ASTM D976-06(2016)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Calculated Cetane Index of Distillate Fuels
Standard Test Method for Calculated Cetane Index of Distillate Fuels
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 The Calculated Cetane Index is one tool available for estimating ASTM cetane number where a test engine is not available for determining this property. It may be employed for approximating cetane number where the quantity of sample is too small for an engine rating. In cases where the cetane number of a fuel has been initially established, the index is useful as a cetane number check on subsequent samples of that fuel, provided its source and mode of manufacture remain unchanged.
3.2 Test Method D4737 may also be used to approximate the ASTM cetane number of diesel fuels.
3.2.1 Procedure A of Test Method D4737 was developed as a result of a larger degree of offset between Test Method D976 Cetane Index and the results of Test Method D613 over the entire range of the correlation. Generally, it has been found that use of Test Method D4737 results in less offset than use of Test Method D976, but there can be specific cases where this is not true.
3.2.2 Procedure A of Test Method D4737 is recommended to estimate the cetane number of diesel fuels with sulfur contents above 500 ppm or No. 1–D diesel fuels.
3.2.3 Procedure B of Test Method D4737 is recommended to estimate the cetane number of No. 2–D diesel fuels with sulfur contents at or below 500 ppm.
3.3 Calculated Cetane Index, as described in Test Method D976–80, is recognized by the United States EPA as an alternative method to meet the U.S. Federal Diesel aromatics limit for diesel fuels containing less than 500 ppm sulfur. The equation for Calculated Cetane Index in Test Method D976–80 and in this version (D976–06) of the test method are the same.
SCOPE
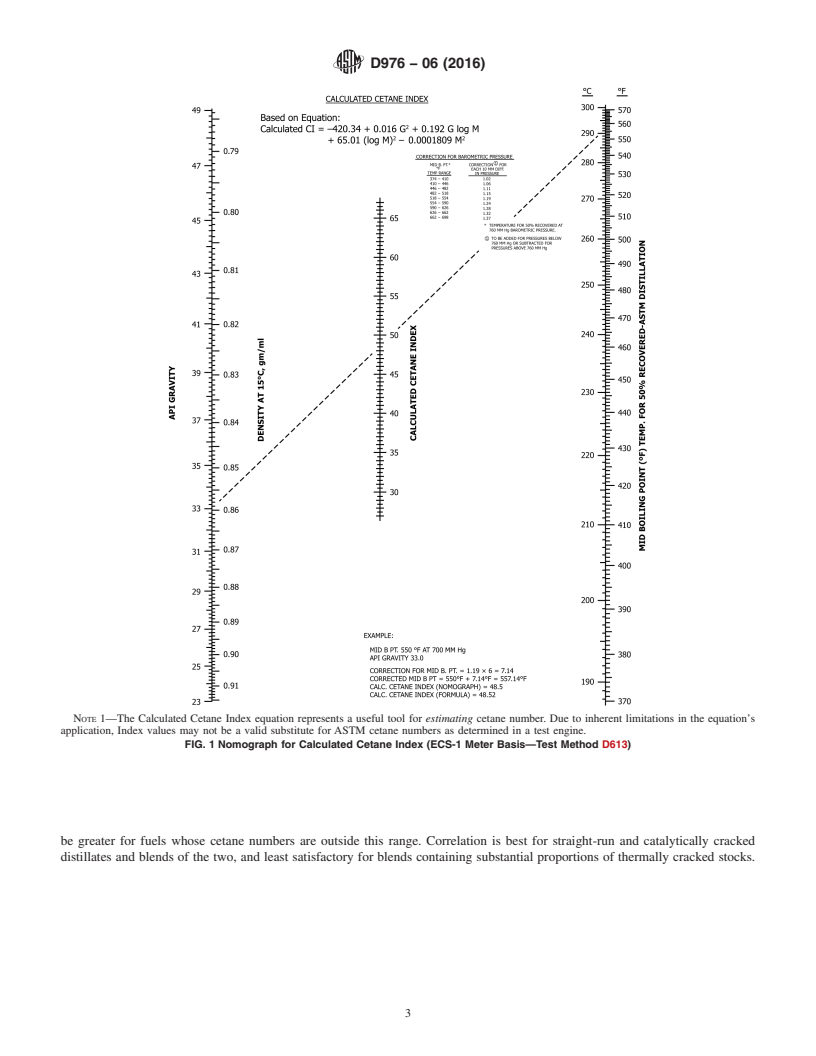
1.1 This test method covers the Calculated Cetane Index formula, which represents a means for directly estimating the ASTM cetane number of distillate fuels from API gravity and mid-boiling point. The index value, as computed from the formula, is termed the Calculated Cetane Index.2
1.2 The Calculated Cetane Index is not an optional method for expressing ASTM cetane number. It is a supplementary tool to estimate cetane number when used with due regard for its limitations.
1.3 The Calculated Cetane Index formula is particularly applicable to straight-run fuels, catalytically cracked stocks, and blends of the two.
