ASTM D1560-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Resistance to Deformation and Cohesion of Bituminous Mixtures by Means of Hveem Apparatus
Standard Test Methods for Resistance to Deformation and Cohesion of Bituminous Mixtures by Means of Hveem Apparatus
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The results of the deformation and cohesion tests can be used for specification purposes or for mix design purposes, or both. For example, these values can be used for specification compliance testing of aggregate properties. They can also be used for specification compliance testing of the mix. The cohesion test is sometimes used for fine mixes such as sand mixes wherein cohesion, or tensile strength, is of major or primary importance. The cohesion test is also sometimes used for the design of cold mixes containing emulsified asphalt.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of (1) the resistance to deformation of compacted bituminous mixtures by measuring the lateral pressure developed when applying a vertical load by means of the Hveem stabilometer and (2) the cohesion of compacted bituminous mixtures by measuring the force required to break or bend the sample as a cantilever beam by means of the Hveem cohesiometer.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1560–09
Standard Test Methods for
Resistance to Deformation and Cohesion of Bituminous
1
Mixtures by Means of Hveem Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1560; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (ϵ) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.3 California Department of Transportation Standards:
2
Test 306 Method of Test for Cohesiometer Value
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of (1) the
2
Test 366 Method of Test for Stabilometer Value
resistance to deformation of compacted bituminous mixtures
by measuring the lateral pressure developed when applying a
3. Significance and Use
vertical load by means of the Hveem stabilometer and (2) the
3.1 The results of the deformation and cohesion tests can be
cohesion of compacted bituminous mixtures by measuring the
used for specification purposes or for mix design purposes, or
force required to break or bend the sample as a cantilever beam
2 both. For example, these values can be used for specification
by means of the Hveem cohesiometer.
compliance testing of aggregate properties. They can also be
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
used for specification compliance testing of the mix. The
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
cohesion test is sometimes used for fine mixes such as sand
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
mixes wherein cohesion, or tensile strength, is of major or
and are not considered standard.
primary importance. The cohesion test is also sometimes used
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
for the design of cold mixes containing emulsified asphalt.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
