ASTM F2523-05
(Practice)Standard Practice for Blowout Resistance of Room-Temperature Vulcanized Elastomers
Standard Practice for Blowout Resistance of Room-Temperature Vulcanized Elastomers
SCOPE
1.1 This practice provides a means to determine the blowout resistance of a room-temperature vulcanized elastomer system (RTV) using a standard fixture.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F2523–05
Standard Practice for
Blowout Resistance of Room-Temperature Vulcanized
Elastomers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2523; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.2.1 Discussion—This interface may exist as a small gap
requiring a material such as room-temperature vulcanized
1.1 Thispracticeprovidesameanstodeterminetheblowout
elastomer (RTV) to seal.
resistance of a room-temperature vulcanized elastomer system
3.3 Acronym:
(RTV) using a standard fixture.
3.3.1 RTV—room-temperature vulcanized elastomer
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
4. Summary of Practice
standard.
4.1 Condensation cures RTVs as a one-component system
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
cure when exposed to moisture in the ambient air or as
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
two-component systems when those components are mixed
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
together. RTVs are often used to seal joints where three flanges
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
meet (T joints) such as an automotive engine’s front cover,
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
engine block, and oil pan. Because of machining and assembly
2. Referenced Documents tolerance variations, these T joints may have a slight misalign-
ment or gap. We also find gaps in the half-round area of the oil
2.1 ASTM Standards:
pan to block and in the valley between the intake manifold and
D 907 Terminology of Adhesives
block on certain V-engines as a result of manufacturing
D 1566 Terminology Relating to Rubber
tolerances.The RTVis used to seal in fluids. In some assembly
F 2468 ClassificationforSpecifyingSiliconeAdhesivesand
line applications, soon after the RTV is applied and the flanges
Sealants for Transportation Applications
fastened together, the system is subjected to an air decay test at
2.2 SAE Standard:
a designated pressure. This test is used to determine an RTV’s
SAE J1199 Mechanical and Material Requirements for
3 capability to withstand loss of integrity at this designated
Metric Externally Threaded Steel Fasteners
pressure.
3. Terminology 4.2 When using this practice, one must first determine the
maximum gap based on stack tolerances of the system. A
3.1 Definitions—Some terms in this practice are defined in
two-piece round fixture uses the top portion to mirror the
Terminologies D 907 and D 1566.
system gap, while the bottom half provides the mating flange
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
and the connection for the pressure input. The gap is machined
3.2.1 blowout, n—disruption of the uncured RTV integrity
into the top half of the fixture in a “pie slice” 60° angle. A
inajointfromsystempressurizationresultinginsuddenlossof
continuous bead of RTV is applied to the entire bottom portion
pressure.
of the fixture, the top half is carefully attached, and the fixture
3.2.2 T–joint, n—interface created in a sealing surface
is pressurized to the prescribed limits and held for a specified
where three structural components meet.
time period. If the RTVis not capable of sealing at the pressure
applied, a sudden loss of pressure will occur.
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F03 on Gaskets and
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F03.70 on Formed in Place Gaskets.
5. Significance and Use
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2005. Published November 2005.
5.1 This practice may be used to determine the viability of
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
an RTV sealant to withstand pressure leak testing before cure
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
at maximum gap conditions of a system. This practice may be
the ASTM website.
usedtoindicateanRTV’sacceptabilitytoundergoanassembly
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
lineleakcheckwithoutbeingdisruptivetothesealantintegrity.
Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2523–05
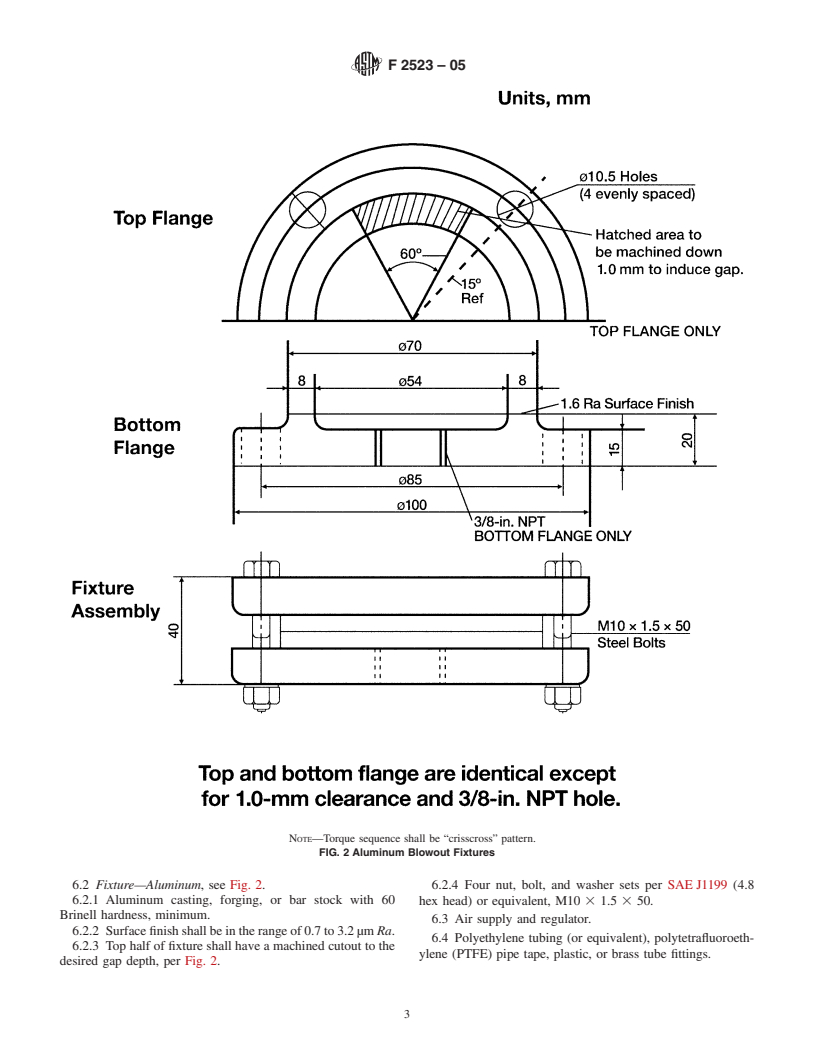
NOTE—Torque sequence shall be “crisscross” pattern.
FIG. 1 Steel Blowout Fixtures
6. Apparatus 6.1.1 Steel casting, forging, or bar stock with a 100 Brinell
hardness, minimum.
6.1 Fixture—Steel, see Fig. 1.
6.1.2 Surfacefinishshallbeintherangeof0.7to3.2µm Ra.
6.1.3 Top half of fixture shall have a machined cutout to the
Thesolesourceofsupplyoftheblowoutfixturesinbothmaterialsknowntothe
committee at this time is Kovil Manufacturing, 925 Sherman Ave., Hamden, CT
desired gap depth per Fig. 1.
06514. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to
6.1.4 Four nut, bolt, and washer sets per SAE J1199 (4.8
ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consider-
ation at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend. hex head) or equivalent, M10 3 1.5 3 50.
F2523–05
NOTE—Torque sequence shall be “crisscross” pattern.
FIG. 2 Aluminum Blowout Fixtures
6.2 Fixture—Aluminum, see Fig. 2. 6.2.4 Four nut, bolt, and washer sets per SAE J1199 (4.8
6.2.1 Aluminum casting, forging, or bar stock with 60 hex head) or equivalent, M10 3 1.5 3 50.
Brinell hardness, minimum.
6.3 Air supply and regulator.
6.2.2 Surfacefinishshallbeintherangeof0.7to3.2µm Ra.
6.4 Polyethylene tubing (or equivalent), polytetrafluoroeth-
6.2.3 Top half of fixture shall have a machined cutout to the
ylene (PTFE) pipe tape, plastic, or brass tube fittings.
desired gap depth, per Fig. 2.
F2523–05
6.5 Inline pressure gage or equivalent, 0 to 138 kPa, 10.4.9 Disassembleandcleanthefixturethoroughly,remov-
accurate to 60.7 kPa. ing all traces of RTV.
6.6 Timing device wi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.