ASTM D7157-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Intrinsic Stability of Asphaltene-Containing Residues, Heavy Fuel Oils, and Crude Oils (n-Heptane Phase Separation; Optical Detection)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Intrinsic Stability of Asphaltene-Containing Residues, Heavy Fuel Oils, and Crude Oils (n-Heptane Phase Separation; Optical Detection)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method describes a sensitive method for estimating the intrinsic stability of an oil. The intrinsic stability is expressed as S-value. An oil with a low S-value is likely to undergo flocculation of asphaltenes when stressed (for example, extended heated storage) or blended with a range of other oils. Two oils each with a high S-value are likely to maintain asphaltenes in a peptized state and not lead to asphaltene flocculation when blended together.
This test method can be used by petroleum refiners to control and optimize the refinery processes and by blenders and marketers to assess the intrinsic stability of blended asphaltene-containing heavy fuel oils.
SCOPE
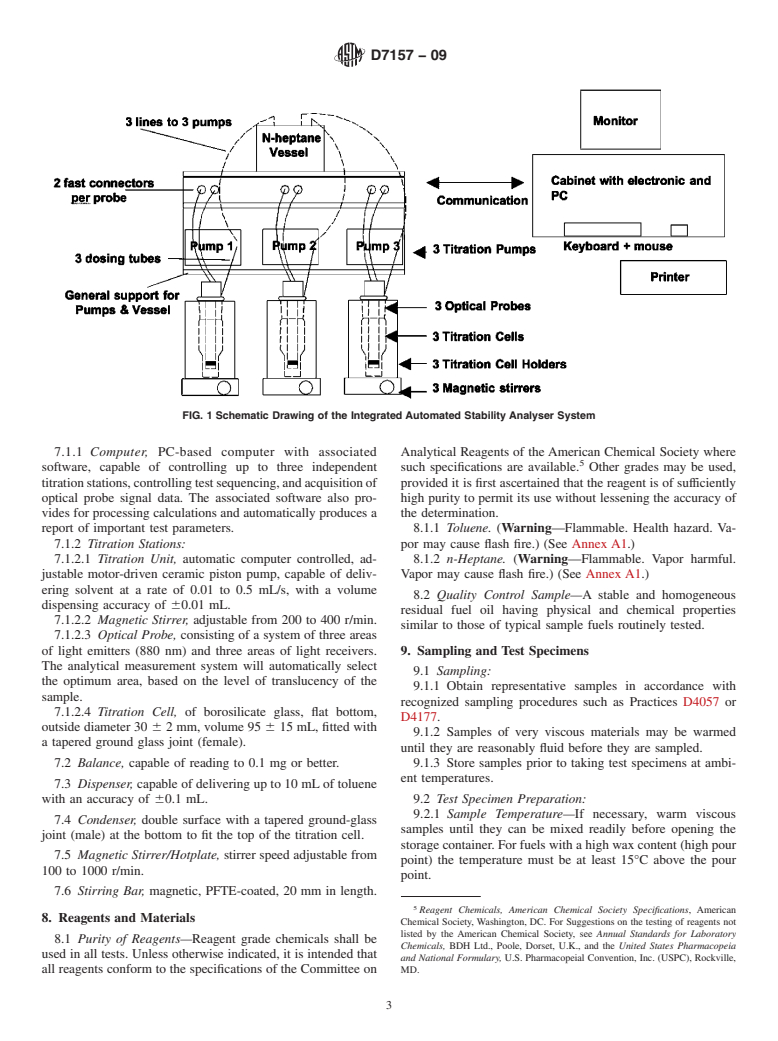
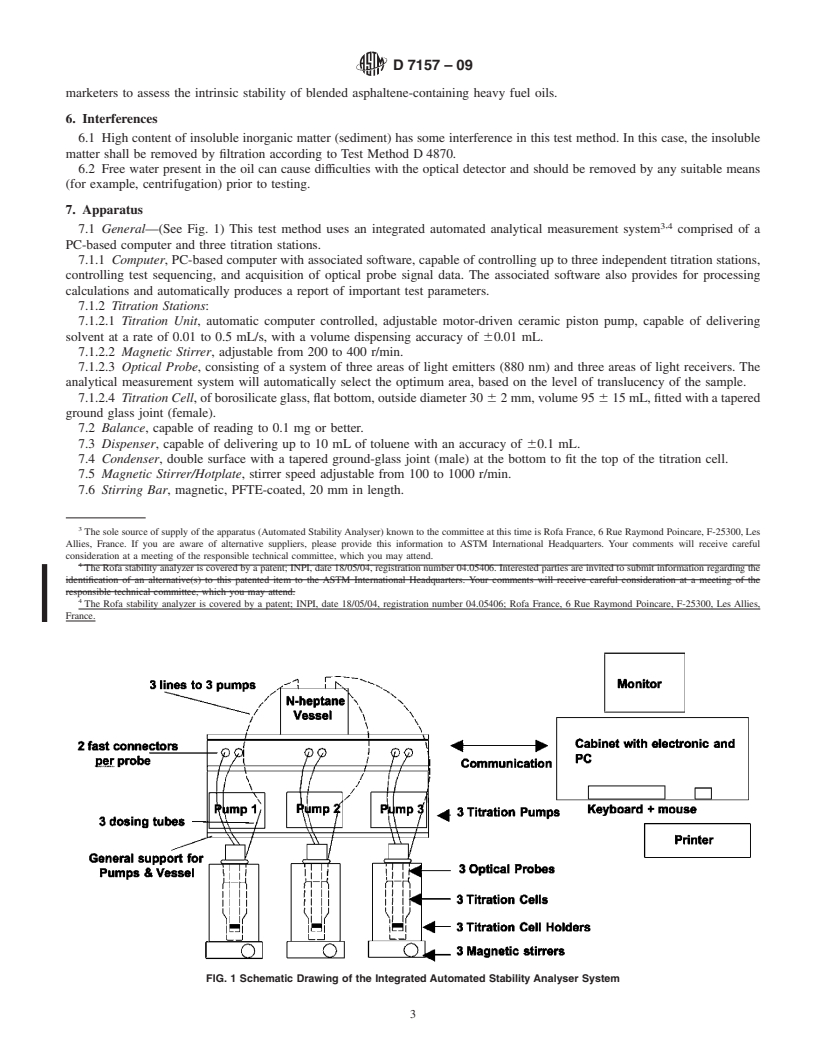
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for quantifying the intrinsic stability of the asphaltenes in an oil by an automatic instrument using an optical device.
1.2 This test method is applicable to residual products from thermal and hydrocracking processes, to products typical of Specifications D 396 Grades No. 5L, 5H, and 6, and D 2880 Grades No. 3-GT and 4-GT, and to crude oils, providing these products contain 0.5 mass% or greater concentration of asphaltenes (see Test Method D 6560).
1.3 This test method quantifies asphaltene stability in terms of state of peptization of the asphaltenes (S-value), intrinsic stability of the oily medium (So) and the solvency requirements of the peptized asphaltenes (Sa).
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7157 − 09 AnAmerican National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Intrinsic Stability of Asphaltene-Containing
