ASTM C793-05(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Effects of Laboratory Accelerated Weathering on Elastomeric Joint Sealants
Standard Test Method for Effects of Laboratory Accelerated Weathering on Elastomeric Joint Sealants
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
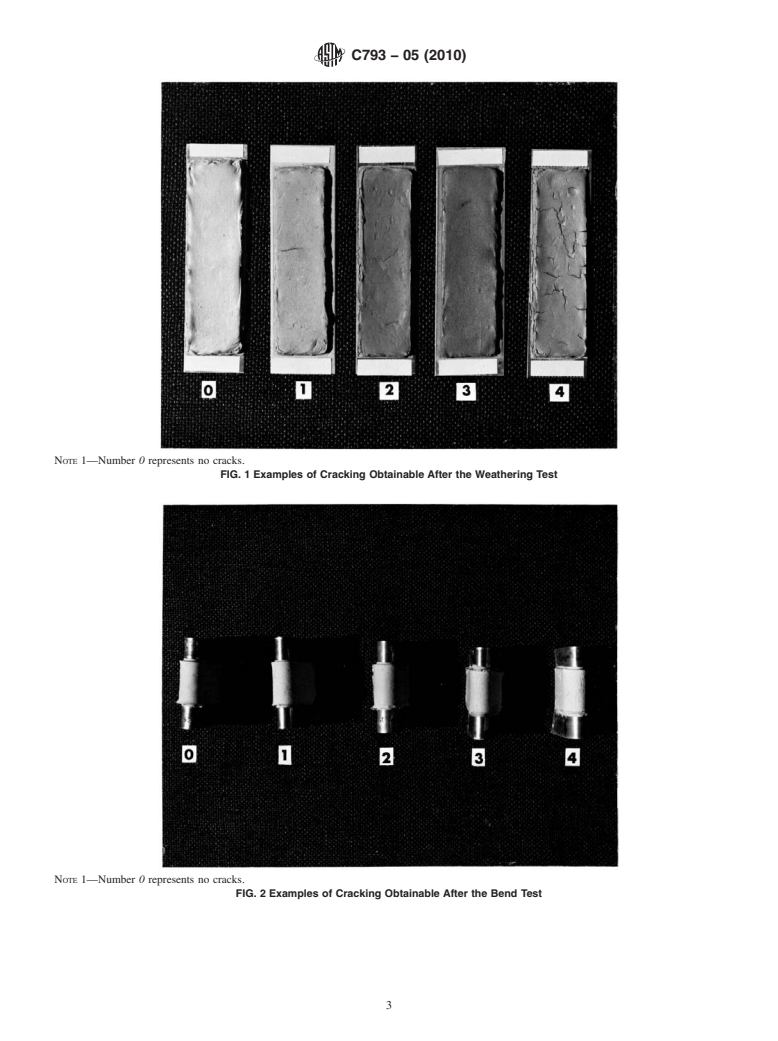
It is known that solar radiation contributes to the degradation of sealants in exterior building joints. The use of a laboratory accelerated weathering machine with actinic radiation, moisture and heat appears to be a feasible means to give indications of early degradation by the appearance of sealant cracking. However, simulated weather factors in combination with extension may produce more severe degradation than weather factors only. Therefore, the effect of the weathering test is made more sensitive by the addition of the bending of the specimen at cold temperature.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure for determining the effects of accelerated weathering on cured-in-place elastomeric joint sealants (single- and multicomponent) for use in building construction.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The committee with jurisdiction over this standard is not aware of any comparable standards published by other ASTM committees or other organizations.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C793 − 05 (Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
Effects of Laboratory Accelerated Weathering on
Elastomeric Joint Sealants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C793; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope chambers specified in Section 6 and operated in accordance
with specifications in Section 8 and Practice C1442.
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure for
determining the effects of accelerated weathering on cured-in-
4.2 Following this treatment the specimens are exposed for
place elastomeric joint sealants (single- and multicomponent)
24 h in a freezer maintained at −26 6 2°C (−15 6 4°F).
for use in building construction.
4.3 At the end of the cold exposure, the specimens are bent
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
over a mandrel within1satthe specified temperature.
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 Thecommitteewithjurisdictionoverthisstandardisnot 5. Significance and Use
aware of any comparable standards published by otherASTM
5.1 It is known that solar radiation contributes to the
committees or other organizations.
degradation of sealants in exterior building joints.The use of a
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
laboratory accelerated weathering machine with actinic
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
radiation, moisture and heat appears to be a feasible means to
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
give indications of early degradation by the appearance of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
sealant cracking. However, simulated weather factors in com-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
bination with extension may produce more severe degradation
than weather factors only. Therefore, the effect of the weath-
2. Referenced Documents
eringtestismademoresensitivebytheadditionofthebending
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of the specimen at cold temperature.
C717Terminology of Building Seals and Sealants
C1442Practice for Conducting Tests on Sealants Using
6. Apparatus
Artificial Weathering Apparatus
6.1 Exposure Apparatus—The exposure apparatus shall be
G151PracticeforExposingNonmetallicMaterialsinAccel-
one of the three types of laboratory accelerated weathering
erated Test Devices that Use Laboratory Light Sources
devices described in Practice C1442 that use either xenon arc,
3. Terminology
fluorescent UV, or open flame carbon arc radiation. Consult
PracticeC1442,Section7forthedifferencesintestparameters
3.1 Definitions—SeeTerminologyC717forapplicabledefi-
among the devices. Because of differences in test conditions,
nitions of the following terms: cure, elastomeric, joint, sealant,
test results may differ with the type of device used.The choice
and substrate.
of device shall be by mutual agreement among the interested
4. Summary of Test Method
parties.
4.1 Three sealant specimens are spread on aluminum plates
6.2 Freezer or Cold Box, having a temperature controlled
and exposed in one of the laboratory accelerated weathering
at−26 6 2°C (−15 6 4°F).
6.3 Rectangular Brass Frame, with inside dimensions 130
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC24onBuilding
1 1
Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.40 on
by40by3mm(5by1 ⁄2 by ⁄8 in.).
Weathering.
6.4 Aluminum Plates,three,each152by80by0.3mm(6by
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2010.PublishedJuly2010.Originallyapproved
in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as C793–05. DOI: 10.1520/
3 by 0.01 in.).
C0793-05R10.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 6.5 Steel Mandrel, 12.7 mm ( ⁄2 in.) in diameter and about
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
102 mm (4 in.) long.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 6.6 Thin-Bladed Knife.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
C793 − 05 (2010)
NOTE 2—See Annex A1 in Practice C1442 for determining the xenon
6.7 Straightedge, metal or plastic, about 152 mm (6 in.)
arc exposure time required to obtain the same radiant exposure at other
long.
irradiance levels.
6.8 Spatula, steel, about 152 mm (6 in.) long.
8.1.4 At the end of exposure, remove the specimens from
the machine and note changes in appearance as compared with
7. Standard Test Conditions
the unexposed file specimen.
7.1 Unless otherwise specified by those authorizing the test,
8.1.5 Place all three specimens and the mandrel in the
standardconditionsshallbeasdescribedinTerminologyC717.
freezer, controlled at−26 6 2°C (−15 6 4°F) for 24 h.At the
endofthisperiod,whileinthefreezeratthistemperature,bend
8. Procedure
each specimen, with sealant side outward, across its width,
8.1 Test of Multicomponent Sealants:
180° around the mandrel within 1 s. Examine each specimen
8.1.1 Condition at least 200 g of base compound and
for crack
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.