ASTM D7737/D7737M-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Individual Geogrid Junction Strength
Standard Test Method for Individual Geogrid Junction Strength
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This index test method is to be used to determine the strength of an individual junction in a geogrid product. The test is performed in isolation, while in service the junction is typically confined. Thus the results from this test method are not anticipated to be related to design performance.
5.2 The value of junction strength can be used for manufacturing quality control, development of new products, or a general understanding of the in-isolation behavior of a particular geogrid’s junction (for example, in relation to handling during shipment and placement of the geogrid).
5.3 This test method is applicable to geogrid products with essentially symmetrical orthogonal or non-orthogonal ribs, yarns or straps, that is, geogrids which are composed of ribs, yarns or straps that are entangled through weaving or knitting, welded, bonded or formed through drawing.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is an index test which provides a procedure for determining the strength of an individual geogrid junction, also called a node. The test is configured such that a single rib is pulled from its junction with a rib(s) transverse to the test direction to obtain the maximum force, or strength of the junction. The procedure allows for the use of two different clamps with the appropriate clamp selected to minimize the influence of the clamping mechanism on the specific type of geogrid to be tested.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7737/D7737M − 15
Standard Test Method for
1
Individual Geogrid Junction Strength
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7737/D7737M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.1 atmosphere for testing geosynthetics, n—air main-
tained at a relative humidity of 50 to 70 % and a temperature
1.1 This test method is an index test which provides a
of 21 6 2°C [70 6 4°F].
procedure for determining the strength of an individual geogrid
junction, also called a node. The test is configured such that a
3.1.2 breaking force, (F), n—the force at failure.
single rib is pulled from its junction with a rib(s) transverse to
3.1.3 geogrid, n—a geosynthetic formed by a regular net-
the test direction to obtain the maximum force, or strength of
work of integrally connected elements with apertures greater
the junction. The procedure allows for the use of two different
than 6.35 mm [0.25 in.] to allow interlocking with surrounding
clamps with the appropriate clamp selected to minimize the
soil, rock, earth, and other surrounding materials to primarily
influence of the clamping mechanism on the specific type of
function as reinforcement. D5262
geogrid to be tested.
3.1.4 index test, n—a test procedure which may contain
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
known bias, but which may be used to establish an order for a
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
set of specimens with respect to the property of interest.
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
3.1.5 integral, adj—in geosynthetics, forming a necessary
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
part of the whole; a constituent.
with the standard.
3.1.6 junction, n—the point where geogrid ribs are intercon-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
nected to provide structure and dimensional stability.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 3.1.7 rib, n—for geogrids, the continuous elements of a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- geogrid which are either in the machine or cross-machine
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. direction as manufactured.
3.1.8 rupture, n—for geogrids, the breaking or tearing apart
2. Referenced Documents
of ribs.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4354 Practice for Sampling of Geosynthetics and Rolled
4. Summary of Test Method
Erosion Control Products(RECPs) for Testing
4.1 This standard proposes a test method for performing
D4439 Terminology for Geosynthetics
tension tests on geogrid junctions. The procedure provides two
D5262 Test Method for Evaluating the Unconfined Tension
clamping techniques for the junction to be tested including:
Creep and Creep Rupture Behavior of Geosynthetics
Method A in which the clamps firmly grip the ribs transverse to
3. Terminology
the test direction on each side of the junction; and, Method B
in which the ribs transverse to the test direction are constrained
3.1 Definitions: Definitions of other terms applying to this
in a slot, constraining rotation of the junction, while the rib in
test method appear in Terminology D4439.
the test direction passes through the slot without the junction
clamp applying confinement to the junction. The junction
1
clamping technique is selected for the specific type of geogrid
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D35 on
Geosynthetics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D35.01 on Mechani-
in order to minimize rotation and corresponding peal of the
cal Properties.
junction during the test. The rib in the test direction going
Current edition approved July 1, 2015. Published September 2015. Originally
through the junction is then clamped at a distance from the
approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D7737–11. DOI:
10.1520/D7737_D7737M-15
junction and the system tensioned until junction (or rib) failure
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
occurs. This forces a tension or shear force to occur within the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
junction in the direction of the applied load. The junction has
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. no normal pressure on it, that is, it is horizontally unconfined.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohoc
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7737 − 11 D7737/D7737M − 15
Standard Test Method for
1
Individual Geogrid Junction Strength
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7737;D7737/D7737M; the number immediately following the designation indicates
the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is an index test which provides a procedure for determining the strength of an individual geogrid junction,
also called a node. The test is configured such that a single rib is pulled from its junction with a cross-rib to rib(s) transverse to
the test direction to obtain the maximum force, or strength of the junction. The procedure allows for the use of two different clamps
with the appropriate clamp selected to minimize the influence of the clamping mechanism on the specific type of geogrid to be
tested.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded as the separately as standard. The values stated
in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values
from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4354 Practice for Sampling of Geosynthetics and Rolled Erosion Control Products(RECPs) for Testing
D4439 Terminology for Geosynthetics
D5262 Test Method for Evaluating the Unconfined Tension Creep and Creep Rupture Behavior of Geosynthetics
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of other terms applying to this test method appear in Terminology D4439.
