ASTM F2661-07(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining the Tribological Behavior and the Relative Lifetime of a Fluid Lubricant using the Spiral Orbit Tribometer
Standard Test Method for Determining the Tribological Behavior and the Relative Lifetime of a Fluid Lubricant using the Spiral Orbit Tribometer
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
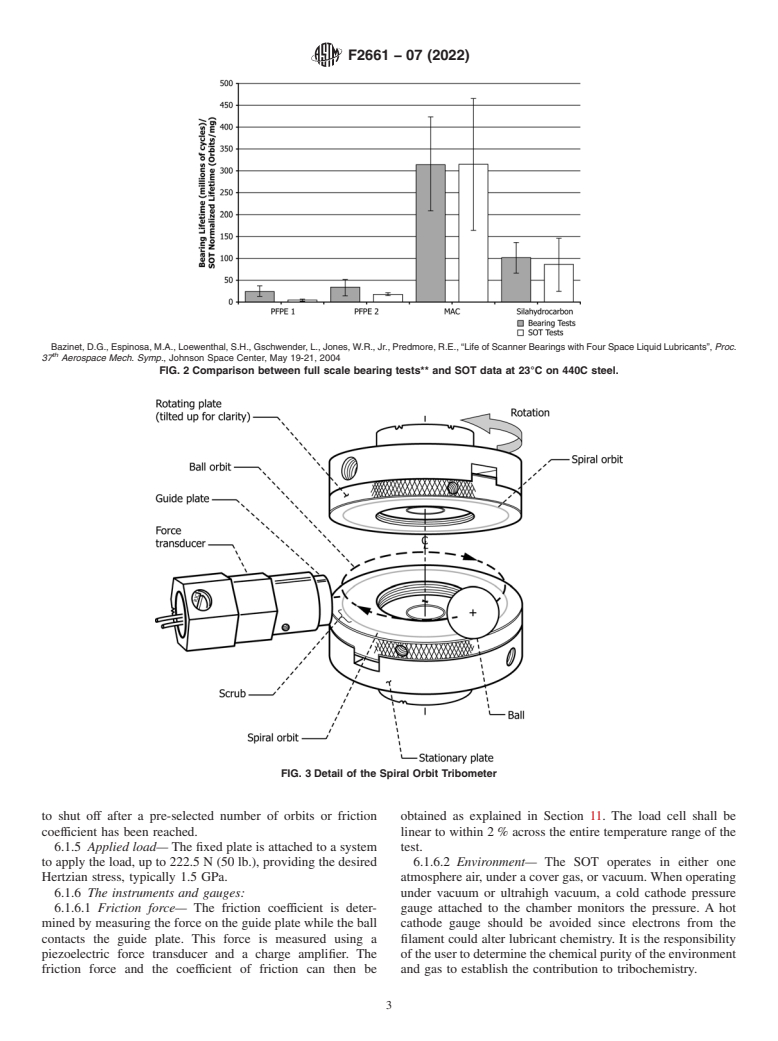
5.1 Relevance of the Spiral Orbit Tribometer (SOT)—The SOT was designed to evaluate the relative degradation rates of liquid lubricants in a contact environment similar to that in an angular contact bearing operating in the boundary lubrication regime. It functions as a screening device to quickly select the lubricants, evaluate the ability of various components of a lubricant (base oil, thickener, or additive) to lubricate a contact in rolling, pivoting, and sliding conditions simultaneously, and study their chemical decomposition if necessary. The SOT provides a means to study the tribological behavior of oils and greases during operation, while they undergo changes as a function of typical parameters encountered in the lubrication field (temperature, environment, materials used, load applied, and speed). Test conclusion is defined to be when a friction coefficient limit (typically an increase of 0.1 above the steady state value) is surpassed. Normalized lubricant lifetime is then defined as the number of orbits completed divided by the initial amount of lubricant used (in μg). The SOT was initially developed to evaluate lubricants for space applications, but is also relevant for conventional environments. Some results in vacuum are presented (Fig. 1). At this time, no data for tests in ambient conditions have been published (see Fig. 2). The user of this test method should determine to their own satisfaction whether results of this test procedure correlate with field performance or other bench test procedures.
