ASTM E837-08e2
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Residual Stresses by the Hole-Drilling Strain-Gage Method
Standard Test Method for Determining Residual Stresses by the Hole-Drilling Strain-Gage Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Summary:
5.1.1 Residual stresses are present in almost all materials. They may be created during the manufacture or during the life of the material. If not recognized and accounted for in the design process, residual stresses can be a major factor in the failure of a material, particularly one subjected to alternating service loads or corrosive environments. Residual stress may also be beneficial, for example, the compressive stresses produced by shot peening. The hole-drilling strain-gage technique is a practical method for determining residual stresses.
SCOPE
1.1 Residual Stress Determination :
1.1.1 This test method specifies a hole-drilling procedure for determining residual stress profiles near the surface of an isotropic linearly elastic material. The test method is applicable to residual stress profile determinations where in-plane stress gradients are small. The stresses may remain approximately constant with depth (“uniform” stresses) or they may vary significantly with depth (“non-uniform” stresses). The measured workpiece may be “thin” with thickness much less than the diameter of the drilled hole or “thick” with thickness much greater than the diameter of the drilled hole. Only uniform stress measurements are specified for thin workpieces, while both uniform and non-uniform stress measurements are specified for thick workpieces.
1.2 Stress Measurement Range:
1.2.1 The hole-drilling method can identify in-plane residual stresses near the measured surface of the workpiece material. The method gives localized measurements that indicate the residual stresses within the boundaries of the drilled hole.
1.2.2 This test method applies in cases where material behavior is linear-elastic. In theory, it is possible for local yielding to occur due to the stress concentration around the drilled hole, for isotropic (equi-biaxial) residual stresses exceeding 50 % of the yield stress, or for shear stresses in any direction exceeding 25 % of the yield stress. However, in practice it is found that satisfactory results can be achieved providing the residual stresses do not exceed about 60 % of the material yield stress.
1.3 Workpiece Damage:
1.3.1 The hole-drilling method is often described as “semi-destructive” because the damage that it causes is localized and often does not significantly affect the usefulness of the workpiece. In contrast, most other mechanical methods for measuring residual stresses substantially destroy the workpiece. Since hole drilling does cause some damage, this test method should be applied only in those cases either where the workpiece is expendable, or where the introduction of a small shallow hole will not significantly affect the usefulness of the workpiece.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´2
Designation: E837 − 08
StandardTest Method for
Determining Residual Stresses by the Hole-Drilling Strain-
1
Gage Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E837; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Eq 27 was editorially corrected in July 2009.
2
ε NOTE—Eq 21 was editorially corrected in March 2013.
INTRODUCTION
The hole-drilling strain-gage method determines residual stresses near the surface of an isotropic
linear-elastic material. It involves attaching a strain rosette to the surface, drilling a hole at the
geometric center of the rosette, and measuring the resulting relieved strains. The residual stresses
withintheremovedmaterialarethendeterminedfromthemeasuredstrainsusingaseriesofequations.
1. Scope drilled hole, for isotropic (equi-biaxial) residual stresses ex-
ceeding 50% of the yield stress, or for shear stresses in any
1.1 Residual Stress Determination:
direction exceeding 25% of the yield stress. However, in
1.1.1 This test method specifies a hole-drilling procedure
practice it is found that satisfactory results can be achieved
for determining residual stress profiles near the surface of an
providingtheresidualstressesdonotexceedabout60%ofthe
isotropiclinearlyelasticmaterial.Thetestmethodisapplicable
material yield stress.
to residual stress profile determinations where in-plane stress
gradients are small. The stresses may remain approximately 1.3 Workpiece Damage:
constant with depth (“uniform” stresses) or they may vary 1.3.1 The hole-drilling method is often described as “semi-
significantly with depth (“non-uniform” stresses). The mea- destructive” because the damage that it causes is localized and
sured workpiece may be “thin” with thickness much less than often does not significantly affect the usefulness of the work-
the diameter of the drilled hole or “thick” with thickness much piece. In contrast, most other mechanical methods for measur-
greater than the diameter of the drilled hole. Only uniform ing residual stresses substantially destroy the workpiece. Since
stress measurements are specified for thin workpieces, while hole drilling does cause some damage, this test method should
both uniform and non-uniform stress measurements are speci- be applied only in those cases either where the workpiece is
fied for thick workpieces. expendable, or where the introduction of a small shallow hole
will not significantly affect the usefulness of the workpiece.
