ASTM D6184-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease (Conical Sieve Method)
Standard Test Method for Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease (Conical Sieve Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 When lubricating grease separates oil, the residual material may change in consistency, which can affect the ability of the product to function as designed. Test results obtained with this procedure are not intended to predict oil separation tendencies of grease under dynamic service conditions.
5.2 This test method is used for specifications and quality control.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the tendency of lubricating grease to separate oil at an elevated temperature. This test method shall be conducted at 100 °C for 30 h unless other conditions are required by the grease specification.
1.2 This test method can be used on any grease with a worked penetration (Test Methods D217) greater than 220 mm/10 (NLGI Consistency Number 3 or softer). However, no precision data exists for greases with a penetration greater than 340 mm/10 (softer than NLGI Consistency Number 1).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The term 60 mesh is used to describe the wire mesh used. This unit was described in the withdrawn E437 standard and there is no exact metric equivalent.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6184 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease (Conical Sieve
1
Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6184; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
The conical sieve method for measuring leakage from lubricating grease (commonly known as the
cone bleed test) uses the same equipment as the obsolete, withdrawn FED-STD-791C (Federal Test
Method (FTM) 791C) Method 321.3, Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease (Static Technique).
Despite the lack of a precision statement, Method 321.3 was used for many years in specifications to
evaluate the tendencies of base fluid separation from military and industrial greases. Test Method
D6184 supersedes the FTM method by overcoming deficiencies of Method 321.3. It includes the
proceduresandprecisiondeterminationsresultantfromacooperativestudyconductedbyparticipating
members of Subcommittee D02.G0.
1. Scope* Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the ten-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
dency of lubricating grease to separate oil at an elevated
temperature. This test method shall be conducted at 100 °C for
2. Referenced Documents
30 h unless other conditions are required by the grease speci-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
fication.
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating
1.2 This test method can be used on any grease with a
Grease
worked penetration (Test Methods D217) greater than
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
220 mm⁄10(NLGIConsistencyNumber3orsofter).However,
Fuels, and Lubricants
no precision data exists for greases with a penetration greater
E437 Specification for Industrial Wire Cloth and Screens
than 340 mm⁄10 (softer than NLGI Consistency Number 1).
(Square Opening Series) (Discontinued 2000) Replaced
3
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
by E 2016 (Withdrawn 2000)
standard. The term 60 mesh is used to describe the wire mesh
2.2 Government Standard (Withdrawn):
used. This unit was described in the withdrawn E437 standard
FED-STD-791C Lubricants, Liquid Fuels, and Related
and there is no exact metric equivalent.
Products; Methods of Testing, Method 321.3 “Oil Sepa-
ration from Lubricating Greases (Static Technique),”
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4
Withdrawn November 2007
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3. Terminology
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1 Definitions:
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
