ASTM A479/A479M-00
(Specification)Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes for Use in Boilers and Other Pressure Vessels
Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes for Use in Boilers and Other Pressure Vessels
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers hot- and cold-finished bars of stainless steel, including rounds, squares, and hexagons, and hot-rolled or extruded shapes such as angles, tees, and channels for use in boiler and pressure vessel construction.
Note 1—There are standards covering high nickel, chromium, austenitic corrosion, and heat-resisting alloy materials. These standards are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Subcommittee B02.07 and may be found in Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.04.
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI (metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within the text and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independent of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.3 Unless the order specifies the applicable "M" specification designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-pound units.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: A 479/A 479M – 00 Used in USDOE-NE Standards
Standard Specification for
Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes for Use in Boilers and
Other Pressure Vessels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 479/A 479M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2.2 Other Document:
SAE J1086 Recommended Practice for Numbering Metals
1.1 This specification covers hot- and cold-finished bars of
and Alloys
stainless steel, including rounds, squares, and hexagons, and
hot-rolled or extruded shapes such as angles, tees, and channels
3. Ordering Information
for use in boiler and pressure vessel construction.
3.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
NOTE 1—There are standards covering high nickel, chromium, austen-
requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
itic corrosion, and heat-resisting alloy materials. These standards are
specification. Such requirements may include, but are not
under the jurisdiction of ASTM Subcommittee B02.07 and may be found
limited to, the following:
in Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.04.
3.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
1.2 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI
3.1.2 Dimensions, including diameter or thickness (and
(metric) units are to be regarded separately as standards; within
width), shape or form, applicable prints or sketches, length,
the text and tables, the SI units are shown in [brackets]. The
etc.,
values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; there-
3.1.3 Type or UNS designation, (Table 1),
fore, each system must be used independent of the other.
3.1.4 ASTM designation and edition year if other than latest
Combining values from the two systems may result in noncon-
edition,
formance with the specification.
3.1.5 Heat treated condition (Section 4.)
1.3 Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specifica-
3.1.6 Finish (see Manufacture section of Specification
tion designation, the material shall be furnished to the inch-
A 484/A 484M).
pound units.
3.1.7 Supplementary Requirements invoked for special ser-
vices (described at the end of this specification):
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.8 Whether bars are to be rolled as bars or cut from strip
2.1 ASTM Standards:
or plate,
A 262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranu-
3.1.9 Preparation for delivery (see Preparation for Delivery
lar Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
section of Specification A 484/A 484M),
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
3.1.10 Marking requirements (see Marking section of
of Steel Products
Specification A 484/A 484M).
A 484/A 484M Specification for General Requirements for
3.1.11 Surface preparation of shapes (see Manufacture sec-
Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
tion of Specification A 484/A 484M),
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for
3.1.12 The intended use of the material, if the purchaser
Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
considers this useful information.
E 112 Test Methods for Determining the Average Grain
NOTE 2—A typical ordering description is as follows: 5000 lb [2000
Size
5 kg]; 1.000 in. [25 mm] round bar by 10 to 12 ft [3 to 4 m]; Type 304 or
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS)
UNS S30400; to Specification A 479 [A 479M]; annealed; centerless
ground; plus any optional supplementary requirements; such as, for
example, special marking instructions.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel,
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4. Heat Treatment
A01.17 on Flat Stainless Steel Products.
Current edition approved March 10, 2000. Published May 2000. Originally
4.1 Austenitic Grades:
published as A 479 – 62 T. Last previous edition A 479/A 479M – 99a.
4.1.1 Except for the strain-hardened grade (see 4.1.3), and
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi-
cation SA-479/SA-479M in Section II of that Code.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
4 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. Available from Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Drive,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01. Warrendale, PA 15096.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 479/A 479M
the hot-rolled grade (see 4.1.4), all austenitic grades of stain- develop the required mechanical properties.
less steel shall be furnished in the solution annealed condition,
4.1.5 Solution annealing of S31254, S32050, and S32654
with subsequent light cold drawing and straightening permitted
shall consist of heating the material to a temperature of 2100°F
(see Supplementary Requirement S5 if annealing must be the [1150°C] minimum, for an appropriate time followed by water
final operation). Solution annealing for all grades, except the H
quenching or rapidly cooling by other means.
