ASTM D2132-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Dust-and-Fog Tracking and Erosion Resistance of Electrical Insulating Materials
Standard Test Method for Dust-and-Fog Tracking and Erosion Resistance of Electrical Insulating Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
6.1 Method—It is possible that electrical insulation in service will fail as a result of tracking, erosion, or a combination of both, if exposed to high relative humidity and contamination environments. This is particularly true of organic insulations in outdoor applications where the surface of the insulation becomes contaminated by deposits of moisture and dirt, for example, coal dust or salt spray. This test method is an accelerated test that simulates extremely severe outdoor contamination. It is believed that the most severe conditions likely to be encountered in outdoor service in the United States will be relatively mild compared to the conditions specified in this test method.
6.2 Test Results—Materials can be classified by this test method as tracking-resistant, tracking-affected, or tracking-susceptible. The exact test values for these categories as they apply to specific uses will be specified in the appropriate material specifications, but guideline figures are suggested in Note 4. Tracking-resistant materials, unless erosion failure occurs first, have the potential to last many hundreds of hours (Note 5). Erosion, though it is possible that it will progress laterally, generally results in a failure perpendicular to the specimen surface. Therefore, compare only specimens of the same nominal thickness for resistance to tracking-induced erosion. Estimate the extent of erosion from measurements of the depth of penetration of the erosion. Place materials that are not tracking-susceptible in three broad categories—erosion-resistant, erosion-affected, and erosion-susceptible. When the standard thickness specimen is tested, the following times to failure typify the categories (Note 6):
Erosion-susceptible
5 to 50 h
Erosion-affected
50 to 200 h
Erosion-resistant
over 200 h
Note 4: Tracking-susceptible materials usually fail within 5 h. Tracking-affected materials usually fail before about 100 h.
Note 5: This information is derived fr...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended to differentiate solid electrical insulating materials with respect to their resistance to the action of electric arcs produced by conduction through surface films of a specified contaminant containing moisture. Test Methods D2302 and D2303 are also useful to evaluate materials.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are the standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for information only. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1: There is no equivalent ISO standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2132 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Dust-and-Fog Tracking and Erosion Resistance of Electrical
1
Insulating Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2132; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* tance of Electrical Insulating Materials with Controlled
3
Water-to-Metal Discharges (Withdrawn 1982)
1.1 This test method is intended to differentiate solid elec-
D2303 Test Methods for Liquid-Contaminant, Inclined-
trical insulating materials with respect to their resistance to the
Plane Tracking and Erosion of Insulating Materials
action of electric arcs produced by conduction through surface
films of a specified contaminant containing moisture. Test
3. Terminology
Methods D2302 and D2303 are also useful to evaluate mate-
3.1 Definitions:
rials.
3.1.1 For definitions pertinent to this test method see Ter-
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are the standard.
minology D1711.
The inch-pound units in parentheses are for information only.
The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact
4. High Voltage Hazard
equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the
4.1 Lethal voltages are a potential hazard during the perfor-
standard, each system shall be used independently of the other,
mance of this test. It is essential that the test apparatus, and all
and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
associated equipment electrically connected to it, be properly
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
designed and installed for safe operation.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.2 Solidly ground all electrically conductive parts which it
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
is possible for a person to contact during the test.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4.3 Provide means for use at the completion of any test to
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ground any parts which were at high voltage during the test or
NOTE 1—There is no equivalent ISO standard.
have the potential for acquiring an induced charge during the
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
test or retaining a charge even after disconnection of the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
voltage source.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.4 Thoroughly instruct all operators as to the correct
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
procedures for performing tests safely.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.5 When making high voltage tests, particularly in com-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
pressed gas or in oil, it is possible for the energy released at
2. Referenced Documents breakdown to be sufficient to result in fire, explosion, or
2
rupture of the test chamber. Design test equipment, test
2.1 ASTM Standards:
chambers, and test specimens so as to minimize the possibility
D709 Specification for Laminated Thermosetting Materials
of such occurrences and to eliminate the possibility of personal
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
injury.
D2302 Method of Test for Differential Wet Tracking Resis-
NOTE 2—If the potential for fire exists, have fire suppression equipment
available.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
5. Summary of Test Method
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D09.07 on Electrical Insulating Materials.