FIG. 1 Relative lifetimes of three typical space lubricants at 23°C in vacuum on 52100 steel
Pepper, S.V., Kingsbury, E.P., “Spiral Orbit Tribometry – Part II: Evaluation of Three Liquid Lubricants in Vacuum”, Tribo. Trans., V 46, 1, pp 65-69, 2003
FIG. 2 Comparison between full scale bearing tests** and SOT data at 23°C on 440C steel.
Bazinet, D.G., Espinosa, M.A., Loewenthal, S.H., Gschwender, L., Jones, W.R., Jr., Predmore, R.E., “Life of Scan...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the quantitative determination of the friction coefficient and the lifetime of oils and greases, when tested on a standard specimen under specified conditions of preparation, speed, Hertzian stress, materials, temperature, and atmosphere, by means of the Spiral Orbit Tribometer (SOT). This test method is intended primarily as an evaluation of the lifetimes of fluid lubricants under vacuum and ambient conditions.
1.2 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F2661 − 07 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Method for
Determining the Tribological Behavior and the Relative
Lifetime of a Fluid Lubricant using the Spiral Orbit
1
Tribometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2661; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope G115Guide for Measuring and Reporting Friction Coeffi-
cients
1.1 This test method covers the quantitative determination
2.2 Anti Friction Bearing Manufacturers Association Stan-
of the friction coefficient and the lifetime of oils and greases,
3
dards
when tested on a standard specimen under specified conditions
ANSI ABMA ISO 3290(AFBMA Standard 10 Balls)
of preparation, speed, Hertzian stress, materials, temperature,
and atmosphere, by means of the Spiral Orbit Tribometer
3. Terminology
(SOT).This test method is intended primarily as an evaluation
3.1 Definitions:
of the lifetimes of fluid lubricants under vacuum and ambient
3.1.1 coeffıcient of friction—the dimensionless ratio of the
conditions.
friction force between two bodies to the normal force pressing
1.2 This standard may involve hazardous materials,
these bodies together.
operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
3.1.2 fixed plate—stationary, horizontal flat plate, typically
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its
through which a force (the “load”) is applied to the ball.
use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental prac- 3.1.3 friction coeffıcient limit—maximum value that the
tices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations friction coefficient is permitted to attain.
prior to use.
3.1.4 guide plate—physical element that deflects the ball to
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
its original orbit radius.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.5 lubricant total amount— mass of lubricant deposited
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
on the entire ball surface at the beginning of the test.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.1.6 normalized lifetime—number of ball orbits performed
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
until the friction coefficient limit is reached divided by the
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
lubricant total amount initially deposited on the ball.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.7 rotary plate—flat plate rotating at a constant rate
2
selected for the test.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
3.1.8 scrub zone—Region of the ball’s orbit in which the
F22Test Method for Hydrophobic Surface Films by the
ball is in contact with the guide plate.
Water-Break Test
3.1.9 spiral orbit—track traced by the ball on the fixed and
F2215Specification for Balls, Bearings, Ferrous and Non-
rotating plates of the Spiral Orbit Tribometer. The track has a
ferrous for Use in Bearings, Valves, and Bearing Appli-
spiral shape.
cations
4. Summary of Test Method
1 4.1 Alubricatedballisclampedbetweentwoparallelplates.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeF34 on Rolling
Element Bearings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F34.02 on One of the plates rotates up to 210 rpm, causing the ball to roll
Tribology.
in a near-circular orbit, but is actually an opening spiral. A
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2022. Published August 2022. Originally
clamping force, the “load”, provides a chosen mean Hertz
approvedin2007.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2015asF2661–07(2015).DOI:
stress (typically 1.5 GPa). The system is targeted to operate in
10.1520/F2661-07R22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American Boiler Manufacturers Association 8221 Old Court-
the ASTM website. house Road, Suite 380 Vienna, Virginia 22182. https://www.abma.com/
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2661 − 07 (2022)
the boundary lubrication regime due to the combination of the developed to evaluate lubricants for space applications, but is
high load, the moderate speed, and the small amount of also relevant for
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.