ASTM F586-79(1989)E01
(Test Method)Test Method for Leak Rates Versus Y Stresses and M Factors for Gaskets (Withdrawn 1998)
Test Method for Leak Rates Versus Y Stresses and M Factors for Gaskets (Withdrawn 1998)
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: F 586 - 79 (Reapproved 1989)“’
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTINO AND MATERIALS
1916 Race 3. Philadelphia, Pa. 19103
Reprinled from the Annual Book of ASTM Slandards. CapVri9hl &?JM
II nol listed in lhe current combined index, will apqaar In tho MXI adilion.
Standard Test Method for
Leak Rates Versus y Stresses and m Factors for Gaskets’
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 586; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapprovrd. A
superscript epsilon (0 indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
‘I NOTE-Editorial change-s were made throughout in July 1989.
1. Scope joint, with no pressure in the assembly.
3.2 Symbols:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of leak
W = total fastener force, N (or lbf)
rates versus y stresses and m factors for gaskets gripped by
D
= outside diameter of gasket, mm (or in.)
pressure-containing flanged connections.
d = inside diameter of gasket, mm (or in.)
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
= gasket area, cm2 (or in.2)
standard. Al
= inside area of gasket, cm2 (or in.2)
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, oper- A2
P
= test pressure, kPa (or psi)
ations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
= yield factor or y stress, kPa (or psi)
Y
address all of the safety problems associated with its use. It is
= maintenance factor or m factor
the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish
Y = standard pressure, 101.3 kPa (or 14.7 psi)
appropriate safety and health practices and determine the
= atmospheric pressure, kPa (or psia)
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
= pressure in buret at height, hl, kPa (or psia)
pt
= pressure in buret at height, ha, kPa (or psia)
2. Referenced Documents p2
= pressure in buret at height, h3, kPa (or psia)
p3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
= standard pressure, kPa (psi)
PS
F 104 Classification System for Nonmetallic Gasket Ma-
= height of water in buret at P,, mm (or in.)
ht
terials2
= height of water after opening valve, mm (or in.)
hz
F 363 Test Method for Corrosion Testing of Gaskets*
= height of water after end of run, mm (or in.)
h3
2.2 ANSI Standard:
= volume of measuring system, cm3 (or in.3)
VI
16.5 Steel Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings3
= volume after opening valve, cm3 (or in.3)
v2
2.3 ASME Standard:
= volume at end of run, cm3 (or in.3)
b
Pressure Vessel Code, Table UA-49.1, Section VIII,
= scale number on buret at start, cm3 (or in.3)
Cl
Div. l4
= scale number on buret after opening valve, cm3
c2
(or in.3)
3. Terminology
= scale number on buret at end of run, cm3 (or ins3)
c-3
3.1 Definitions:
= temperature, at start, K
Tt
3.1.1 gasket contact area-the area of the gasket that is
= temperature, open valve, K
T2
under load from the flange surfaces.
= temperature, end of run, K
T3
3.1.2 leak rate-the leakage in cubic centimetres of fluid
l-!3 = 273.15 K
per second passing through or around the gasket under the
TA = ambient temperature, K
conditions of this test, reduced to standard.
= time of run, s
3.1.3 maintenance factor, m-the factor that provides the
fu = 0.00142 psi/mm Hz0
additional preload capability in the flange fasteners to
= leakage in standard, cm3 (or in.3)
maintain sealing pressure on a gasket after internal pressure
vLs/t = leak rate, cm3/s (or in.3/s)
is applied to a joint.
VLA = leak volume under ambient conditions; cm3 (or
3.1.4 yield factor, y-the factor that represents the pres-
in.3)
sure in kilopascals (or pounds-force per square inch) over the
4. Significance and Use
contact area of the gasket that is required to provide a sealed
4.1 This test method determix& both the y stress and the
m factor as curves rather than as single or constant numbers.
‘This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-3 on
Gaskets and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Fo3.20 on Methods of 5. Apparatus
Test for Nonmetallic Gaskets.