Residues, Heavy Fuel Oils, and Crude Oils (n-Heptane
1
Phase Separation; Optical Detection)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7157; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Products, and Lubricants
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for quantifying the
Petroleum Products
intrinsic stability of the asphaltenes in an oil by an automatic
D4870 Test Method for Determination of Total Sediment in
instrument using an optical device.
Residual Fuels
1.2 This test method is applicable to residual products from
D6560 Test Method for Determination ofAsphaltenes (Hep-
thermal and hydrocracking processes, to products typical of
tane Insolubles) in Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Prod-
Specifications D396 Grades No. 5L, 5H, and 6, and D2880
ucts
Grades No. 3-GT and 4-GT, and to crude oils, providing these
D6792 Practice for Quality System in Petroleum Products
products contain 0.5 mass% or greater concentration of as-
and Lubricants Testing Laboratories
phaltenes (see Test Method D6560).
1.3 This test method quantifies asphaltene stability in terms
3. Terminology
of state of peptization of the asphaltenes (S-value), intrinsic
3.1 Definitions:
stabilityoftheoilymedium(So)andthesolvencyrequirements
3.1.1 For definitions of some terms used in this test method,
of the peptized asphaltenes (Sa).
refer to Terminology D4175.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1.2 asphaltene, n—in petroleum technology,amoleculeof
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
high molecular mass, high carbon/hydrogen ratio, and contain-
standard.
ing hetero-atoms.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Asphaltenes are found largely in crude
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
oils and in heavy fuel oils containing residual fractions. They
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
are insoluble in alkanes such as n-heptane and cetane, but
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
soluble in aromatic solvents such as benzene, toluene, and
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use
1-methylnaphthalene.
