ASTM E363-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Chromium and Ferrochromium
Standard Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Chromium and Ferrochromium
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 These test methods for the chemical analysis of chromium metal and ferrochromium alloy are primarily intended to test such materials for compliance with compositional specifications such as Specifications A101 and A481. It is assumed that all who use these test methods will be trained analysts capable of performing common laboratory procedures skillfully and safely. It is expected that work will be performed in a properly equipped laboratory.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analysis of chromium and ferrochromium having chemical compositions within the following limits:
Element
Composition, %
Aluminum
0.25 max
Antimony
0.005 max
Arsenic
0.005 max
Bismuth
0.005 max
Boron
0.005 max
Carbon
9.00 max
Chromium
51.0 to 99.5
Cobalt
0.10 max
Columbium
0.05 max
Copper
0.05 max
Lead
0.005 max
Manganese
0.75 max
Molybdenum
0.05 max
Nickel
0.50 max
Nitrogen
6.00 max
Phosphorus
0.03 max
Silicon
12.00 max
Silver
0.005 max
Sulfur
0.07 max
Tantalum
0.05 max
Tin
0.005 max
Titanium
0.50 max
Vanadium
0.50 max
Zinc
0.005 max
Zirconium
0.05 max
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
Sections
Arsenic by the Molybdenum Blue Spectrophotometric Test Method
[0.001 % to 0.005 %]
10 – 20
Lead by the Dithizone Spectrophotometric Test Method
[0.001 % to 0.05 %]
21 – 31
Chromium by the Sodium Peroxide Fusion-Titrimetric Test Method
[50 % to 75 %]
32 – 38
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 6 and in special ”Warning” paragraphs throughout these test methods.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E363 − 16
Standard Test Methods for
1
Chemical Analysis of Chromium and Ferrochromium
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E363; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope responsibility of whoever uses this standard to consult and
establish appropriate safety and health practices and deter-
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analysis of
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
chromium and ferrochromium having chemical compositions
Specific hazard statements are given in Section6 and in special
within the following limits:
”Warning” paragraphs throughout these test methods.
Element Composition, %
Aluminum 0.25 max
2. Referenced Documents
Antimony 0.005 max
Arsenic 0.005 max
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Bismuth 0.005 max
Boron 0.005 max A101 Specification for Ferrochromium
Carbon 9.00 max
A481 Specification for Chromium Metal
Chromium 51.0 to 99.5
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
Cobalt 0.10 max
Columbium 0.05 max
Determine Conformance with Specifications
Copper 0.05 max
E32 Practices for Sampling Ferroalloys and Steel Additives
Lead 0.005 max
for Determination of Chemical Composition
Manganese 0.75 max
Molybdenum 0.05 max
E50 Practices for Apparatus, Reagents, and Safety Consid-
Nickel 0.50 max
erations for Chemical Analysis of Metals, Ores, and
Nitrogen 6.00 max
Related Materials
Phosphorus 0.03 max
Silicon 12.00 max E60 Practice for Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related
Silver 0.005 max
Materials by Spectrophotometry
Sulfur 0.07 max
E135 Terminology Relating to Analytical Chemistry for
Tantalum 0.05 max
Tin 0.005 max
Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
Titanium 0.50 max
E173 Practice for Conducting Interlaboratory Studies of
Vanadium 0.50 max
Methods for Chemical Analysis of Metals (Withdrawn
Zinc 0.005 max
3
Zirconium 0.05 max
1998)
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following order: E1601 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Evaluate the Performance of an Analytical Method
Sections
Arsenic by the Molybdenum Blue 10–20
Spectrophotometric Test Method
3. Terminology
[0.001 % to 0.005 %]
Lead by the Dithizone Spectrophotometric Test 21–31 3.1 For definition of terms used in this test method, refer to
Method
Terminology E135.
[0.001 % to 0.05 %]
Chromium by the Sodium Peroxide Fusion- 32–38
4. Significance and Use
Titrimetric Test Method
[50 % to 75 %]
4.1 These test methods for the chemical analysis of chro-
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
mium metal and ferrochromium alloy are primarily intended to
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
test such materials for compliance with compositional specifi-
standard.
cations such as Specifications A101 and A481. It is assumed
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
that all who use these test methods will be trained analysts
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1 2
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E01 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials and are the direct contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
responsibility of Subcommittee E01.01 on Iron, Steel, and Ferroalloys. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved May 1, 2016. Published June 2016. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as E363 – 09. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/E0363-16. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E363 − 16
capable of performing common laboratory procedures skill- 12. Concentration Range
fully and safely. It is expected that work will be performed in
12.1 The recommended concentration range is 0.01 mg to
a properly equipped laboratory.
