ASTM E1037-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Particle Size Distribution of RDF-5
Standard Test Method for Measuring Particle Size Distribution of RDF-5
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The particle size distribution of RDF-5 strongly influences the storage and handling characteristics of the fuel. Small particles tend to block flow through storage bins and feed hoppers, although correct bin and hopper designs will alleviate this blockage problem.
4.2 This test method for measuring size manually allows for accurate description of RDF-5 particle size distribution. Manual measurement is superior to sieving techniques, wherein particles may be broken by the size separation technique itself. However, hand measurement is more time consuming than sieving techniques.
SCOPE
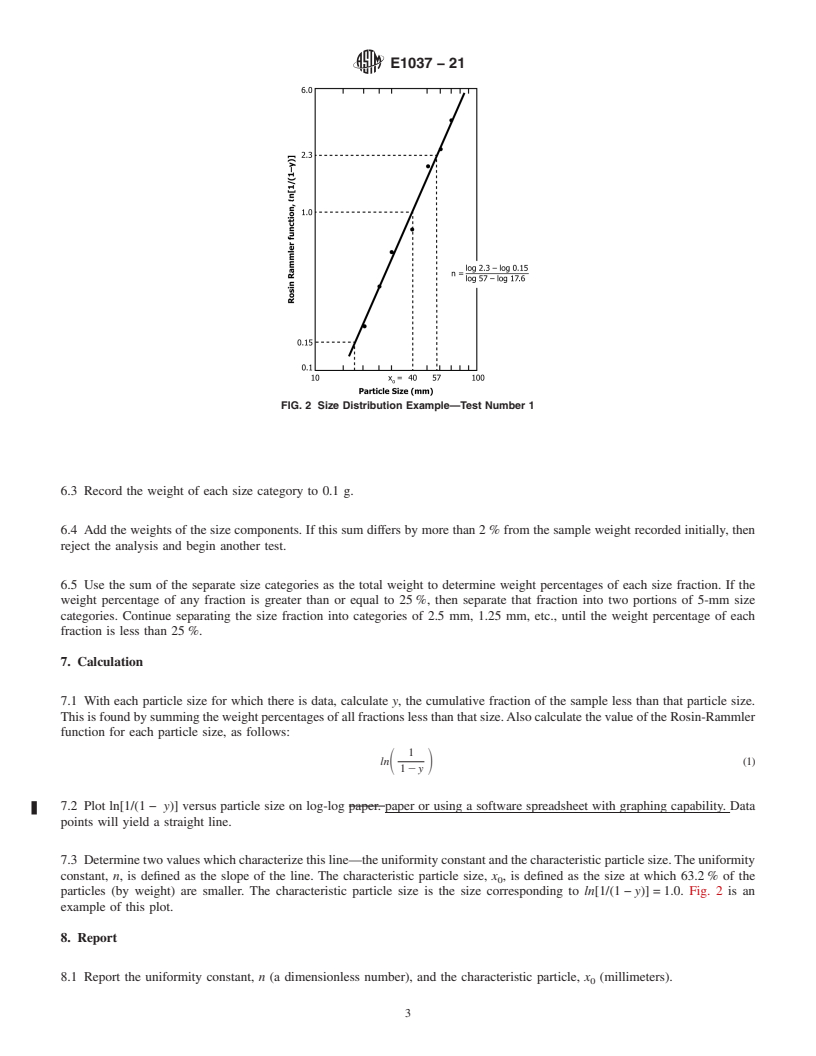
1.1 This test method is used to determine the size distribution of a RDF-5 sample. Size is defined as the maximum length of the particle, where length is determined by the RDF-5 manufacturing process. That is, a pellet, cubette, or briquette all have a recognizable length. Fig. 1 displays the sizes and shapes of some RDF-5 particles.
FIG. 1 RDF-5 Sizes
1.2 An air-dried RDF-5 sample is separated into categories of differing particle sizes. The size distribution is measured as the weight percentage of each size category. A graph of a function of the cumulative fraction of material by weight finer than particle size versus particle size is plotted. From this plot are taken values which describe the size distribution—the uniformity constant and the characteristic particle size.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E1037 − 21
Standard Test Method for
1
Measuring Particle Size Distribution of RDF-5
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1037; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 RDF-5—solidfuelderivedfrommunicipalsolidwaste
1.1 This test method is used to determine the size distribu-
in which the processed combustible fraction is densified
tionofaRDF-5sample.Sizeisdefinedasthemaximumlength
(compressed) into the form of pellets, cubettes, or briquettes.
of the particle, where length is determined by the RDF-5
manufacturing process. That is, a pellet, cubette, or briquette
4. Significance and Use
all have a recognizable length. Fig. 1 displays the sizes and
shapes of some RDF-5 particles. 4.1 The particle size distribution of RDF-5 strongly influ-
encesthestorageandhandlingcharacteristicsofthefuel.Small
1.2 An air-dried RDF-5 sample is separated into categories
particles tend to block flow through storage bins and feed
of differing particle sizes. The size distribution is measured as
hoppers, although correct bin and hopper designs will alleviate
the weight percentage of each size category. A graph of a
this blockage problem.
function of the cumulative fraction of material by weight finer
than particle size versus particle size is plotted. From this plot
4.2 Thistestmethodformeasuringsizemanuallyallowsfor
are taken values which describe the size distribution—the accurate description of RDF-5 particle size distribution.
uniformity constant and the characteristic particle size.
