ASTM C892-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for High-Temperature Fiber Blanket Thermal Insulation
Standard Specification for High-Temperature Fiber Blanket Thermal Insulation
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the standard for high-temperature fiber blanket thermal insulation for use at various temperatures. The insulation should be tested and comply accordingly to physical and mechanical properties of the insulation such as apparent thermal conductivity, density, and temperature of use. The insulation shall also be tested for non-fibrous content, linear shrinkage, and tensile strength.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers high-temperature fiber blanket thermal insulation for use from ambient up to 3000°F (1649°C).
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 When the potential exists that the installation or use of thermal insulation materials, accessories, and systems will pose safety or health problems, the manufacturers shall provide the user with appropriate current information regarding any known problems associated with the recommended use of the products, and shall also recommend protective measures to be employed in their safe utilization. The user shall establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C892 −10
Standard Specification for
1
High-Temperature Fiber Blanket Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C892; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C356 Test Method for Linear Shrinkage of Preformed High-
Temperature Thermal Insulation Subjected to Soaking
1.1 This specification covers high-temperature fiber blanket
Heat
thermal insulation for use from ambient up to 3000°F
C390 Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal
(1649°C).
Insulation Lots
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
C411 Test Method for Hot-Surface Performance of High-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Temperature Thermal Insulation
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
C447 Practice for Estimating the Maximum Use Tempera-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ture of Thermal Insulations
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
C665 Specification for Mineral-Fiber Blanket Thermal Insu-
1.3 When the potential exists that the installation or use of
lation for Light Frame Construction and Manufactured
thermalinsulationmaterials,accessories,andsystemswillpose
Housing
safety or health problems, the manufacturers shall provide the
C680 Practice for Estimate of the Heat Gain or Loss and the
userwithappropriatecurrentinformationregardinganyknown
Surface Temperatures of Insulated Flat, Cylindrical, and
problems associated with the recommended use of the
Spherical Systems by Use of Computer Programs
products, and shall also recommend protective measures to be
C795 Specification for Thermal Insulation for Use in Con-
employed in their safe utilization. The user shall establish
tact with Austenitic Stainless Steel
appropriate safety and health practices and determine the
C1045 Practice for Calculating Thermal Transmission Prop-
applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use.
erties Under Steady-State Conditions
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded C1058 Practice for Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating
asthestandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesaremathemati-
and Reporting Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
cal conversions to SI units which are provided for information C1101/C1101M Test Methods for Classifying the Flexibility
only and are not considered standard. or Rigidity of Mineral Fiber Blanket and Board Insulation
C1104/C1104M Test Method for Determining the Water
2. Referenced Documents
Vapor Sorption of Unfaced Mineral Fiber Insulation
2
C1335 Test Method for Measuring Non-Fibrous Content of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Man-Made Rock and Slag Mineral Fiber Insulation
C71 Terminology Relating to Refractories
C167 Test Methods for Thickness and Density of Blanket or
3. Terminology
Batt Thermal Insulations
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
3.1 Definitions—Terminology C71 and Terminology C168
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measure-
shall be considered as applying to the terms used in this
ments and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of
standard.
the Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
C209 Test Methods for Cellulosic Fiber Insulating Board
3.2.1 fibers—the fibers shall be refractory oxides, processed
from a molten state into fibrous form.
3.2.2 high-temperature fiber thermal insulation— a thermal
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on
insulation, varying in flexibility, composed of refractory inor-
Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.23 on
Blanket and Loose Fill Insulation. ganic fibers, with or without binder added, and furnished in
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2010. Published October 2010. Originally
either flat sheets or rolls.
approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as C892 – 05. DOI:
10.1520/C0892-10.