Note 1: This test method is temporarily retained because the proposal to the U.S. EPA to control diesel fuel aromatics concentrations via a 40 Calculated Cetane Index minimum is based on the correlation between Test Method D976 and aromatics concentration. Test Method D4737 is the preferred method as estimator of cetane number.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D976 − 06 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Test Method for
1
Calculated Cetane Index of Distillate Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D976; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure
D287 Test Method for API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and
1.1 This test method covers the Calculated Cetane Index
Petroleum Products (Hydrometer Method)
formula, which represents a means for directly estimating the
D613 Test Method for Cetane Number of Diesel Fuel Oil
ASTM cetane number of distillate fuels from API gravity and
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API
mid-boiling point. The index value, as computed from the
2 Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Prod-
formula, is termed the Calculated Cetane Index.
ucts by Hydrometer Method
1.2 The Calculated Cetane Index is not an optional method
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Pe-
forexpressingASTMcetanenumber.Itisasupplementarytool
troleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
to estimate cetane number when used with due regard for its
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
limitations.
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D4737 Test Method for Calculated Cetane Index by Four
1.3 The Calculated Cetane Index formula is particularly
applicable to straight-run fuels, catalytically cracked stocks, Variable Equation
4
and blends of the two.
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
NOTE 1—This test method is temporarily retained because the proposal
Nomograph for Calculated Cetane Index
to the U.S. EPA to control diesel fuel aromatics concentrations via a 40
Calculated Cetane Index minimum is based on the correlation between
3. Significance and Use
TestMethodD976andaromaticsconcentration.TestMethodD4737isthe
preferred method as estimator of cetane number.
3.1 The Calculated Cetane Index is one tool available for
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
estimating ASTM cetane number where a test engine is not
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
available for determining this property. It may be employed for
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
approximating cetane number where the quantity of sample is
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
too small for an engine rating. In cases where the cetane
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
number of a fuel has been initially established, the index is
useful as a cetane number check on subsequent samples of that
2. Referenced Documents
fuel, provided its source and mode of manufacture remain
3
2.1 ASTM Standards: unchanged.
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and
3.2 Test Method D4737 may also be used to approximate
the ASTM cetane number of diesel fuels.
3.2.1 ProcedureAof Test Method D4737 was developed as
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
a result of a larger degree of offset between Test Method D976
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Cetane Index and the results of Test Method D613 over the
Subcommittee D02.E0 on Burner, Diesel, Non-Aviation Gas Turbine, and Marine
Fuels.
entirerangeofthecorrelation.Generally,ithasbeenfoundthat
Current edition approved April 1, 2016. Published May 2016. Originally
use ofTest Method D4737 results in less offset than use ofTest
approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D976 – 06 (2011).
Method D976, but there can be specific cases where this is not
DOI: 10.1520/D0976-06R16.
2
A method of calculating cetane index was developed by the Diesel Fuels true.
Division, Coordinating Fuel and Equipment Research Committee of the Coordinat-
3.2.2 Procedure A of Test Method D4737 is recommended
ing Research Council. SeeYoung, H. D., “Methods for Estimating Cetane Number,”
to estimate the cetane number of diesel fuels with sulfur
Proceedings, PPIRA, American Petroleum Institute, Vol. 30 M [III], 1950. This
contents above 500 ppm or No. 1–D diesel fuels.
method was revised in 1960 by Research Division I of Committee D02 to conform
to the revised Test Method D613.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
the ASTM website. ADJD0976. Origina
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D976 − 06 (Reapproved 2011) D976 − 06 (Reapproved 2016)
Standard Test Method for
1
Calculated Cetane Index of Distillate Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D976; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the Calculated Cetane Index formula, which represents a means for directly estimating the ASTM
cetane number of distillate fuels from API gravity and mid-boiling point. The index value, as computed from the formula, is termed
2
the Calculated Cetane Index.
1.2 The Calculated Cetane Index is not an optional method for expressing ASTM cetane number. It is a supplementary tool to
estimate cetane number when used with due regard for its limitations.
1.3 The Calculated Cetane Index formula is particularly applicable to straight-run fuels, catalytically cracked stocks, and blends
of the two.
NOTE 1—This test method is temporarily retained because the proposal to the U.S. EPA to control diesel fuel aromatics concentrations via a 40
Calculated Cetane Index minimum is based on the correlation between Test Method D976 and aromatics concentration. Test Method D4737 is the
preferred method as estimator of cetane number.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure
D287 Test Method for API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Products (Hydrometer Method)
D613 Test Method for Cetane Number of Diesel Fuel Oil
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by
Hydrometer Method
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Petroleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D4737 Test Method for Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation
4
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
Nomograph for Calculated Cetane Index
3. Significance and Use
3.1 The Calculated Cetane Index is one tool available for estimating ASTM cetane number where a test engine is not available
for determining this property. It may be employed for approximating cetane number where the quantity of sample is too small for
an engine rating. In cases where the cetane number of a fuel has been initially established, the index is useful as a cetane number
check on subsequent samples of that fuel, provided its source and mode of manufacture remain unchanged.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.E0 on Burner, Diesel, Non-Aviation Gas Turbine, and Marine Fuels.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2011April 1, 2016. Published October 2011May 2016. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 20062011 as
D976D976 – 06 (2011).–06. DOI: 10.1520/D0976-06R11.10.1520/D0976-06R16.
2
A method of calculating cetane index was developed by the Diesel Fuels Division, Coordinating Fuel and Equipment Research Committee of the Coordinating Research
Council. See Young, H. D., “Methods for Estimating Cetane Number,” Proceedings, PPIRA, American Petroleum Institute, Vol. 30 M [III], 1950. This method was revised
in 1960 by Research Division I of Committee D02 to conform to the revised Test Method D613.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No. ADJD0976. Original adjunct produced in 1989.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D976 − 06 (2016)
3.2 Test Method D4737 m
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.