ASTM D7140-05
(Test Method)Standard Test Method to Measure Heat Transfer Through Textile Thermal Barrier Materials
Standard Test Method to Measure Heat Transfer Through Textile Thermal Barrier Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of heat transfer of textile materials which are used as thermal barriers when exposed to a calibrated convective and radiant energy heat source for 60 seconds.
1.1.1 This standard is used to determine if the heat transfer is sufficient to ignite flammable materials which are contiguous to the textile thermal barriers.
1.2 This standard is used as a means to differentiate textile materials.
1.3 This test method is not intended to measure the insulation properties of materials used in protective clothing.
1.4 The values stated in either acceptable metric units or in other units shall be regarded separately as standard. The values expressed in each system must be used independently of each other, without combining values in any way.
1.5 This standard measures and describes the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the materials, products or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7140–05
Standard Test Method to
Measure Heat Transfer Through Textile Thermal Barrier
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 7140; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Boxspring Set to a Large Open Flame, January, 2004
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of heat transfer
3. Terminology
of textile materials which are used as thermal barriers when
3.1 Definitions:
exposed to a calibrated convective and radiant energy heat
3.1.1 exposure energy to thermal end point, n—the thermal
source for 60 seconds.
energytransferredthroughaspecimenthatissufficienttocause
1.1.1 This standard is used to determine if the heat transfer
ignition of contiguous materials.
is sufficient to ignite flammable materials which are contiguous
3.2 The following terms are relevant to this standard: break
to the textile thermal barriers.
open, charring, dripping, embrittlement, heat flux, ignition,
1.2 This standard is used as a means to differentiate textile
melting, shrinkage.
materials.
3.3 For all terminology relating to D13.52, Flammability,
1.3 This test method is not intended to measure the insula-
refer to Terminology D 4391.
tion properties of materials used in protective clothing.
3.3.1 For all terminology related to Textiles see Terminol-
1.4 The values stated in either acceptable metric units or in
ogy D 123
other units shall be regarded separately as standard.The values
expressed in each system must be used independently of each
4. Summary of Test Method
other, without combining values in any way.
4.1 A textile thermal barrier that is used to prevent transfer
1.5 This standard measures and describes the response of
of heat to flammable materials which are contiguous to this
materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under
barrier are exposed to a controlled radiant and convective heat
controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all
source for 60 seconds.
factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the
4.2 The heat transfer is measured using a data collection
materials, products or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
system.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.3 Performance of thermal barrier textile material is deter-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
mined by the amount of heat transferred through the specimen.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.1 This test method measures the level of heat transfer
through the thermal barrier textile material within a specific
2. Referenced Documents
2 period of time.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.2 This test method is used to evaluate thermal barriers and
D 123 Standard Terminology Related to Textiles
determine if they are able to withstand impingement by an
D 4391 Standard Terminology Relating to Burning Behav-
open flame.
ior of Textiles
5.2.1 Thistestmethodisusedtoevaluateheattransferwhen
2.2 Other Standards:
thermal barrier textile materials are used in conjunction with
State of California, Technical Bulletin 603 Requirements
materials that demonstrate any of the following behaviors
and Test Procedures for Resistance of a Mattress/
when exposed to high heat:
break open
1 charring
This standard is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D 13.52 on Flammability of dripping
Textiles.
embrittlement
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2005. Published October 2005.
ignition
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. Available from the State of California.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D7140–05
melting 6.7 Any strip chart recorder with full scale deflection of at
shrinkage least 150° C (300°F) or 10 mV and sufficient sensitivity and
5.3 Thistestmethodcannotbeusedinplaceofthefullscale scaledivisionstoreadsensorresponseto1°C(2°F)or+/-0.05
test method TB603. mv. A chart speed to read exposure time to +/- 0.01 sec. is
required.
NOTE 1—This test method is intended to be used to evaluate thermal
6.8 Specimen Holder, see Fig. 3 Three complete assemblies
barrier textile materials used as the thermal barrier component for
are desirable.
mattresses which are tested to comply with California Technical Bulletin
603 (TB603). Data obtained by using this method may provide sufficient 6.9 Laboratory standard ring support and clamp are used to
information to proceed with this more expensive full scale testing.
hold specimen holder assembly and position the burner.
5.3.1 This test method can be used as part of a supplier
7. Hazards
quality assurance program.
7.1 Perform the test in a hood or ventilated area to carry
5.4 This test method is not intended to be used in evaluating
combustion products away. If air currents disturb the flame,
heat transfer of thermal barrier textile materials used in
shield the apparatus or turn off the hood while running the test,
protective clothing.
thenturnthehoodonafterthetesttoclearfumes.Exercisecare
5.5 This test method is not recommended for acceptance
in handling the burner with the open flame. Maintain adequate
testing of commercial shipments, since information on inter-
separation between flame and combustible materials.
laboratory precision is incomplete. In some cases the purchaser
7.2 The specimen holder and calorimeter assembly can
and the supplier shall agree to test a commercial shipment of
become heated during prolonged testing. Use protective gloves
one or more specific materials and establish their own inter-
when handling these hot objects.
laboratory precision and bias, and also agree on acceptability
limits.
NOTE 2—Some test specimens are hazardous when exposed to direct
flames. Use care when the ignited specimen releases combustible gases.
