ASTM D4151-92(1998)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Flammability of Blankets
Standard Test Method for Flammability of Blankets
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides a means to identify blanket fabrics which ignite easily and propagate flame across the surface.
1.2 This test method specifies the procedures described in the "Voluntary Blanket Flammability Standard" which has been used by the blanket industry in the United States since 1972.
1.3 This test method should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test may be used as elements of a fire risk assessment which takes into account all of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard of a particular end use.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
Designation: D 4151 – 92 (Reapproved 1998)
Standard Test Method for
Flammability of Blankets
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4151; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e NOTE—Editorial changes were made to footnotes 5, 6, and 7 in December 1998.
1. Scope 3.1.1.1 Discussion—Blankets may be made by any textile
process from various types of fibers and may or may not have
1.1 This test method provides a means to identify blanket
a raised fiber surface. Construction may be woven, knitted,
fabrics which ignite easily and propagate flame across the
flocked, or nonwoven.
surface.
3.1.1.2 Discussion—Electric blankets include resistance
1.2 This test method specifies the procedures described in
heating wires and can provide heat as well as thermal insula-
the“ Voluntary Blanket Flammability Standard” which has
tion.
been used by the blanket industry in the United States since
3.1.2 flammability, n—those characteristics of a material
1972.
that pertain to its relative ease of ignition and relative ability to
1.3 This test method should be used to measure and describe
sustain combustion.
the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response
to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and
NOTE 1—In this test, evidence of ignition is shown by discoloration,
should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or
charring, or burning of the paper monitor.
fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire
3.1.3 ignition, n—initiation of combustion.
conditions. However, results of this test may be used as
3.2 For definitions of other textile terms used in this test
elements of a fire risk assessment which takes into account all
method, refer to Terminology D 123.
of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire
hazard of a particular end use. 4. Summary of Test Method
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 Specimens cut from the blanket fabric are prepared by
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
brushing if they have a raised fiber surface and by drying. The
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
dried specimen is held in a special apparatus, a standardized
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
flame is applied to the surface for a specified time under
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
controlled conditions, and burning, charring, or discoloration
of a paper monitor is noted. Two classes of flammability are
2. Referenced Documents
described.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1.1 A burn of sufficient intensity to discolor a paper
D 123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
monitor in specified contact with the surface of the test
D 1230 Test Method for Flammability of Apparel Textiles
specimen indicates ignition of the blanket surface (see 11.4.1).
D 1776 Practice for Conditioning Textiles for Testing
D 3411 Test Methods for Flammability of Textile Materials
5. Significance and Use
2.2 Federal Specification:
5.1 This test method for the determination of the flamma-
NNN-P-40b
bility of blankets is considered satisfactory for acceptance
testing of commercial shipments of blankets since this test
3. Terminology
method has been used extensively in the trade for acceptance
3.1 Definitions:
testing.
3.1.1 blanket, n—for bedding, an unquilted fabric covering
5.2 This test method may be used to evaluate electric
designed primarily to provide thermal insulation.
blanket fabric, but tests should be performed on the fabric itself
without the resistance heating wires inserted.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-13 on Textiles 5.3 All fabrics made of natural or regenerated cellulose, as
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.52 on Flammability.
well as many made from other natural or synthetic fibers, are
Current edition approved July 30, 1982. Published September 1982. Originally
combustible. Some combustible fabrics when used for blankets
published as D 4151 – 82. Last previous edition D 4151 – 82.
are potentially dangerous to the user because of the ease of
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.01.
Discontinued, see 1980 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Part 32.
ignition, rapidity, and intensity of burning. The first character-
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
istic can be judged with the aid of the flammability tester.
Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 4151
FIG. 1 Flammability Tester
scribed in A1.1.1, A1.1.2, and A1.1.9 of Test Method D 1230.
