ASTM C1323-96(2001)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Ultimate Strength of Advanced Ceramics with Diametrally Compressed C-Ring Specimens at Ambient Temperature
Standard Test Method for Ultimate Strength of Advanced Ceramics with Diametrally Compressed C-Ring Specimens at Ambient Temperature
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of ultimate strength under monotonic loading of advanced ceramics in tubular form at ambient temperatures. Note that ultimate strength as used in this test method refers to the strength obtained under monotonic compressive loading of C-ring specimens where monotonic refers to a continuous nonstop test rate with no reversals from test initiation to final fracture.
1.2 Values expressed in this test method are in accordance with the International System of Units (SI) and Practice E380.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C 1323 – 96 (Reapproved 2001)
Standard Test Method for
Ultimate Strength of Advanced Ceramics with Diametrally
1
Compressed C-Ring Specimens at Ambient Temperature
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1323; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Fracture Origins in Advanced Structural Ceramics
MIL-STD-1942(A) Flexural Strength of High Performance
1.1 This test method covers the determination of ultimate
Ceramics at Ambient Temperature
strength under monotonic loading of advanced ceramics in
tubular form at ambient temperatures. Note that ultimate
3. Terminology
strength as used in this test method refers to the strength
3.1 Definitions:
obtained under monotonic compressive loading of C-ring
3.1.1 advancedceramic—anengineered,high-performance,
specimenswheremonotonicreferstoacontinuousnonstoptest
predominatelynonmetallic,inorganic,ceramicmaterialhaving
rate with no reversals from test initiation to final fracture.
specific functional qualities. (C 1145)
1.2 Values expressed in this test method are in accordance
3.1.2 breaking load—the load at which fracture occurs.
withtheInternationalSystemofUnits(SI)andPracticeE380.
(E 6)
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.3 C-ring—circular test specimen geometry with the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
mid-section (slot) removed to allow bending displacement
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
(compression or tension). (E 6)
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.4 flexural strength—a measure of the ultimate strength
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
of a specified beam in bending.
2. Referenced Documents 3.1.5 modulus of elasticity—the ratio of stress to corre-
2
sponding strain below the proportional limit. (E 6)
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.6 slow crack growth—subcritical crack growth (exten-
C1145 Terminology on Advanced Ceramics
sion) which may result from, but is not restricted to, such
C1161 Test Method for Flexural Strength of Advanced
mechanisms as environmentally assisted stress corrosion or
Ceramics at Ambient Temperature
diffusive crack growth.
C1239 Practice for Reporting Uniaxial Strength Data and
Estimating Weibull Distribution Parameters for Advanced
4. Significance and Use
Ceramics
4.1 Thistestmethodmaybeusedformaterialdevelopment,
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
material comparison, quality assurance, and characterization.
E6 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Test-
Extremecareshouldbeexercisedwhengeneratingdesigndata.
ing
4.2 For a C-ring under diametral compression, the maxi-
E337 TestMethodforMeasuredHumiditywithPsychrom-
mum tensile stress occurs at the outer surface. Hence, the
eter (Measurement of Wet- and Dry-Bulb Temperatures)
C-ring specimen loaded in compression will predominately
E380 PracticeforUseofInternationalSystemofUnits(SI)
evaluate the strength distribution and flaw population(s) on the
(the Modernized Metric System)
3 external surface of a tubular component. Accordingly, the
2.2 Military Standards:
condition of the inner surface may be of lesser consequence in
MIL-HDBK-790 Fractography and Characterization of
specimen preparation and testing.
NOTE 1—AC-ring in tension or an O-ring in compression may be used
to evaluate the internal surface.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C28 on
Advanced Ceramics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C28.04.08 on
4.3 The flexure stress is computed based on simple curved-
Thermal Systems.
4
beamtheory(1) withassumptionsthatthematerialisisotropic
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 1996. Published April 1996.
2
and homogeneous, the moduli of elasticity are identical in
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
AvailablefromStandardizationDocumentsOrderDesk,Bldg.4SectionD,700 The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to a list of references at the end of
Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS. this test method.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
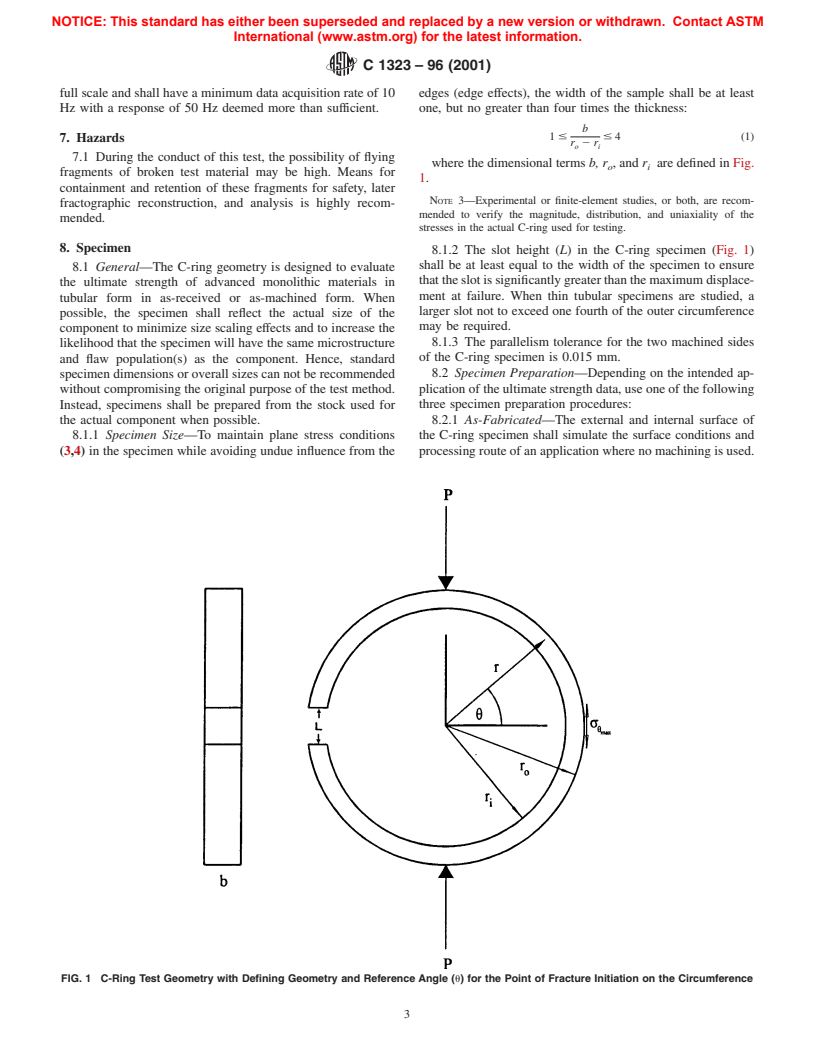
C 1323
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.