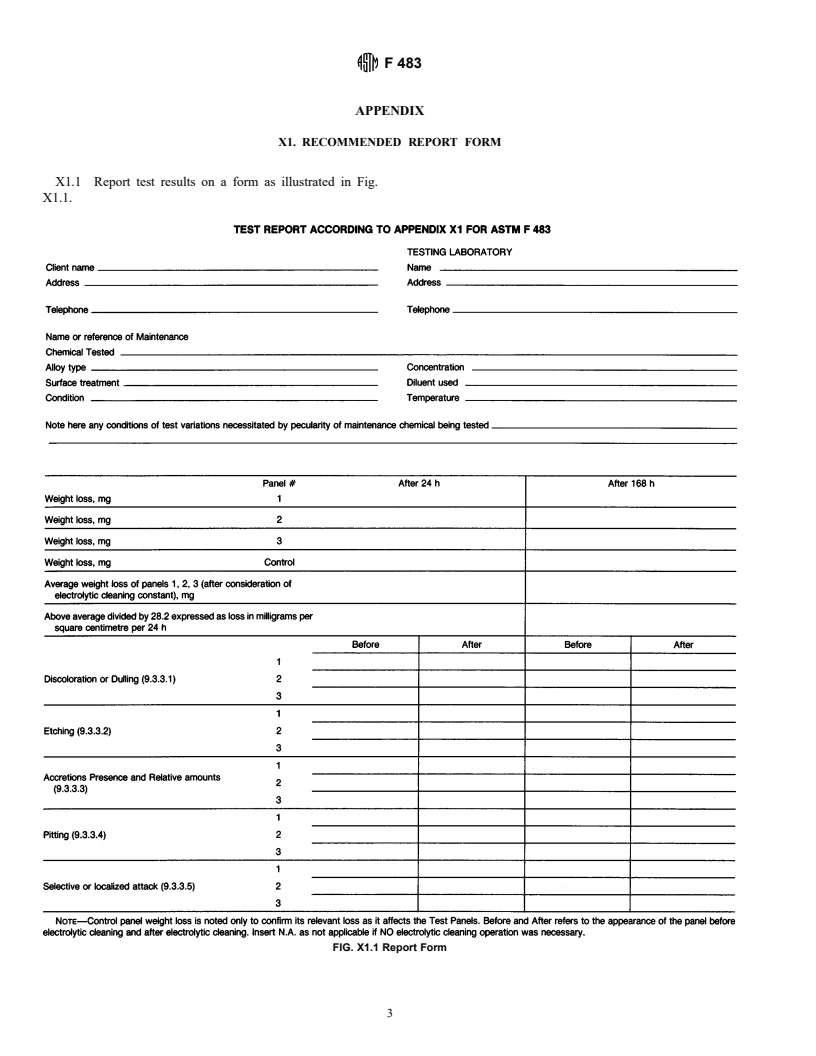
ASTM F483-98
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Total Immersion Corrosion Test for Aircraft Maintenance Chemicals
Standard Test Method for Total Immersion Corrosion Test for Aircraft Maintenance Chemicals
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the corrosiveness of aircraft maintenance chemicals on aircraft metals with time under conditions of total immersion by a combination of weight change measurements and visual qualitative determination of change.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 483 – 98 An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Total Immersion Corrosion Test for Aircraft Maintenance
1
Chemicals
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 483; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4.1.1 Caution—Some aircraft maintenance chemicals when
heated have high vapor pressures or may produce gases during
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the corro-
testing. Suitable precautions should be taken to prevent the
siveness of aircraft maintenance chemicals on aircraft metals
containing vessel from exploding or the vessel should be so
with time under conditions of total immersion by a combina-
chosen as to withstand the resulting pressure.
tion of weight change measurements and visual qualitative
4.2 Specimen-Supporting Device—A glass of fluorocarbon
determination of change.
plastic supporting system designed to keep the specimen fully
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
immersed while ensuring free contact with the solution, and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
designed to isolate the specimens from each other physically.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.3 For materials containing low boiling point solvents, a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
means of preventing evaporation losses shall be used.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.4 Constant-Temperature Device—Any suitable regulated
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
heating device (mantle, hot plate, or bath) may be used to
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
maintain the solution at the required temperature.
2. Referenced Documents
4.5 Thermometer, having a range from 0 to 302°F and
conforming to requirements for Thermometer 1F in accordance
2.1 ASTM Standards:
with Specification E 1.
D 235 Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits)
2
4.6 Oven, low temperature explosion-proof, capable of
(Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent)
2
maintaining 38 6 3°C (100 6 5°F) through 120 6 5°C (248 6
D 329 Specification for Acetone
2
5°F).
D 740 Specification for Methyl Ethyl Ketone
3
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
5. Reagents and Materials
4
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
5.1 Acetone—conforming to Specification D 329.
3. Significance and Use
5.2 Methyl Ethyl Ketone—conforming to Specification
D 740.
3.1 Many aircraft maintenance chemicals are used on com-
5.3 Mineral Spirits, Type II—conforming to Specification
ponents and structures which would be adversely affected by
D 235.
excessive dimensional change. This test method screens these
chemicals to ensure compliance with specified weight change
6. Test Specimens
criteria.
6.1 Take test specimens of a given alloy from the same sheet
4. Apparatus stock and measure 50.8 by 25.4 by 1.6 mm (2 by 1 by 0.06 in.)
with a 3.2-mm (0.125-in.) diameter mounting hole suitably
4.1 Wide-Mouth Sealable Glass Jar or Stoppered Flask of
located at one end of the specimen. Test three replicate
Suitable Size—The glass jar or flask should be so chosen so
specimens in each concentration of maintenance chemical
that the specimens will remain fully immersed in a vertical
solution in accordance with 8.2.1. Take the total area of the
position during testing and the ratio of area of immersed metal
2 2
specimen as 28.2 cm (4.4 in. ).
to volume of solution will be in accordance with 8.1.
6.1.1 Identify each panel with Numbers 1, 2, 3, or 4.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-7 on
7. Precleaning Test Specimens
Aerospace and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.07 on
7.1 Immerse the test specimens in a beaker of mineral
Qualification Testing of Aircraft Cleaning Materials.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1998. Published March 1999. Originally
spirits, Type II, conforming to Specification D 235 at room
e1
published as F 483 – 77. Last previous edition F 483 – 90 (Reapproved 1991) .
temperature and swab the surface of the individual specimen
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.04.
3 thoroughly using clean forceps to hold the test specimen and
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01.
4
the cotton swab.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 483
7.2 Shake off excess solvent. Transfer and immerse the test 9.3 A
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.