Change
% Width Change
Pilling
Seam Puckering
Snagging
Washdown (Hand)
Wear Wrinkling
Etc.
FIG. 1 Wear Test Work Sheet
D3181–95 (2002)
TABLE 1 Properties That May Be Examined After Each Wear- TABLE 2 Examples of Areas of Potential Wear That May Be
Refurbishing Cycle or Evaluation Period Evaluated
Existing Test Methods or Garment Area
Property
Other Standards
Shirts and blouses collar, right and left
Possibilities for Apparel Evaluation cuff, right and left
Abrasion Resistance D 3884, D 3885 elbow, right and left
D 3886, D 4157 underarm, right and left
Appearance of collar D 4231
pocket, right and left
Appearance of creases AATCC 88-C front, right and left
Appearance of pocket D 4231 back
Appearance of placket D 4231 placket
Appearance of seams AATCC 88-B, Trousers and ladies slacks front pocket area and below right and left
AATCC 119 fly
Appearance of zippers D 2051, D 2052 knee, right and left
D 2057, D 2058
crotch area
Color change, frosting AATCC 119, AATCC 120 back pocket area, right and left
Color change, crocking AATCC 8
seat
Dimensional stability AATCC 96 cuffs
Fabric smoothness AATCC 124 crease
Fabric hand AATCC Eval. 5 Dresses collar or neckline
Pilling resistance D 3511, D 3512 cuff, right and left
D 3514 elbow, right and left
Snagging resistance D 3939 underarm, right and left
Wear wrinkling
bodice, front and back
Possibilities for Carpet Evaluation skirt, front and back
Abrasion resistance D 3884 pocket
Delamination of backing D 3936 hem line
Shampooing AATCC 138 pleats
Soiling AATCC 121 Floor coverings traffic path areas
AATCC 122 seamed areas
AATCC 123 Upholstery armrest
Tuft bind D 1335 head rest
Possibilities for Upholstery Fabric Evaluation
seating area
Abrasion resistance D 4157, 63-110 Joint Ind edges in cushions and frame
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.