grades (see 4.1.2), N08367 (see 4.1.8), S31254 (see 4.1.5),
4.1.6 Solution annealing of S34565 shall consist of heating
S32050 (see 4.1.5), S33228 (see 4.1.7), S34565 (see 4.1.6), and
the material in the range of temperature from 2050°F [1120°C]
S35315 (see 4.1.9), shall consist of (1) heating the material to
to 2140°F [1170°C] for an appropriate time, followed by water
a temperature of 1900°F [1040°C] minimum so that grain
quenching or rapidly cooling by other means.
boundary carbides enter into solution, and cooling rapidly to
4.1.7 Solution annealing of S33228 shall consist of heating
prevent grain boundary carbide precipitation; or alternatively
the material in the temperature range 2050 to 2160°F [1120 to
(2) (except for the columbium and titanium stabilized grades
1180°C] for an appropriate time followed by water quenching
309Cb, 310Cb, 316Cb, 316Ti, 321, 347, and 348) immediately
or rapid cooling by other means.
following hot working while the temperature is above 1750°F
4.1.8 Solution annealing of N08367 shall consist of heating
[955°C] so that grain boundary carbides are in solution,
the material to a temperature of 2025°F [1105°C] minimum for
cooling rapidly to prevent grain boundary carbide precipita-
an appropriate time followed by water quenching or rapidly
tion. When Supplementary Requirement S2 is invoked, all
cooling by other means.
austenitic grades except S30815 shall pass the intergranular
4.1.9 Solution annealing of S35315 shall consist of heating
corrosion test requirements described in S2.
the material to a temperature of 2100°F [1150°C] minimum,
4.1.2 For H grades, the minimum solution annealing tem-
for an appropriate time followed by water quenching or rapidly
peratures shall be as follows:
cooling by other means.
4.1.2.1 When hot finished, 1900°F [1040°C] for Types
4.2 Austenitic-Ferritic Grades:
304H, 309H, 310H, and 316H; 1925°F [1050°C] for Types
4.2.1 S31803, S32205, and S32550 shall be furnished in the
321H, 347H, and 348H,
annealed condition with subsequent straightening permitted.
4.1.2.2 When cold worked prior to solution annealing,
The annealing treatment of S31803 and S32550 shall consist of
1900°F [1040°C] for Types 304H, 309H, 310H, and 316H;
heating the material to a temperature of 1900°F [1040°C]
2000°F [1095°C] for Types 321H, 347H, and 348H.
minimum for an appropriate time followed by water quenching
or rapid cooling by other means. The annealing treatment for
NOTE 3—Solution annealing temperatures above 1950°F [1065°C] may
impair the resistance to intergranular corrosion after subsequent exposure
S32205 shall consist of heating the material to a temperature of
to sensitizing conditions in the stabilized grades, Types 321, 321 H, 347,
1900°F [1040°C] minimum for an appropriate time followed
347 H, 348 and 348 H. When intergranular corrosion is of concern, the
by water quenching.
purchaser should specify the corrosion test of S2 (to be conducted on
4.2.2 S32950 shall be annealed by heating the material to a
sensitized specimens). The manufacturer may, if necessary, use a lower
temperature of 1825°F [995°C] to 1875°F [1025°C] for an
temperature resolution anneal or a stabilization anneal after a high
appropriate time followed by water quenching or rapid cooling
temperature solution anneal in order to meet corrosion test requirements.
Consideration should be given to the corrosive media before using a by other means.
stabilization anneal at less than 1800°F [980°C], as such a treatment may
4.2.3 S32750 shall be annealed by heating the material to a
not be fully effective for all media.
temperature of 1880°F [1025°C] to 2060°F [1125°C] for an
NOTE 4—Grain size requirements for the H grades are described in
appropriate time followed by water quenching or rapid cooling
Section 7.
by other means. Subsequent straightening shall be permitted.
4.1.3 Strain Hardened Austenitic Type 316—When Type
4.2.4 S32760 shall be annealed by heating the material to a
316 is desired with increased mechanical properties, the strain
temperature of 2010°F [1100°C] to 2085°F [1140°C] for an
hardened condition may be specified and is produced by
appropriate time followed by water quenching or rapid cooling
solution annealing, as described in 4.1.1, followed by strain
by other means.
hardening sufficient to meet the required mechanical proper-
4.2.5 UNS S32906 shall be annealed by heating the material
ties. Solution annealed and strain hardened material shall be
to a temperature of 1900°F (1040°C) to 1980°F (1080°C) for
capable of meeting the intergranular corrosion test of Supple-
an appropriate time followed by rapid cooling in air or water.
mentary Requirement S2.