6. Apparatus and Materials
6.1.1 The test cabinet shall be equipped with a system to
6.1 Flammability Tester, as shown in Figs. 1-4 and de-
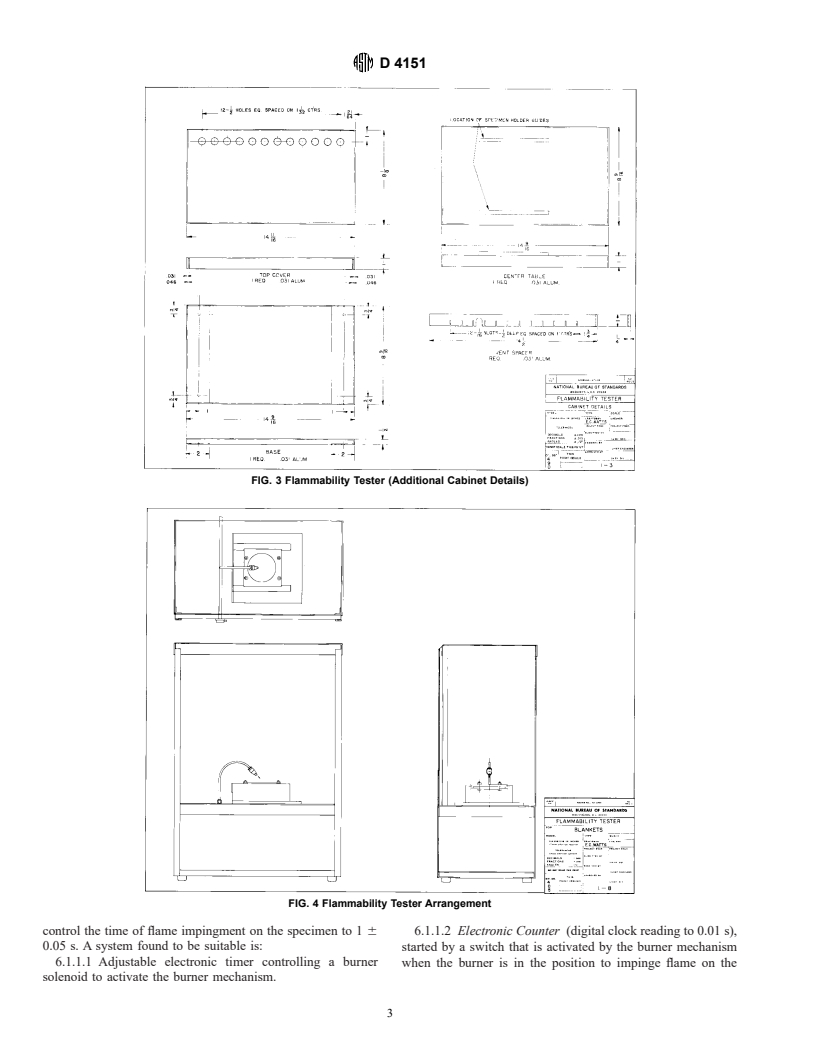
FIG. 2 Flammability Tester (Cabinet Details)
D 4151
FIG. 3 Flammability Tester (Additional Cabinet Details)
FIG. 4 Flammability Tester Arrangement
control the time of flame impingment on the specimen to 1 6 6.1.1.2 Electronic Counter (digital clock reading to 0.01 s),
0.05 s. A system found to be suitable is:
started by a switch that is activated by the burner mechanism
6.1.1.1 Adjustable electronic timer controlling a burner
when the burner is in the position to impinge flame on the
solenoid to activate the burner mechanism.
D 4151
specimen and is stopped when the burner retracts from the mately 200 mm (8 in.) long is soldered or cemented with epoxy
specimen. adhesive into the ferrule of the hypodermic needle. The other
end is soldered to the gas feeding tube which is part of the
NOTE 2—A flammability tester made for use in Test Method D 1230 has
mechanism used to impinge the flame on the specimen (see
to be modified when used with Test Method D 4151 by changing the
Figs. 1-7).
burner, specimen holder, and timing mechanism.
6.4 Methane, technical grade (at least 97 % pure).
6.2 Specimen Holder and Base, as shown in Figs. 5 and 6.
6.4.1 The gas line to the burner shall be equipped with a
6.2.1 The base shall be mounted on the floor of the cabinet
needle valve to control the flame length.
approximately center on both axes. The position of the base
6.4.2 Gas shall be supplied to the burner at a pressure of
shall be adjustable along both the length and width axes of the
17.2 6 3.4 kPa (2.5 6 0.5 psig) at the needle valve inlet.
flammability test cabinet.
6.3 Burner, as shown in Fig. 7. 6.5 Brushing Device, as shown in Fig. 8 and described in
6.3.1 The burner is a No. 18 hypodermic needle. The needle A1.2 of Test Method D 1230, except that the brush rests on the
is cut off below the ferrule approximately 1.5 mm ( ⁄16 in.) carriage vertically with a pressure of 75 6 10 g instead of 150
long. One end of an 3-mm ( ⁄8-in.) OD copper tube approxi- g as described in A1.2.1 of Test Method D 1230.
FIG. 5 Specimen Holder Assembly
D 4151
FIG. 6 Specimen Holder Details
FIG. 7 Burner Details
6.6 Laboratory Drying Oven, forced-draft. 6.8 Silica Gel Desiccant, indicating type.
6.7 Desiccator(s) of sufficient size to hold five mounted
specimens at one time.
D 4151
FIG. 8 Brushing Device
6.9 Paper Monitor, conforming to Federal Specification the outside of each roll in the lot sample or from one end of
NNN-P-40b, Type II. each piece in the lot sample, after first discarding a full width
6.10 Laboratory Hood, or other suitable enclosure, to pro- length of 1 m from the very end of each roll or piece. For fabric
vide a draft free environment surrounding the flammability already made up into end-use items, such as blankets, all of the
tester. items in the lot sample will constitute the laboratory sample.
7.4 Conditions for Sampling—Sample and test the finished
7. Sampling
fabric as it will reach th
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.