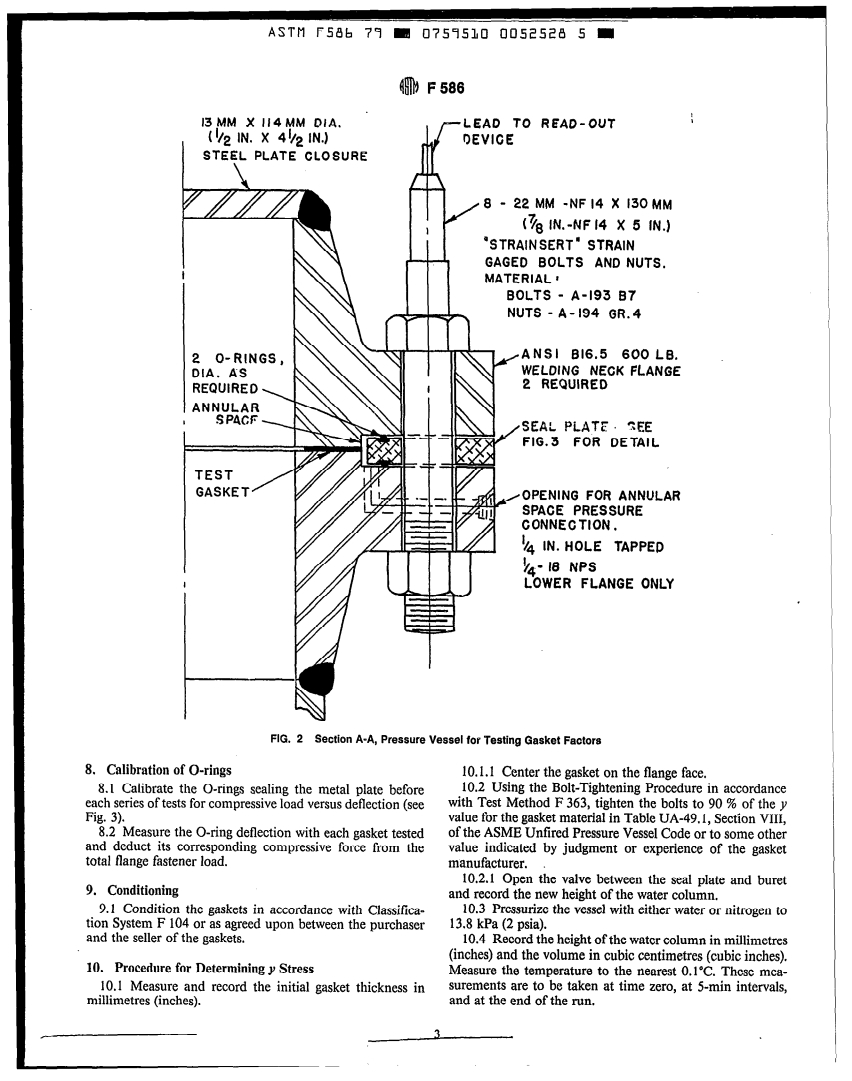
5.1 Pressure Vessel, Fig. 1, fabricated from two 600-psi
Current edition approved Jan. 5, 1979. Published June 1979. Originally
published as F 586 - 78. Last previous edition F 586 - 78. welding flanges in accordance with ANSI B16.5, to remove
’ Antural Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.02.
flange bending from consideration. See Figs. 2 and 3 for
3 Available from American National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New
details. One flange is welded to a short pipe and suitable base
York. NY 10018.
plate, and one flange is welded shut at the neck with a
4 Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 345 E. 47th St.,
New York. NY 10017.
suitable closure. Both fabrications shall be hydrotested at 1.5
ASTM F586 79 W 0759530 0052527 3 W
INLET PRESSURE LINE
,/
r
305 MM
(12 IN.)
PRESSURE RELIEF LINE
I
b305MM 4
( 12 IN.)
140 MM (5j2 IN.)
III I
t
I
I3 MM 02 IN.1
FIG. 1 Pressure Vessel for Testing Gasket Factors
times the rated pressure or 6.205 MPa (900 psi). If necessary,
(0.250 to 0.500 in.) larger than the inside diameter of the
both fabrications shall be remachined after hydrotest to pipe and an outside diameter no larger than the 157.2-mm
conform to the details in Fig. 1. The vessel shall be fitted with (6.1875~in.) outside diameter of a standard raised-face
calibrated strain-gaged bolts, each capable of 53 378-N
gasket.
(12 OOO-lbf) axial load. The top part of the vessel shall be 6.2 A minimum of six gaskets are required for determina-
fitted with one vent valve and with one pressure inlet that is
tion of any y stress and leak rate combination.
also connected to a pressure gage. The pressure gage shall be
7. Preparation of Apparatus
a 0 to 5000-kPa (0 to 500-psi) oil-filled type, accurate to f
7.1 Buret:
0.25 %, and having a face at least 152.4 mm (6 in.) in
7.1.1 Measure the length of the buret scale in millimetres
diameter to provide sufficient resolution. The vessel shall be
(inches) and make a conversion chart for the correction of
fitted further with a metal seal plate and two O-rings in the
the actual height of the water to the standard height of each
manner detailed on Fig, 2 for containment of leakage past
cubic centimetre. For example, if a 570-mm (22.5-m.) long
the gasket.
scale represents 50 cm3 (3 in3) in the buret, the actual
5.2 Buret Assembly, consisting of one 50-mL buret with
measured heights (h,, hz, and ha) must be multiplied by a
stand, one 152.4-mm (6-in.) diameter battery jar, one
factor of 570:500 to arrive at the standard height for the
203.2-mm (8-m) diameter battery jar, suitable length of 6.4
given cubic centimetre.
mm (0.250 in.) in inside diameter plastic tubing, and one
7.1.2 Lift a column of water into the buret by suction and
tubing-to-buret clamp.
close the buret stop cock.
7.1.3 Fill the inner battery jar to overflowing.
6. Test Specimen
7.1.4 Set zero on the buret to the liquid level of the inner
6.1 The test specimen shall be a nominal 4-in. pipe size, battery jar,
raised-
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.