0.15 mg of arsenic per 50 mL of solution using a 1-cm cell.
NOTE2—Thistestmethodhasbeenwrittenforcellshavinga1-cmlight
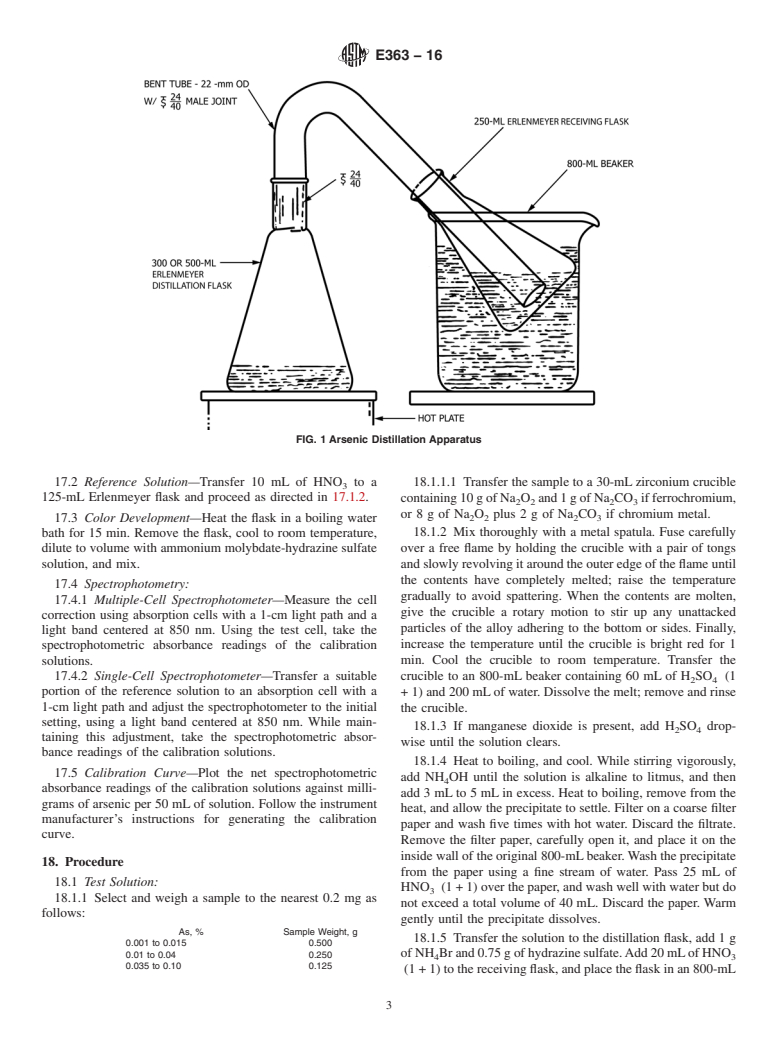
5. Apparatus, Reagents, and Spectrophotometric Practice
path. Cells having other dimensions may be used, provided suitable
5.1 Apparatus, standard solutions, and other reagents re-
adjustments can be made in the amount of sample and reagents used.
quired for each determination are listed in separate sections
13. Stability of Color
preceding the procedure. Spectrophotometers sha
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E363 − 09 E363 − 16
Standard Test Methods for
1
Chemical Analysis of Chromium and Ferrochromium
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E363; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analysis of chromium and ferrochromium having chemical compositions within the
following limits:
Element Concentration, %
Element Composition, %
Aluminum 0.25 max
Antimony 0.005 max
Arsenic 0.005 max
Bismuth 0.005 max
Boron 0.005 max
Carbon 9.00 max
Chromium 51.0 to 99.5
Cobalt 0.10 max
Columbium 0.05 max
Copper 0.05 max
Lead 0.005 max
Manganese 0.75 max
Molybdenum 0.05 max
Nickel 0.50 max
Nitrogen 6.00 max
Phosphorus 0.03 max
Silicon 12.00 max
Silver 0.005 max
Sulfur 0.07 max
Tantalum 0.05 max
Tin 0.005 max
Titanium 0.50 max
Vanadium 0.50 max
Zinc 0.005 max
Zirconium 0.05 max
1.2 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
Sections
Arsenic by the Molybdenum Blue Photometric 10 – 20
Test Method
[0.001 % to 0.005 %]
Arsenic by the Molybdenum Blue Spectropho- 10 – 20
tometric Test Method
[0.001 % to 0.005 %]
Lead by the Dithizone Photometric Test 21 – 31
Method
[0.001 % to 0.05 %]
Lead by the Dithizone Spectrophotometric Test 21 – 31
Method
[0.001 % to 0.05 %]
Chromium by the Sodium Peroxide Fusion- 32 – 38
Titrimetric Test Method
[50 % to 75 %]
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E01 on Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials and are the direct responsibility
of Subcommittee E01.01 on Iron, Steel, and Ferroalloys.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2009May 1, 2016. Published November 2009June 2016. Originally approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 20022009 as
