ASTM D5528-01
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites
Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites
SCOPE
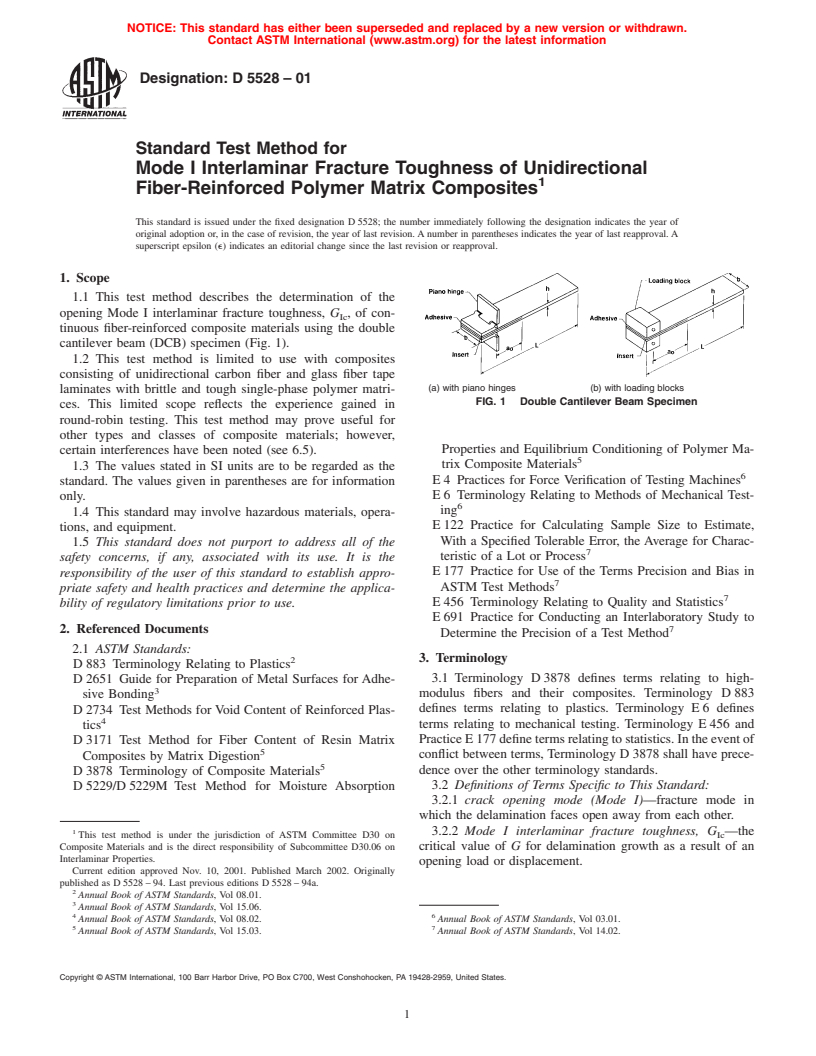
1.1 This test method describes the determination of the opening Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness, G Ic, of continuous fiber-reinforced composite materials using the double cantilever beam (DCB) specimen (Fig. 1).
1.2 This test method is limited to use with composites consisting of unidirectional carbon fiber and glass fiber tape laminates with brittle and tough single-phase polymer matrices. This limited scope reflects the experience gained in round-robin testing. This test method may prove useful for other types and classes of composite materials; however, certain interferences have been noted (see 6.5).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 5528 – 01
Standard Test Method for
Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional
1
Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5528; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes the determination of the
opening Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness, G , of con-
Ic
tinuous fiber-reinforced composite materials using the double
cantilever beam (DCB) specimen (Fig. 1).
1.2 This test method is limited to use with composites
consisting of unidirectional carbon fiber and glass fiber tape
(a) with piano hinges (b) with loading blocks
laminates with brittle and tough single-phase polymer matri-
FIG. 1 Double Cantilever Beam Specimen
ces. This limited scope reflects the experience gained in
round-robin testing. This test method may prove useful for
other types and classes of composite materials; however,
Properties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Ma-
certain interferences have been noted (see 6.5).
5
trix Composite Materials
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
6
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
E 6 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Test-
only.
6
ing
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials, opera-
E 122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate,
tions, and equipment.
With a Specified Tolerable Error, the Average for Charac-
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
7
teristic of a Lot or Process
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
E 177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
7
ASTM Test Methods
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
7
E 456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
7
2. Referenced Documents
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3. Terminology
2
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
3.1 Terminology D 3878 defines terms relating to high-
D 2651 Guide for Preparation of Metal Surfaces for Adhe-
3
modulus fibers and their composites. Terminology D 883
sive Bonding
defines terms relating to plastics. Terminology E 6 defines
D 2734 Test Methods for Void Content of Reinforced Plas-
4
terms relating to mechanical testing. Terminology E 456 and
tics
PracticeE 177definetermsrelatingtostatistics.Intheeventof
D 3171 Test Method for Fiber Content of Resin Matrix
5
conflict between terms, Terminology D 3878 shall have prece-
Composites by Matrix Digestion
5
dence over the other terminology standards.
D 3878 Terminology of Composite Materials
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
D 5229/D 5229M Test Method for Moisture Absorption
3.2.1 crack opening mode (Mode I)—fracture mode in
which the delamination faces open away from each other.
1
3.2.2 Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness, G —the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D30 on Ic
Composite Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D30.06 on critical value of G for delamination growth as a result of an
Interlaminar Properties.
opening load or displacement.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 2001. Published March 2002. Originally
published as D 5528 – 94. Last previous editions D 5528 – 94a.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.06.
4 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
5 7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.03. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5528–01
3.2.3 energy release rate, G—the loss of energy, dU, in the displacement or the crosshead movement, while the load and
test specimen per unit of specimen width for an infinitesimal delamination length are recorded.
increaseindelaminationlength,da,foradelaminationgrowing 4.2 A record of the applied load versus opening displace-
under a constant displacement. In mathematical form, ment is recorded on an X-Y recorder, or equivalent real-time
plotting device or stored digitally and postprocessed. Instanta-
1 dU
G52 (1)
neous delamination front locations are marked on the chart at
b da
intervals of delamination growth. The Mode I interlaminar
where:
fracture tou
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.