Remove the burner using gloves and allow the sample to burn out, or
6. Apparatus
smother it with a plate.
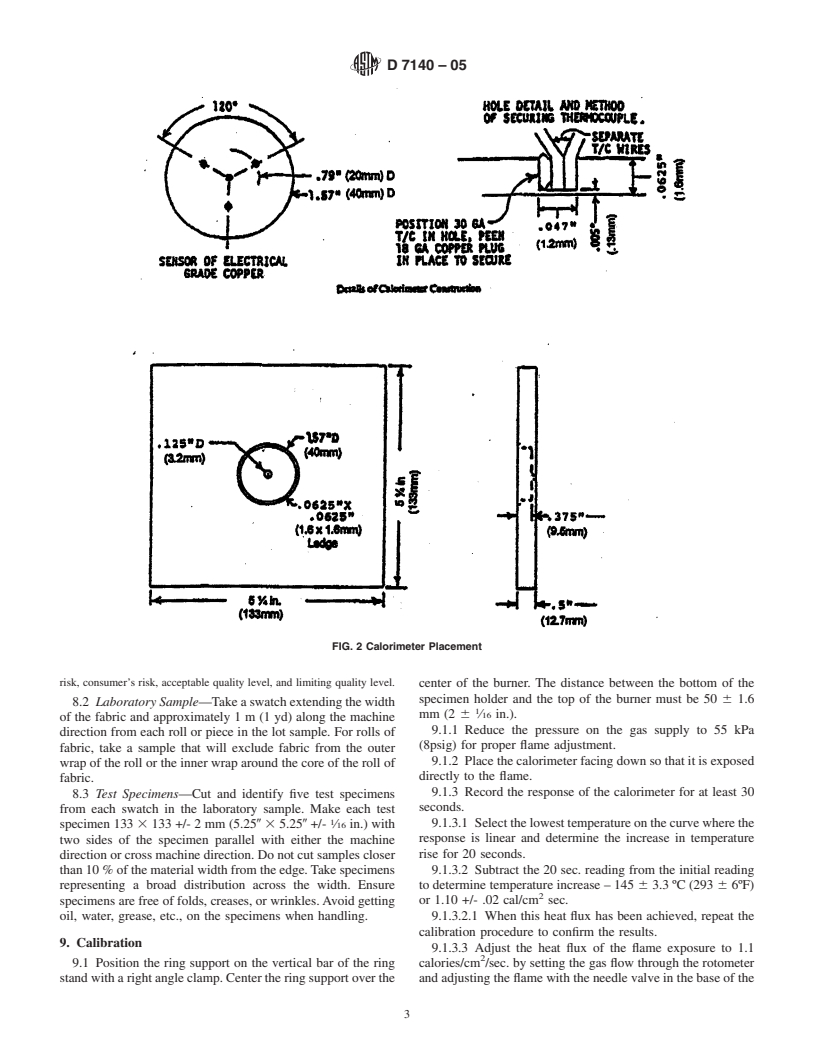
6.1 Arrange components as shown in Fig. 1.
7.3 Shut off the gas supply at the cylinder and allow flame
6.1.1 Details of the calorimeter construction are shown in
to burn the gas from the lines when testing is completed.
Fig. 2.
6.2 Liquid propane or natural gas with appropriate reducer
8. Sampling and Test Specimen Preparation
and valving arrangement.
8.1 Lot Sample—Randomly select the number of rolls or
6.3 Agas rotometer with range to give flow equivalent to 2
L (.007 ft )/min. air at standard conditions. pieces of fabric directed in an applicable material specification
or other agreement between the purchaser and the supplier.
6.4 Meeker or Fisher burner with 38 mm (1.59) diameter top
and with orifice size of 1.2 mm (3/649) for natural gas. Propane Consider the rolls or pieces of fabric to be the primary
requires a special orifice. sampling units. In the absence of such an agreement, take the
number of fabric rolls specified in Table 1. Consider a single
6.5 Copper calorimeter mounted in an insulating block and
constructed as shown in Fig. 2. shipment of one style of fabric as the lot. A lot may constitute
part of a single customer order.
6.5.1 Calorimeter is painted black using a high temperature
flat black stove pipe primer.
NOTE 3—An adequate specification or other agreement between the
6.6 Dimensions for two (2) mounting plates are shown in
purchaserandsupplierrequirestakingintoaccountthevariabilitybetween
Fig. 3. The bottom plate which faces the flame must be made
rolls or pieces of fabric and between specimens from a swatch from a roll
of steel. The top plate must also be made of steel. or piece of fabric to provide a sampling plan with a meaningful producer’s
FIG. 1 Test Apparatus
D7140–05
FIG. 2 Calorimeter Placement
risk, consumer’s risk, acceptable quality level, and limiting quality level.
center of the burner. The distance between the bottom of the
specimen holder and the top of the burner must be 50 6 1.6
8.2 Laboratory Sample—Takeaswatchextendingthewidth
mm (2 6 ⁄16 in.).
of the fabric and approximately1m(1yd) along the machine
9.1.1 Reduce the pressure on the gas supply to 55 kPa
direction from each roll or piece in the lot sample. For rolls of
(8psig) for proper flame adjustment.
fabric, take a sample that will exclude fabric from the outer
9.1.2 Place the calorimeter facing down so that it is exposed
wrap of the roll or the inner wr
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.