1.2 Stress Measurement Range:
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.2.1 The hole-drilling method can identify in-plane re-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
sidual stresses near the measured surface of the workpiece
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
material. The method gives localized measurements that indi-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
cate the residual stresses within the boundaries of the drilled
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
hole.
1.2.2 This test method applies in cases where material
2. Referenced Documents
behavior is linear-elastic. In theory, it is possible for local
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
yielding to occur due to the stress concentration around the
E251Test Methods for Performance Characteristics of Me-
tallic Bonded Resistance Strain Gauges
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E28 on
Mechanical Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E28.13 on
2
Residual Stress Measurement. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved July 23, 2009. Published April 2008. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ε1
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as E837–01 . DOI:
Standards volumeinformation,refertothestandard’sDocumentSummarypageon
10.1520/E0837-08E01.
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´2
E837 − 08
3. Terminology
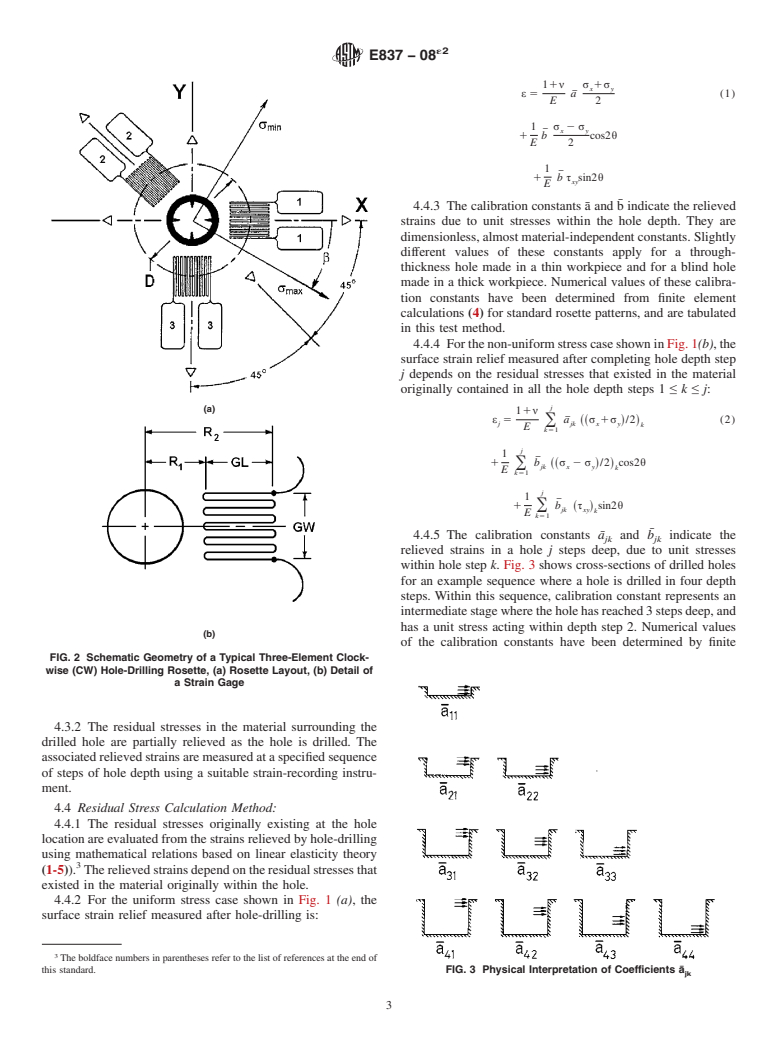
3.1 Symbols:
a¯ = calibration constant for isotropic stresses
¯
b = calibration constant for shear stresses
a¯ = calibration matrix for isotropic stresses
jk
¯
b = calibration matrix for shear stresses
jk
D = diameter of the gage circle, see Table1.
D = diameter of the drilled hole
0
E = Young’s modulus
j = number of hole depth steps so far
k = sequence number for hole depth steps
P = uniform isotropic (equi-biaxial) stress
P = isotropic stress within hole dept
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.