RESISTANCE TO DEFORMATION
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4. Apparatus
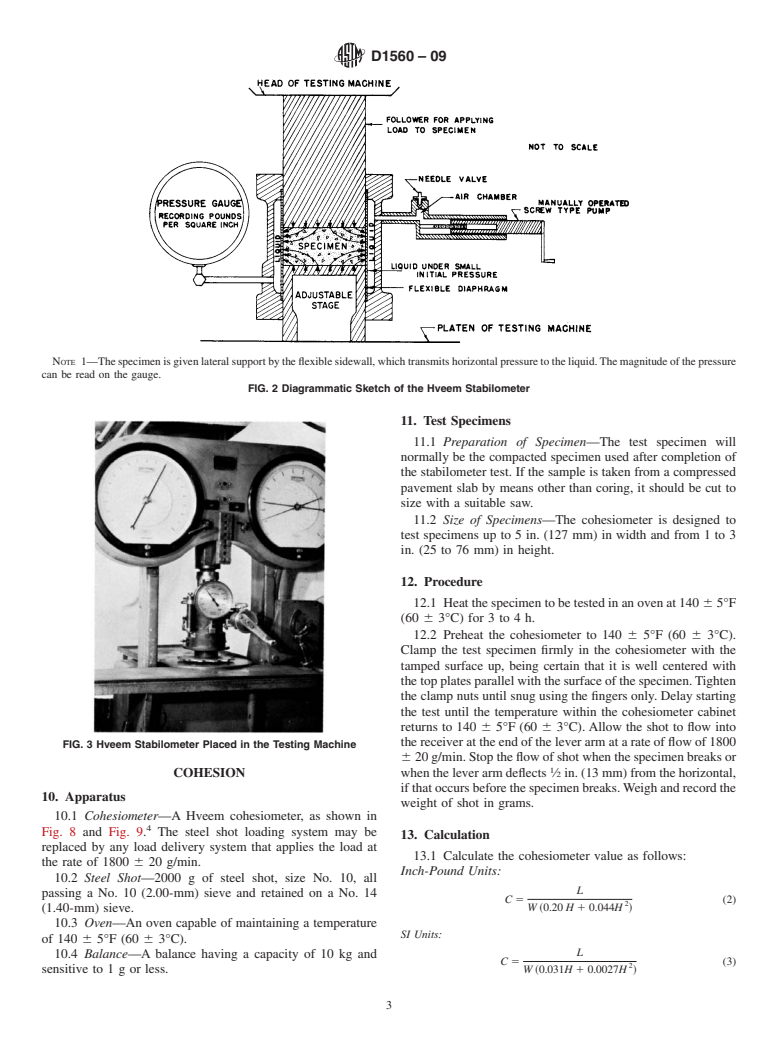
4.1 Stabilometer—TheHveemstabilometer(Fig.1andFig.
2. Referenced Documents
2) is a triaxial testing device consisting essentially of a rubber
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
sleeve within a metal cylinder containing a liquid which
D1561 Practice for Preparation of Bituminous Mixture Test
registers the horizontal pressure developed by a compacted test
Specimens by Means of California Kneading Compactor
specimen as a vertical load is applied.
D3666 Specification for Minimum Requirements forAgen-
4.2 Testing Machine—Acompression testing machine hav-
cies Testing and Inspecting Road and Paving Materials
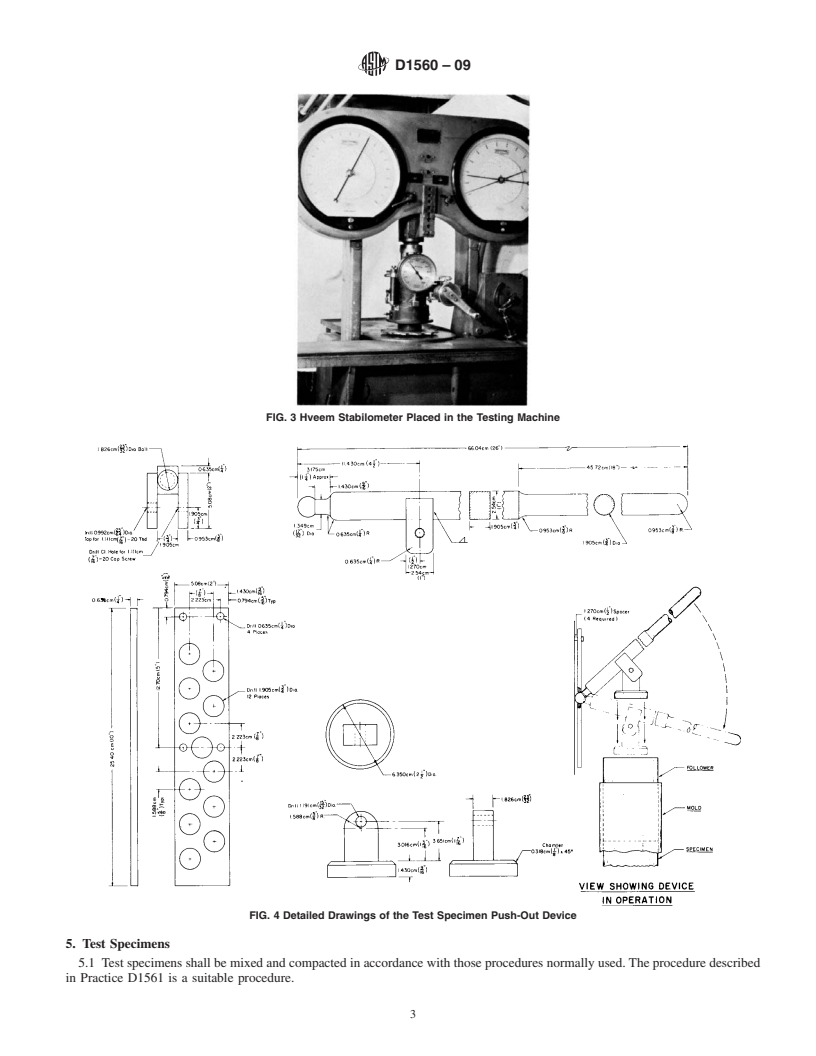
ing a minimum capacity of 10 000 lbf (44.5 kN). Fig. 3 shows
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
the stabilometer in a testing machine. The 50 000 lbf (22-kN)
4
Cohesiometer
capacity compression testing machine specified in Practice
D1561, is normally used to perform the stabilometer test.
1
4.3 Test Specimen Push-Out Device—A device, to push the
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on
Road and Paving Materials and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
specimen out of the mold (see Fig. 4 for an example).
