ASTM D4212-16(2023)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Viscosity by Dip-Type Viscosity Cups
Standard Test Method for Viscosity by Dip-Type Viscosity Cups
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Viscosity is a measure of the fluidity of a material. Viscosity data are useful in the determination of the ease of stirring, pumping, dip coating, or other flow-related properties of paints and related fluids.
5.2 This type of cup is used to measure viscosity because it is easy to use, robust, and may be used in tanks, reservoirs, and reactors.
5.3 There are other types of apparatus for measuring viscosity in the laboratory that provide better precision and bias, including the Ford viscosity cup (Test Method D1200), and the rotational viscometer (Test Methods D2196).
5.4 Certain higher shear rate devices such as cone/plate viscometers (Test Method D4287) provide more information about sprayability, roll coatability, and other high-shear rate related properties of coatings.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of viscosity of paints, varnishes, lacquers, inks, and related liquid materials by dip-type viscosity cups. This test method is recommended for viscosity control work within one plant or laboratory and should be used to check compliance with specifications only when sufficient controls have been instituted to ensure adequate comparability of results.
1.2 Viscosity cups are designed for testing of Newtonian and near-Newtonian liquids. If the test material is non-Newtonian, for example, shear-thinning or thixotropic, another method, such as Test Methods D2196, should be used. Under controlled conditions, comparisons of the viscosity of non-newtonian materials may be helpful, but viscosity determination methods using controlled shear rate or shear stress are preferred.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4212 − 16 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Test Method for
1
Viscosity by Dip-Type Viscosity Cups
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4212; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D2196 Test Methods for Rheological Properties of Non-
Newtonian Materials by Rotational Viscometer
1.1 This test method covers the determination of viscosity
D4287 Test Method for High-Shear Viscosity Using a Cone/
of paints, varnishes, lacquers, inks, and related liquid materials
Plate Viscometer
by dip-type viscosity cups. This test method is recommended
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
for viscosity control work within one plant or laboratory and
should be used to check compliance with specifications only
3. Terminology
when sufficient controls have been instituted to ensure ad-
3.1 Definitions:
equate comparability of results.
3.1.1 near-Newtonian liquid, n—a liquid in which the varia-
1.2 Viscosity cups are designed for testing of Newtonian
tion of viscosity with shear rate is small and the effect on
and near-Newtonian liquids. If the test material is non-
viscosity of mechanical disturbances such as stirring is negli-
Newtonian, for example, shear-thinning or thixotropic, another
gible.
method, such as Test Methods D2196, should be used. Under
3.1.2 Newtonian liquid, n—a liquid in which the viscosity is
controlled conditions, comparisons of the viscosity of non-
independent of the shear stress or shear rate. If the ratio of
newtonian materials may be helpful, but viscosity determina-
shear stress to shear rate is not constant, the liquid is non-
tion methods using controlled shear rate or shear stress are
Newtonian.
preferred.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
4. Summary of Test Method
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
4.1 The cup is completely immersed in the material to be
only.
tested, withdrawn, and the time for the material to flow through
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
a hole in the base of the cup is measured.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Significance and Use
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
5.1 Viscosity is a measure of the fluidity of a material.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Viscosity data are useful in the determination of the ease of
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
stirring, pumping, dip coating, or other flow-related properties
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
of paints and related fluids.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
5.2 This type of cup is used to measure viscosity because it
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
is easy to use, robust, and may be used in tanks, reservoirs, and
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
reactors.
5.3 There are other types of apparatus for measuring vis-
2. Referenced Documents
cosity in the laboratory that provide better precision and bias,
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
including the Ford viscosity cup (Test Method D1200), and the
D1200 Test Method for Viscosity by Ford Viscosity Cup
rotational viscometer (Test Methods D2196).
1 5.4 Certain higher shear rate devices such as cone/plate
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of viscometers (Test Method D4287) provide more information
Subcommittee D01.24 on Physical Properties of Liquid Paints & Paint Materials.
about sprayability, roll coatability, and other high-shear rate
Current edition approved July 1, 2023. Published August 2023. Originally
related properties of coatings.
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D4212 – 16. DOI:
10.1520/D4212-16R23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 6. Apparatus
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
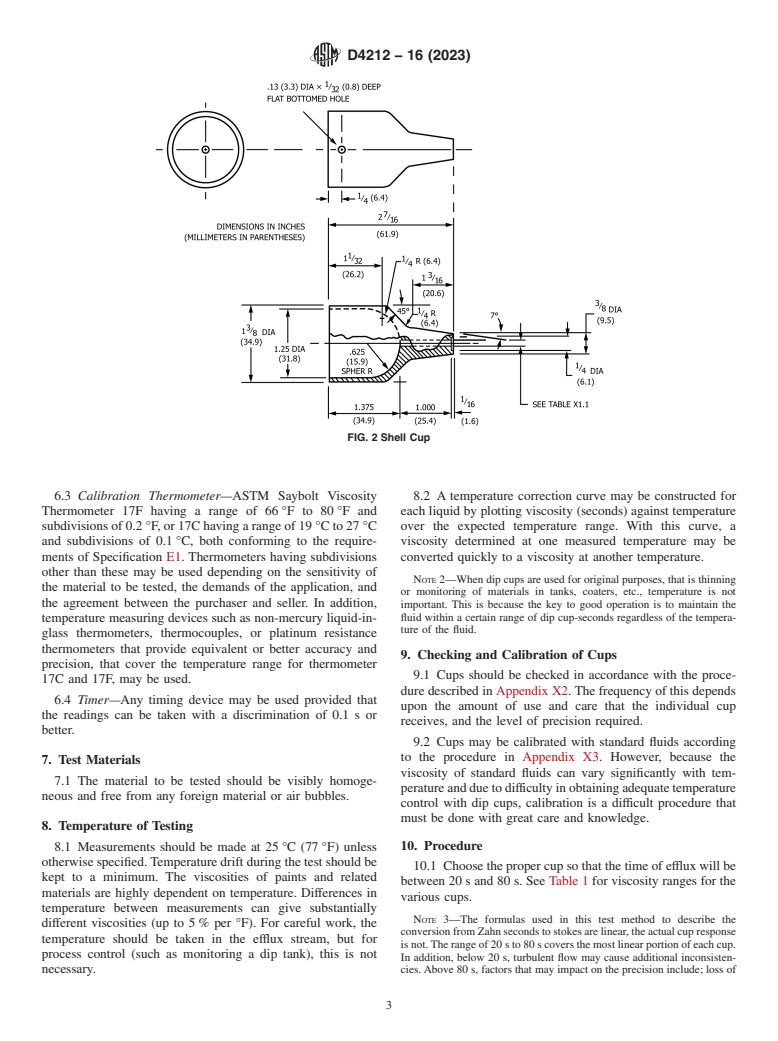
6.1 Zahn Viscosity Cup—No. 1 through No. 5 Zahn viscos-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. ity cups made of corrosion- and solvent-resistant materials.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Con
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.