3.1 Definitions: Definitions of other terms applying to this test method appear in Terminology D4439.
3.1.1 atmosphere for testing geosynthetics, n—air maintained at a relative humidity of 50 to 70 % and a temperature of 21 6
2°C (70[70 6 4°F).4°F].
3.1.2 breaking force, (F), n—the force at failure.
3.2.3 geogrid, n—the force at failure.
3.1.3 integral,geogrid, adj—n—a geosynthetic formed by a regular network of integrally connected elements with apertures
greater than 6.35 mm (1⁄4 inch)[0.25 in.] to allow interlocking with surrounding soil, rock, earth, and other surrounding materials
to primarily function as reinforcement. (D5262) D5262
3.1.4 index test, n—a test procedure which may contain known bias, but which may be used to establish an order for a set of
specimens with respect to the property of interest.
3.1.5 integral, adj—in geosynthetics, forming a necessary part of the whole; a constituent.
3.1.6 junction, n—the point where geogrid ribs are interconnected to provide structure and dimensional stability.
3.1.7 rib, n—for geogrids, the continuous elements of a geogrid which are interconnected to a node or junction.either in the
machine or cross-machine direction as manufactured.
3.1.8 rupture, n—for geogrids, the breaking or tearing apart of ribs.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D35 on Geosynthetics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D35.01 on Mechanical Properties.
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 2011July 1, 2015. Published November 2011September 2015. Originally approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved in 2011
as D7737–11. DOI: 10.1520/D7731–1110.1520/D7737_D7737M-15
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7737/D7737M − 15
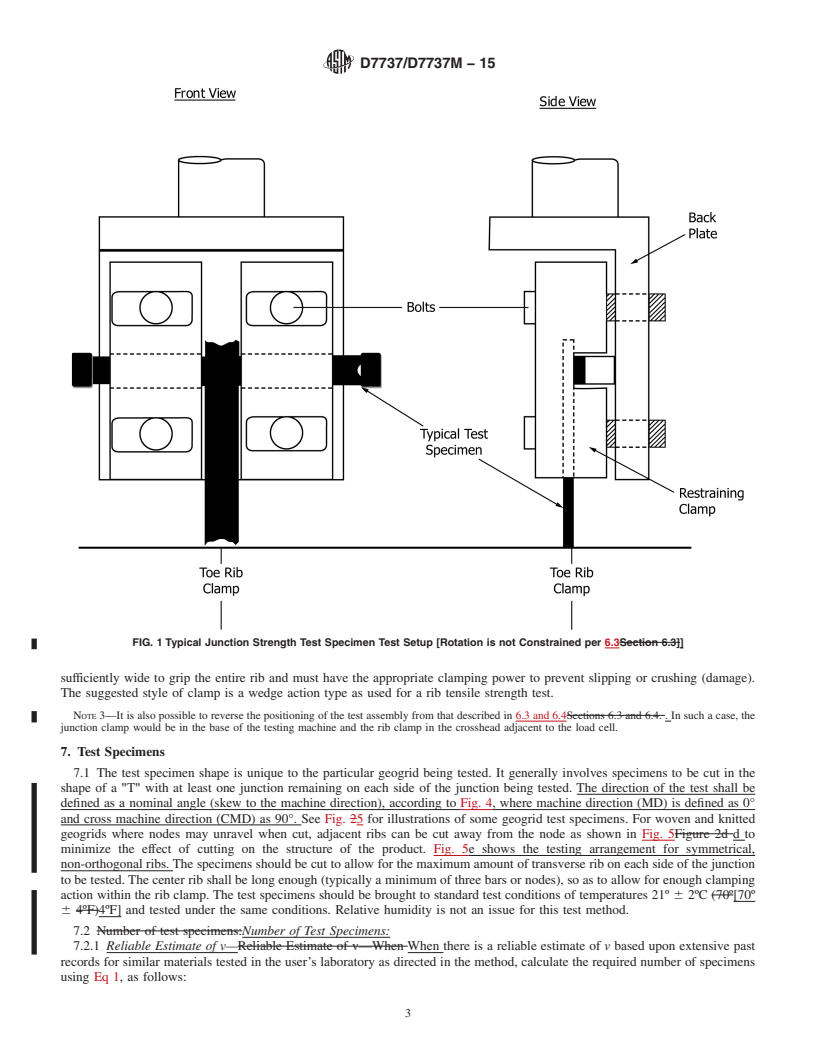
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 This standard proposes a test method for performing tension tests on geogrid junctions. The procedure provides two
clamping techniques for the junction to be tested including: Method A in which the clamps firmly grip the ribs transverse to the
test direction on each side of the junction; and, Method B in which the ribs transverse to the test direction are constrained in a slot,
constraining rotation of the j
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.