2. Referenced Documents 3.1.3 compatibility, n—of crude oils or of heavy fuel oils,
2
the ability of two or more crude oils or fuel oils to blend
2.1 ASTM Standards:
together within certain concentration ranges without evidence
D396 Specification for Fuel Oils
of separation, such as the formation of multiple phases.
D2880 Specification for Gas Turbine Fuel Oils
3.1.3.1 Discussion—Incompatible heavy fuel oils or crude
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
oils, when mixed or blended, result in the flocculation or
Petroleum Products
precipitation of asphaltenes. Some oils may be compatible
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum
within certain concentration ranges in specific mixtures, but
incompatible outside those ranges.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum
3.1.4 flocculation, n—of asphaltenes from crude oils or
Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.14 on
Stability and Cleanliness of Liquid Fuels.
heavy fuel oils, the aggregation of colloidally dispersed as-
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2009.PublishedJuly2009.Originallyapproved
phaltenes into visible larger masses which may or may not
in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D7157–05. DOI: 10.1520/
settle.
D7157-09.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.1.5 peptization, n—of asphaltenes in crude oils or heavy
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
oils, the dispersion of asphaltenes to produce a colloidal
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. dispersion.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7157 − 09
3.1.6 stability reserve, n—in petroleum technology, the
So = the peptizing power of an oil
property of an oil to maintain asphaltenes in a peptized state
X = paraffinic solvent consumption of undiluted oil, in
min
and prevent flocculation of asphaltenes.
mL/g of oil
3.1.6.1 Discussion—An oil wi
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation:D7157–05 Designation: D 7157 – 09
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Intrinsic Stability of Asphaltene-Containing
Residues, Heavy Fuel Oils, and Crude Oils (n-Heptane Phase
1
Separation; Optical Detection)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 7157; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for quantifying the intrinsic stability of the asphaltenes in an oil by an automatic
instrument using an optical device.
1.2 This test method is applicable to residual products from thermal and hydrocracking processes, to products typical of
Specifications D 396 Grades No. 5L, 5H, and 6, and D 2880 Grades No. 3-GT and 4-GT, and to crude oils, providing these
products contain 0.5 mass% or greater concentration of asphaltenes (see Test Method D 6560).
1.3 Thistestmethodquantifiesasphaltenestabilityintermsofstateofpeptizationoftheasphaltenes(S-value),intrinsicstability
of the oily medium (So) and the solvency requirements of the peptized asphaltenes (Sa).
1.4The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 396 Specification for Fuel Oils
D 2880 Specification for Gas Turbine Fuel Oils
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D 4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum Products, and Lubricants
D 4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D 4870 Test Method for Determination of Total Sediment in Residual Fuels
D 6560 Test Method for Determination of Asphaltenes (Heptane Insolubles) in Crude Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D 6792 GuidePractice for a Quality System in Petroleum Products and Lubricants Testing Laboratories
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of some terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D 4175.
3.1.2 asphaltene, n—in petroleum technology , a molecule of high molecular mass, high carbon/hydrogen ratio, and containing
hetero-atoms.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Asphaltenes are found largely in crude oils and in heavy fuel oils containing residual fractions. They are
insoluble in alkanes such as n-heptane and cetane, but soluble in aromatic solvents such as benzene, toluene, and
1-methylnaphthalene.
3.1.3 compatibility, n—of crude oils or of heavy fuel oils, the ability of two or more crude oils or fuel oils to blend together
within certain concentration ranges without evidence of separation, such as the formation of multiple phases.
3.1.3.1 Discussion—Incompatible heavy fuel oils or crude oils, when mixed or blended, result in the flocculation or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.14 on Stability
and Cleanliness of Liquid Fuels.
Current edition approved May 1, 2005. Published May 2005.
Current edition approved June 1, 2009. Published July 2009. Originally approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D 7157–05.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7157–09
precipitation of asphaltenes. Some oils may be compatible within certain concentration ranges in specific mixtures, but
incompatible outside those ranges.
3.1.4 flocculation, n—of asphaltenes from crude oils or heavy fuel oils,theaggregationofcolloidallydispersedasphaltenesinto
visible larger masses which may or may not settle.
3.1.5 peptization
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.