Manual measurement is superior to sieving techniques,
wherein particles may be broken by the size separation
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
technique itself. However, hand measurement is more time
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
consuming than sieving techniques.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
5. Apparatus
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
5.1 Labelled Containers, used to hold the particles which
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
are separated by size. Appropriate containers are beakers or
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
pans labelled “≥70 mm,” “≥60 mm to <70 mm,” etc. The tare
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
weight of each container shall be recorded to 0.1 g.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5.2 Scale, capable of weighing the sample and container
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
with an accuracy of 0.1 g.
2. Referenced Documents 5.3 Vernier Calipers, a length-measuring instrument having
2
an accuracy of 0.1 mm.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D5681Terminology for Waste and Waste Management
6. Procedure
3. Terminology
6.1 The sample shall weigh 1.0 6 0.1 kg (2.2 6 0.2 lb)
unless otherwise specified. Record the weight of the sample to
3.1 For definitions of general terms used in this standard,
the nearest 0.1 g.
refer to Terminology D5681.
6.2 Beginning with the largest particles, measure the length
of each particle in the sample. Separate the particles into
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D34 on Waste
containers labelled as the size categories of less than 10 mm,
ManagementandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD34.03onTreatment,
10 to less than 20 mm, 20 to less than 30 mm, 30 to less than
Recovery and Reuse.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2021. Published October 2021. Originally 40 mm, etc. as needed.
approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as E1037–15. DOI:
6.3 Record the weight of each size category to 0.1 g.
10.1520/E1037-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.4 Add the weights of the size components. If this sum
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
differs by more than 2% from the sample weight recorded
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. initially, then reject the analysis and begin another test.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1037
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1037 − 15 E1037 − 21
Standard Test Method for
1
Measuring Particle Size Distribution of RDF-5
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1037; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is used to determine the size distribution of a RDF-5 sample. Size is defined as the maximum length of the
particle, where length is determined by the RDF-5 manufacturing process. That is, a pellet, cubette, or briquette all have a
recognizable length. Fig. 1 displays the sizes and shapes of some RDF-5 particles.
1.2 An air dried air-dried RDF-5 sample is separated into categories of differing particle sizes. The size distribution is measured
as the weight percentage of each size category. A graph of a function of the cumulative fraction of material by weight finer than
particle size versus particle size is plotted. From this plot are taken values which describe the size distribution—the uniformity
constant and the characteristic particle size.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D5681 Terminology for Waste and Waste Management
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of general terms used in this standard, refer to Terminology D5681.
3.2 Definitions:Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 RDF-5—solid fuel derived from municipal solid waste in which the processed combustible fraction is densified (compressed)
into the form of pellets, cubettes, or briquettes.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D34 on Waste Management and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D34.03 on Treatment,
Recovery and Reuse.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2015Oct. 1, 2021. Published September 2015October 2021. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 20092015
as E1037 – 84 (2009).E1037 – 15. DOI: 10.1520/E1037-15.10.1520/E1037-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1037 − 21
FIG. 1 RDF-5 Sizes
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The particle size distribution of RDF-5 strongly influences the storage and handling characteristics of the fuel. Small particles
tend to block flow through storage bins and feed hoppers, although correct bin and hopper designs will alleviate this problem of
blockage.blockage problem.
4.2 This test method offor measuring size manually allows for accurate description of RDF-5 particle size distribution. Manual
measurement is superior to sieving techniques, wherein particles may be broken by the size separation technique itself. However,
hand measurement is more time-consuming time consuming than sieving techniques.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Labelled Containers, used to hold the particles which are separated by size. Appropriate containers are beakers or pans labelled
“≥70 mm”, “≥60 mm − <70 mm”, mm,” “≥60 mm to <70 mm,” etc. The tare weight of each container shall be recorded to 0.1
g.
5.2 Scale, capable of weighing the sample and container with an accuracy of 0.1 g.
5.3 Vernier Calipers, a length-measuring instrument having an accuracy of 0.1 mm.
6. Procedure
6.1 The sample shall weigh 1.0 6 0.1 kg (2.2 6 0.2 lb) unless otherwise specified. Record the weight of the sample to the nearest
0.1 g.
6.2 Beginning with the largest particles, measure the length of each particle in the sample. Separate the particles into containers
labelled
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.