ε1
E363 – 83 (2002)E363 . – 09. DOI: 10.1520/E0363-09.10.1520/E0363-16.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E363 − 16
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 6. and in special ”Warning” paragraphs
throughout these test methods.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A101 Specification for Ferrochromium
A481 Specification for Chromium Metal
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E32 Practices for Sampling Ferroalloys and Steel Additives for Determination of Chemical Composition
E50 Practices for Apparatus, Reagents, and Safety Considerations for Chemical Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
E60 Practice for Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related Materials by Spectrophotometry
E135 Terminology Relating to Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
3
E173 Practice for Conducting Interlaboratory Studies of Methods for Chemical Analysis of Metals (Withdrawn 1998)
E1601 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Evaluate the Performance of an Analytical Method
3. Terminology
3.1 For definition of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology E135.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 These test methods for the chemical analysis of metals and alloys chromium metal and ferrochromium alloy are primarily
intended to test such materials for compliance with compositional specifications such as SpecificationSpecifications A101 and
A481. It is assumed that all who use these test methods will be trained analysts capable of performing common laboratory
procedures skillfully and safely. It is expected that work will be performed in a properly equipped laboratory.
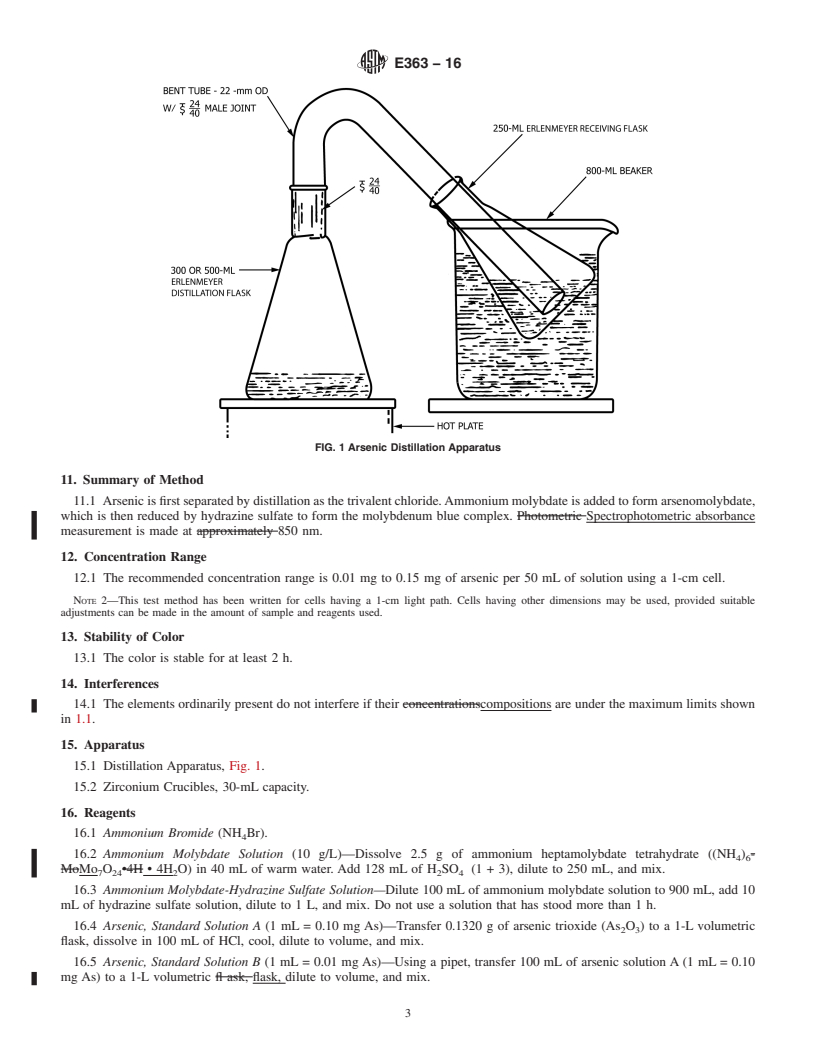
5. Apparatus, Reagents, and PhotometricSpectrophotometric Practice
5.1 Apparatus, standard solutions, and other reagents required for each determination are listed in separate sections preceding
the procedure. PhotometersSpectrophotometers shall conform to the requirements prescribed in Practice E60. .(Note 1)
NOTE 1—In these methods, cells
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.