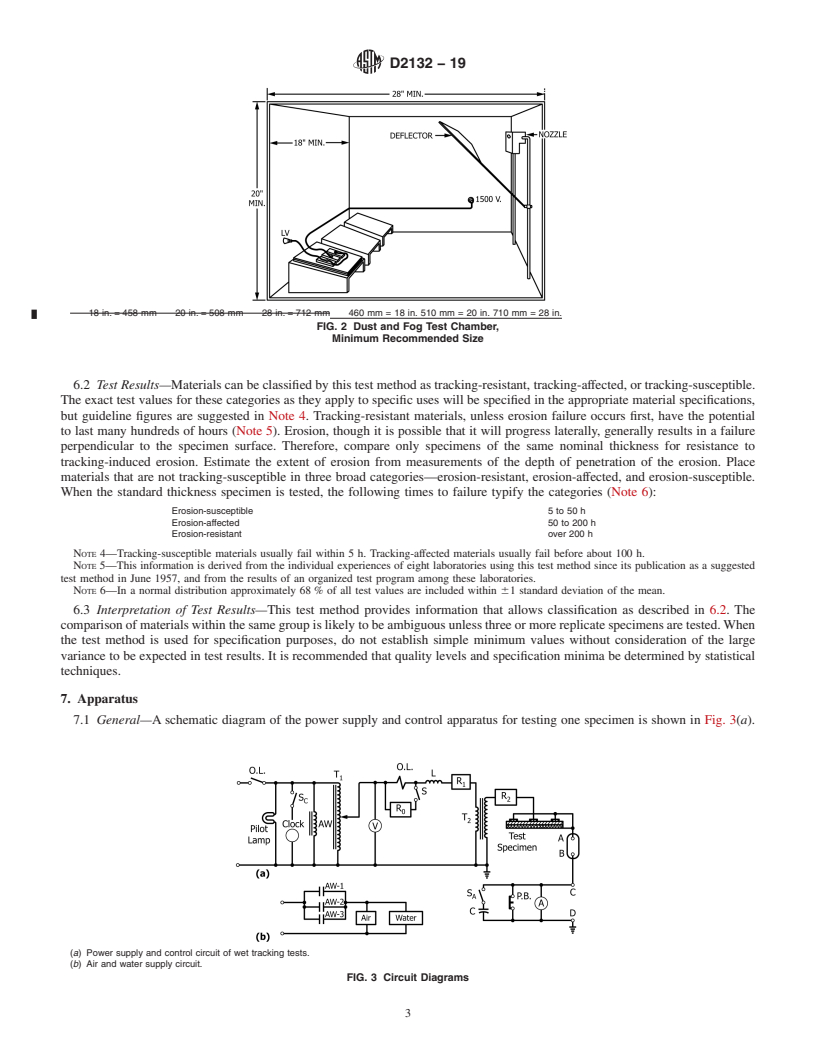
5.1 With electrodes mounted as shown in Fig. 1, coat test
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2019. Published August 2019. Originally
specimens with a synthetic dust and test in a chamber shown in
approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as D2132 – 12 (2018).
Fig. 2. Direct a water spray at the test specimen. After the
DOI: 10.1520/D2132-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2132 − 19
5.2 Rate materials that track in terms of the time required to
form a track between the el
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2132 − 12 (Reapproved 2018) D2132 − 19
Standard Test Method for
Dust-and-Fog Tracking and Erosion Resistance of Electrical
1
Insulating Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2132; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method is intended to differentiate solid electrical insulating materials with respect to their resistance to the action
of electric arcs produced by conduction through surface films of a specified contaminant containing moisture. Test Methods D2302
and D2303 are also useful to evaluate materials.
1.2 Units—The values stated in inch-poundSI units are the standard, except in cases where SI units are more appropriate. The
values standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for information only. Specific precautionary statements are given inThe
values stated in each system are not necessarily 12.4.exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each
system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—There is no equivalent ISO standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D709 Specification for Laminated Thermosetting Materials
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
D2302 Method of Test for Differential Wet Tracking Resistance of Electrical Insulating Materials with Controlled Water-to-
3
Metal Discharges (Withdrawn 1982)
D2303 Test Methods for Liquid-Contaminant, Inclined-Plane Tracking and Erosion of Insulating Materials
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions pertinent to this test method see Terminology D1711.
4. High Voltage Hazard
4.1 Lethal voltages are a potential hazard during the performance of this test. It is essential that the test apparatus, and all
associated equipment electrically connected to it, be properly designed and installed for safe operation.
4.2 Solidly ground all electrically conductive parts which it is possible for a person to contact during the test.
4.3 Provide means for use at the completion of any test to ground any parts which were at high voltage during the test or have
the potential for acquiring an induced charge during the test or retaining a charge even after disconnection of the voltage source.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D09.07 on Electrical Insulating Materials.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2018Aug. 1, 2019. Published November 2018August 2019. Originally approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 20122018
as D2132 – 12.D2132 – 12 (2018). DOI: 10.1520/D2132-18.10.1520/D2132-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2132 − 19
4.4 Thoroughly instruct all operators as to the correct procedures for performing tests safely.
4.5 When making high voltage tests, particularly in compressed gas or in oil, it is possible for the energy released at breakdown
to be sufficient to result in fire, explosion, or rupture of the test chamber. Design test equipment, test chambers, and test specimens
so as to mini
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.