2
4. Classification
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.1 The general-type product governed by this specification
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. is blanket or batt composed of inorganic refractory fibers.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C892 − 10
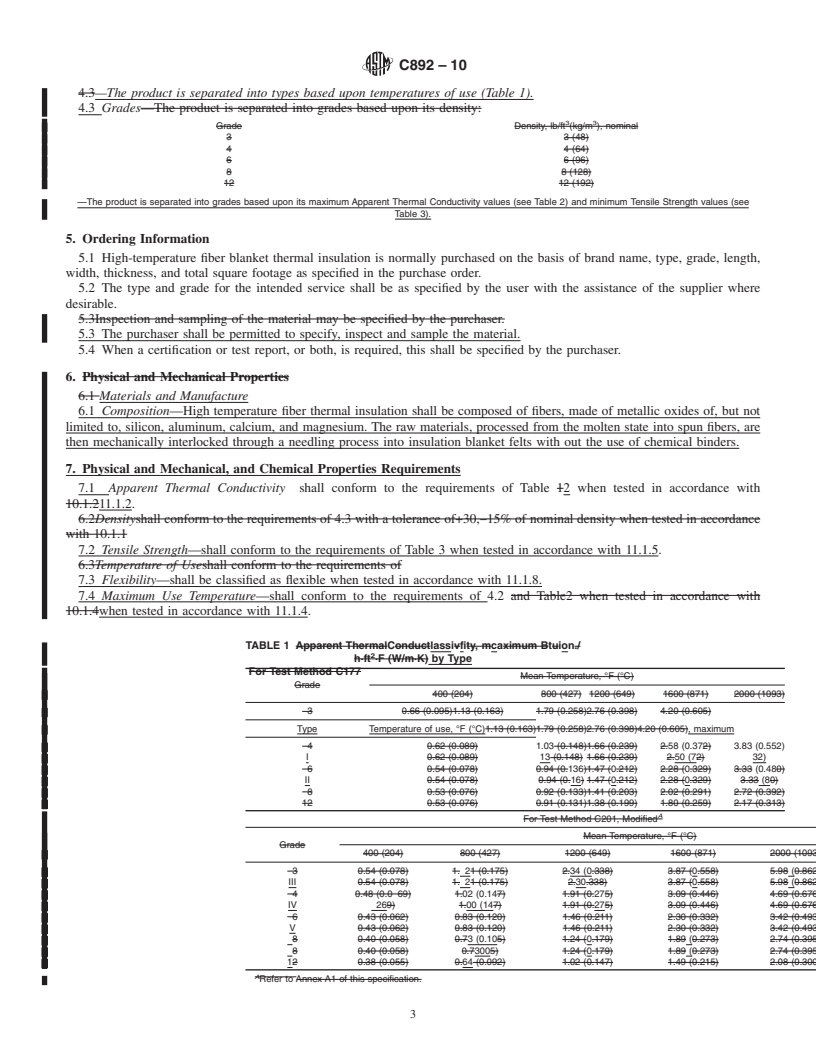
4.2 Types—The product is separated into types based upon 8.2 The standard length, width, and thickness combinations
temperatures of us
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C892–05 Designation: C892 – 10
Standard Specification for
1
High-Temperature Fiber Blanket Thermal Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C892; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1This specification covers high-temperature fiber blanket thermal insulation for use at various temperatures from 1350°F
(732°C) up to 3000°F (1649°C), except when used in high-temperature furnaces.
1.1 This specification covers high-temperature fiber blanket thermal insulation for use from ambient up to 3000°F (1649°C).
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.3 When the potential exists that the installation or use of thermal insulation materials, accessories, and systems maywill pose
safety or health problems, the manufacturers shall provide the user with appropriate current information regarding any known
problems associated with the recommended use of the company’s products, and shall also recommend protective measures to be
employed in their safe utilization. The user shall establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability
of regulatory requirements prior to use.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C71 Terminology Relating to Refractories
C167 Test Methods for Thickness and Density of Blanket or Batt Thermal Insulations
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
C177 Test Method for Steady-State Heat Flux Measurements and Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the
Guarded-Hot-Plate Apparatus C201Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Refractories
C209 Test Methods for Cellulosic Fiber Insulating Board
C356 Test Method for Linear Shrinkage of Preformed High-Temperature Thermal Insulation Subjected to Soaking Heat
C390 Practice for Sampling and Acceptance of Thermal Insulation Lots
C411 Test Method for Hot-Surface Performance of High-Temperature Thermal Insulation
C447 Practice for Estimating the Maximum Use Temperature of Thermal Insulations
C665 Specification for Mineral-Fiber Blanket Thermal Insulation for Light Frame Construction and Manufactured Housing
C680 PracticeforEstimateoftheHeatGainorLossandtheSurfaceTemperaturesofInsulatedFlat,Cylindrical,andSpherical
Systems by Use of Computer Programs
C795 Specification for Thermal Insulation for Use in Contact with Austenitic Stainless Steel
C1045 Practice for Calculating Thermal Transmission Properties Under Steady-State Conditions
C1058 Practice for Selecting Temperatures for Evaluating and Reporting Thermal Properties of Thermal Insulation
C1101/C1101M Test Methods for Classifying the Flexibility or Rigidity of Mineral Fiber Blanket and Board Insulation
C1104/C1104M Test Method for Determining the Water Vapor Sorption of Unfaced Mineral Fiber Insulation
C1335 Test Method for Measuring Non-Fibrous Content of Man-Made Rock and Slag Mineral Fiber Insulation
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Terminology C71 and Terminology C168 shall be considered as applying to the terms used in this standard.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC16onThermalInsulationandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeC16.23onBlanketandLoose
Fill Insulation.
Current edition approved Nov.Sept. 1, 2005.2010. Published December 2005.October 2010. Originally approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 20002005 as
C892–005. DOI: 10.1520/C0892-105.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C892 – 10
3.2.1 fibers—the fibers shall be refract
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.