Subsequent straightening shall be permitted.
4.1.3.1 Two strain hardened conditions have been estab-
4.2.6 S39277 shall be annealed by heating the material to
lished for different applications: Level 1 and Level 2 (see the
1940°F [1060°C] to 2060°F [1125°C] for an appropriate time
Mechanical Property Requirements table).
followed by water quenching or rapid cooling by other means.
4.1.4 High tensile Type XM-19 shall be in the hot-rolled or
Subsequent straightening shall be permitted.
strain-hardened condition and shall be capable of meeting the
4.3 Ferritic Grades—Ferritic grades shall be annealed to
mechanical property requirements of the Mechanical Property
meet the requirements of the Mechanical Property Require-
Requirements table and passing the intergranular corrosion test
ments table.
prescribed in S2. The strain hardened condition is achieved by
4.4 Martensitic Grades:
solution annealing followed by cold working sufficient to
4.4.1 All grades of martensitic steels shall be supplied in
either the annealed condition or in the tempered condition as
For explanation see Appendix X1. specified by the purchaser (see 3.1.3). Tempered material shall
A 479/A 479M
be normalized, or shall be liquid quenched from 1700°F tempering temperature for at least 1 h/in. (25.4 mm) of cross
[925°C], minimum, followed by tempering in accordance with section as follows:
4.4.2, 4.4.3, or 4.4.5.
4.4.2 Types 403 and 410 tempered material shall be held at
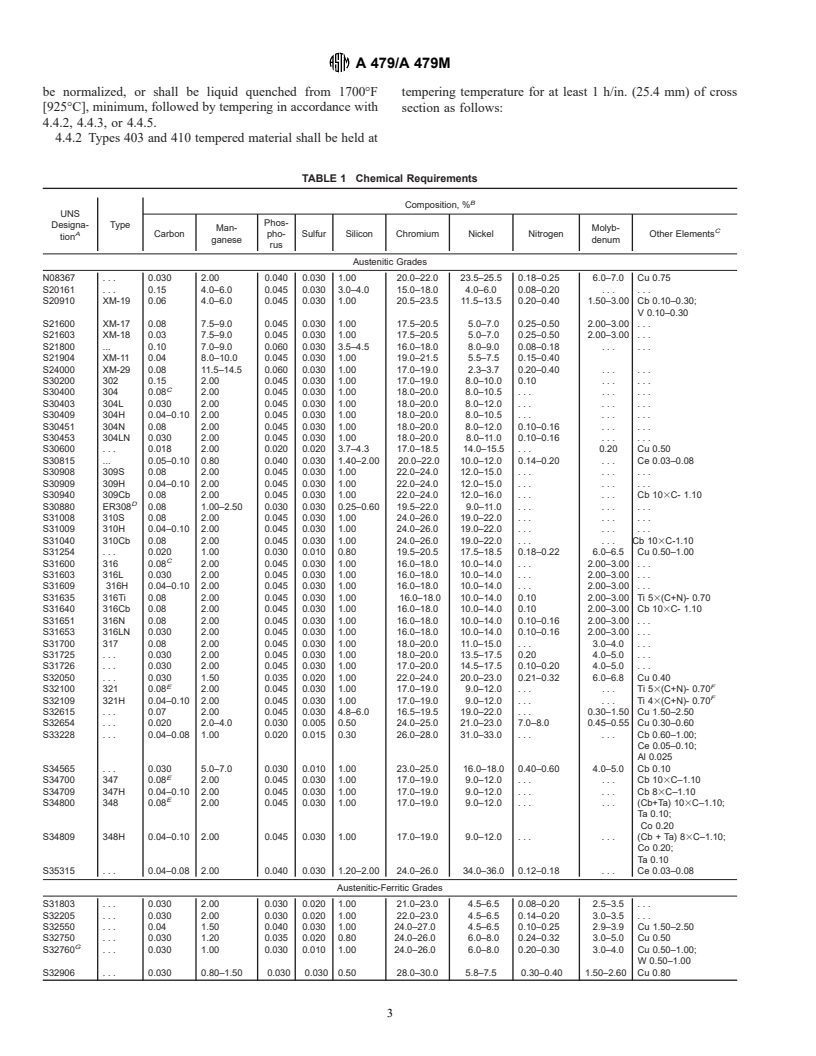
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
B
Composition, %
UNS
Phos-
Designa- Type
Man- Molyb-
C
A Carbon pho- Sulfur Silicon Chromium Nickel Nitrogen Other Elements
tion
ganese denum
rus
Austenitic Grades
N08367 . . . 0.030 2.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 20.0–22.0 23.5–25.5 0.18–0.25 6.0–7.0 Cu 0.75
S20161 . . . 0.15 4.0–6.0 0.045 0.030 3.0–4.0 15.0–18.0 4.0–6.0 0.08–0.20 . . . . . .