to Terminology D4175.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Subcommittee D02.G0.03 on Physical Tests the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2022. Published December 2022. Originally The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D6184 – 17. DOI: www.astm.org.
4
10.1520/D6184-22. Available online at ASSIST Quick Search (http://quicksearch.dla.mil).
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6184 − 22
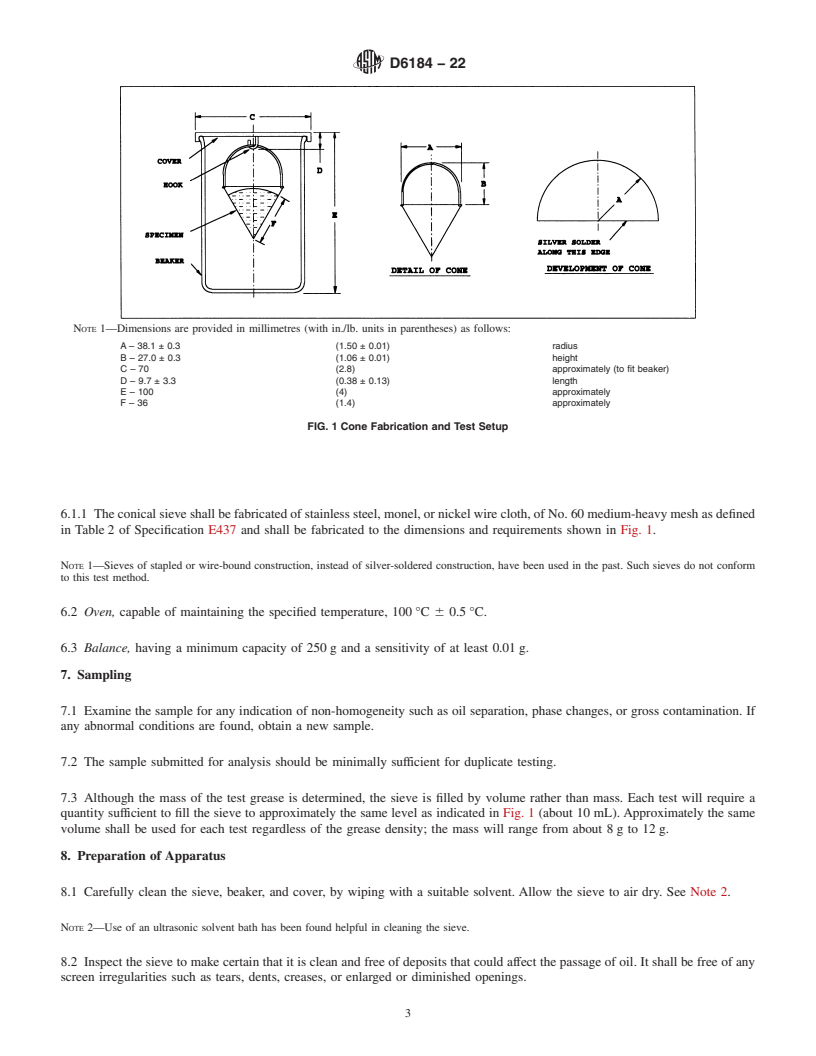
NOTE 1—Dimensions are provided in millimetres (with in./lb. units in parentheses) as follows:
A – 38.1 ± 0.3 (1.50 ± 0.01) radius
B – 27.0 ± 0.3 (1.06 ± 0.01) height
C – 70 (2.8) approximately (to fit beaker)
D – 9.7 ± 3.3 (0.38 ± 0.13) length
E – 100 (4) approximately
F – 36 (1.4) approximately
FIG. 1 Cone Fabrication and Test Setup
3
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6184 − 17 D6184 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease (Conical Sieve
1
Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6184; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
The conical sieve method for measuring leakage from lubricating grease (commonly known as the
cone bleed test) uses the same equipment as the obsolete, withdrawn FED-STD-791C (Federal Test
Method (FTM) 791C) Method 321.3, Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease (Static Technique).
Despite the lack of a precision statement, Method 321.3 was used for many years in specifications to
evaluate the tendencies of base fluid separation from military and industrial greases. Test Method
D6184 supersedes the FTM method by overcoming deficiencies of Method 321.3. It includes the
procedures and precision determinations resultant from a cooperative study conducted by participating
members of Subcommittee D02.G0.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the tendency of lubricating grease to separate oil at an elevated temperature. This
test method shall be conducted at 100 °C for 30 h unless other conditions are required by the grease specification.
1.2 This test method can be used on any grease with a worked penetration (Test Methods D217) greater than 220 mm ⁄10 (NLGI
Consistency Number 3 or softer). However, no precision data exists for greases with a penetration greater than 340 mm ⁄10 (softer
than NLGI Consistency Number 1).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The term 60 mesh is used to describe the wire mesh used. This
unit was described in the withdrawn E437 standard and there is no exact metric equivalent.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.G0.03 on Physical Tests
Current edition approved May 1, 2017Dec. 1, 2022. Published June 2017December 2022. Originally approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 20162017 as
D6184 – 16.D6184 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/D6184-17.10.1520/D6184-22.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6184 − 22
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating Grease
D1742D4175 Test Method for Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease During StorageTerminology Relating to Petroleum
Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
E437 Specification for Industrial Wire Cloth and Screens (Square Opening Series) (Discontinued 2000) Replaced by E 2016
3
(Withdrawn 2000)
2.2 Government Standard (Withdrawn):
FED-STD-791C Lubricants, Liquid Fuels, and Related Products; Methods of Testing, Method 321.3 “Oil Separation from
4
Lubricating Greases (Static Technique),” Withdrawn November 2007
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D4175.
3.1.2 lubricating grease, n—a semifluid to solid product of a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—
The dispersion of the thickener forms a two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by surface tension and other
physical forces. Other ingredients imparting special properties are often included. D217
3.1.3 oil separation, n—the appearance of a liquid fraction from an otherwise homogeneous lubricating composition. D1742
3.1.4 th
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.