D04.20 on Mechanical Tests of Bituminous Mixtures.
4.4 Oven—An oven capable of maintaining a temperature
Current edition approved June 1, 2009. Published June 2009. Originally
´1 of 140 6 5°F (60 6 3°C).
approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D1560 – 05 . DOI:
10.1520/D1560-09. 4.5 Calibration Cylinder—A hollow metal cylinder 4.000
2
A more detailed description of the procedures for performing the tests is
6 0.005 in. (101.6 6 0.13 mm) in outside diameter by 5.50 6
available on request from the California Dept. of Transportation, 5900 Folsom
0.25 in. (140 6 6.4 mm) high (for calibration purposes).
Blvd., Sacramento, CA 95819. Also available is a procedure containing details
4.6 Rubber Bulb—For introducing air into the stabilometer.
regarding the operation and calibration of the stabilometer and the replacement of
the stabilometer diaphragm.
4.7 Follower—One solid wall metal follower 3.985 in.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 1
(101.2 mm) in diameter by 5 ⁄2 in. (140 mm) high (see Fig. 5
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and Fig. 6).
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
4
Detailed working drawings of the apparatus illustrated in Fig. 9 are available
fromASTM International Headquarters. OrderAdjunct No.ADJD156001. Original
adjunct produced in 1960.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, Unit
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D1560–09
Standard Test Methods for
Resistance to Deformation and Cohesion of Bituminous
1
Mixtures by Means of Hveem Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1560; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of (1) the resistance to deformation of compacted bituminous mixtures by
measuring the lateral pressure developed when applying a vertical load by means of the Hveem stabilometer and (2) the cohesion
of compacted bituminous mixtures by measuring the force required to break or bend the sample as a cantilever beam by means
2
of the Hveem cohesiometer.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1561 Practice for Preparation of Bituminous Mixture Test Specimens by Means of California Kneading Compactor
D3666 Specification for Minimum Requirements for Agencies Testing and Inspecting Road and Paving Materials
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
4
Cohesiometer
2.3 California Department of Transportation Standards:
2
Test 306 Method of Test for Cohesiometer Value
2
Test 366 Method of Test for Stabilometer Value
3. Significance and Use
3.1 The results of the deformation and cohesion tests can be used for specification purposes or for mix design purposes, or both.
For example, these values can be used for specification compliance testing of aggregate properties. They can also be used for
specification compliance testing of the mix. The cohesion test is sometimes used for fine mixes such as sand mixes wherein
cohesion, or tensile strength, is of major or primary importance. The cohesion test is also sometimes used for the design of cold
mixes containing emulsified asphalt.
RESISTANCE TO DEFORMATION
4. Apparatus
4.1 Stabilometer— The Hveem stabilometer (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2) is a triaxial testing device consisting essentially of a rubber
sleeve within a metal cylinder containing a liquid which registers the horizontal pressure developed by a compacted test specimen
as a vertical load is applied.
4.2 Testing Machine— A compression testing machine having a minimum capacity of 10 000 lbf (44.5 kN). Fig. 3 shows the
stabilometer in a testing machine. The 50 000 lbf (22-kN) capacity compression testing machine specified in Practice D1561, is
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road and Paving Materials and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.20 on
Mechanical Tests of Bituminous Mixtures.
´1
Current edition approved June 1, 2009. Published June 2009. Originally approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D1560 – 05 . DOI:
10.1520/D1560-09.
2
AmoredetaileddescriptionoftheproceduresforperformingthetestsisavailableonrequestfromtheCaliforniaDept.ofTransportation,5900FolsomBlvd.,Sacramento,
CA 95819. Also available is a procedure containing details regarding the operation and calibration of the stabilometer and the replacement of the stabilometer diaphragm.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Detailed working drawings of the apparatus illustrated in Fig. 9 are available fromASTM International Headquarters. OrderAdjunct No.ADJD156001. Original adjunct
produced in 1960.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1560–09
TABLE 1
A—Air cell.
B—Displacement pump.
C—200-psi pressure gauge.
D—Ames dial.
E—Base adjustment nut.
F—Bottom of upper tapered ring.
FIG. 1 Hveem Stabilometer
NOTE 1—Thespecimenisgivenlateralsupportbytheflexiblesidewall,whichtransmitshorizontalpressuretotheliquid.The
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.