S20910 XM-19 0.06 4.0–6.0 0.045 0.030 1.00 20.5–23.5 11.5–13.5 0.20–0.40 1.50–3.00 Cb 0.10–0.30;
V 0.10–0.30
S21600 XM-17 0.08 7.5–9.0 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.5–20.5 5.0–7.0 0.25–0.50 2.00–3.00 . . .
S21603 XM-18 0.03 7.5–9.0 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.5–20.5 5.0–7.0 0.25–0.50 2.00–3.00 . . .
S21800 . 0.10 7.0–9.0 0.060 0.030 3.5–4.5 16.0–18.0 8.0–9.0 0.08–0.18 . .
S21904 XM-11 0.04 8.0–10.0 0.045 0.030 1.00 19.0–21.5 5.5–7.5 0.15–0.40
S24000 XM-29 0.08 11.5–14.5 0.060 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 2.3–3.7 0.20–0.40 . . . . . .
S30200 302 0.15 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 8.0–10.0 0.10 . . . . . .
C
S30400 304 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–10.5 . . . . . . . . .
S30403 304L 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–12.0 . . . . . . . . .
S30409 304H 0.04–0.10 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–10.5 . . . . . . . . .
S30451 304N 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–12.0 0.10–0.16 . . . . . .
S30453 304LN 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–11.0 0.10–0.16 . . . . . .
S30600 . . . 0.018 2.00 0.020 0.020 3.7–4.3 17.0–18.5 14.0–15.5 . . . 0.20 Cu 0.50
S30815 . 0.05–0.10 0.80 0.040 0.030 1.40–2.00 20.0–22.0 10.0–12.0 0.14–0.20 . . . Ce 0.03–0.08
S30908 309S 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 22.0–24.0 12.0–15.0 . . . . . . . . .
S30909 309H 0.04–0.10 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 22.0–24.0 12.0–15.0 . . . . . . . . .
S30940 309Cb 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 22.0–24.0 12.0–16.0 . . . . . . Cb 103C- 1.10
D
S30880 ER308 0.08 1.00–2.50 0.030 0.030 0.25–0.60 19.5–22.0 9.0–11.0 . . . . . . . . .
S31008 310S 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 24.0–26.0 19.0–22.0 . . . . . . . . .
S31009 310H 0.04–0.10 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 24.0–26.0 19.0–22.0 . . . . . . . . .
S31040 310Cb 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 24.0–26.0 19.0–22.0 . . . . . . Cb 103C-1.10
S31254 . . . 0.020 1.00 0.030 0.010 0.80 19.5–20.5 17.5–18.5 0.18–0.22 6.0–6.5 Cu 0.50–1.00
C
S31600 316 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 . . . 2.00–3.00 . . .
S31603 316L 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 . . . 2.00–3.00 . . .
S31609 316H 0.04–0.10 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 . . . 2.00–3.00 . . .
S31635 316Ti 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 0.10 2.00–3.00 Ti 53(C+N)- 0.70
S31640 316Cb 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 0.10 2.00–3.00 Cb 103C- 1.10
S31651 316N 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 0.10–0.16 2.00–3.00 . . .
S31653 316LN 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 0.10–0.16 2.00–3.00 . . .
S31700 317 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 11.0–15.0 . . . 3.0–4.0 . . .
S31725 . . . 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 13.5–17.5 0.20 4.0–5.0 . . .
S31726 . . . 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–20.0 14.5–17.5 0.10–0.20 4.0–5.0 . . .
S32050 . . . 0.030 1.50 0.035 0.020 1.00 22.0–24.0 20.0–23.0 0.21–0.32 6.0–6.8 Cu 0.40
E F
S32100 321 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–12.0 . . . . . . Ti 53(C+N)- 0.70
F
S32109 321H 0.04–0.10 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–12.0 . . . . . . Ti 43(C+N)- 0.70
S32615 . . . 0.07 2.00 0.0
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.