ASTM D5508-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Residual Acrylonitrile Monomer in Styrene-Acrylonitrile Copolymer Resins and Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber by Headspace-Capillary Gas Chromatography (HS-CGC)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Residual Acrylonitrile Monomer in Styrene-Acrylonitrile Copolymer Resins and Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber by Headspace-Capillary Gas Chromatography (HS-CGC)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 A measurement of the residual acrylonitrile in nitrile rubbers (NBR), styrene-acrylonitrile copolymers or ABS terpolymers will determine the polymer's suitability for various applications.
4.2 Under optimum conditions, the minimum level of detection of RAN in NBR, SAN, or ABS terpolymers is approximately 50 ppb.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the residual acrylonitrile (RAN) content in nitrile-butadiene rubbers (NBR), styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) copolymers, and rubber-modified acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) resins.
1.2 Any components that can generate acrylonitrile in the headspace procedure will constitute an interference. The presence of 3-hydroxypropionitrile in latices limits this procedure to dry rubbers and resins.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 6.3 and 6.4.
Note 1: There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5508 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Residual Acrylonitrile Monomer in Styrene-
Acrylonitrile Copolymer Resins and Nitrile-Butadiene
Rubber by Headspace-Capillary Gas Chromatography (HS-
1
CGC)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5508; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the re-
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
sidual acrylonitrile (RAN) content in nitrile-butadiene rubbers
E2935 Practice for Evaluating Equivalence of Two Testing
(NBR), styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) copolymers, and rubber-
Processes
modified acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) resins.
1.2 Any components that can generate acrylonitrile in the
3. Summary of Test Method
headspace procedure will constitute an interference. The pres-
3.1 Two dispersions (in o-dichlorobenzene) are prepared
ence of 3-hydroxypropionitrile in latices limits this procedure
and sealed in headspace vials for each polymer; one vial
to dry rubbers and resins.
contains the polymer in solvent while the second vial contains
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
the polymer, solvent, plus a known standard addition of
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
acrylonitrile (AN). Both vials are agitated for a specified time
standard.
under ambient conditions. After agitation, the vials are ther-
mally equilibrated in a constant-temperature bath.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2 After completion of the timed equilibration, an aliquot
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
of the heated headspace gas from each vial is injected into a
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
capillary gas-chromatographic column using an automated
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
injection system. The capillary column will provide the chro-
Specific precautionary statements are given in 6.3 and 6.4.
matographic resolution necessary to isolate the AN from other
volatiles potentially present. The AN response is measured
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
using a nitrogen-specific detector (NPD). The raw data signal
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
is converted to a relative RAN concentration through a
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
standard addition calculation.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4. Significance and Use
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.1 A measurement of the residual acrylonitrile in nitrile
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
rubbers (NBR), styrene-acrylonitrile copolymers or ABS ter-
polymers will determine the polymer’s suitability for various
2. Referenced Documents
applications.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.2 Under optimum conditions, the minimum level of de-
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
tection of RAN in NBR, SAN, or ABS terpolymers is approxi-
mately 50 ppb.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods.
5. Apparatus
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2023. Published October 2023. Originally
5.1 Gas Chromatograph, equipped with a nitrogen-
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D5508 - 16. DOI:
10.1520/D5508-23.
phosphorus specific detector, backflush valve (see Fig. 1), split
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
injector, and capable of accepting megabore (0.53 mm inside
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
diameter) fused silica capillary columns. Detector make-up gas
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. is required.
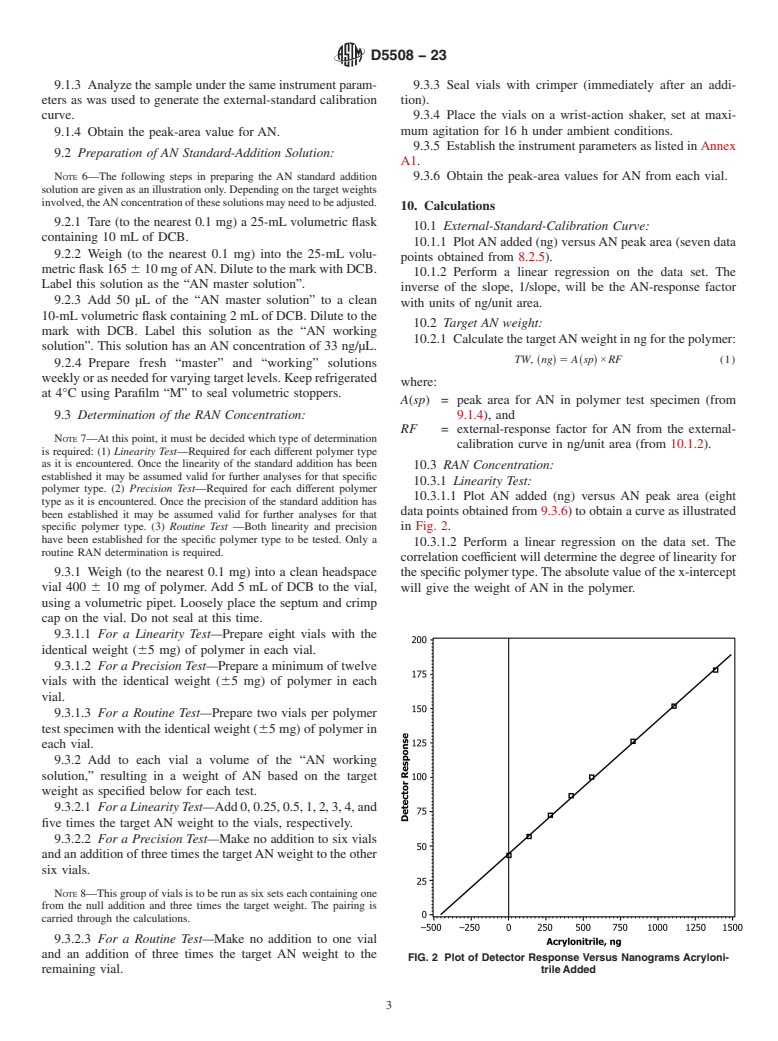
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5508 − 23
6.4 o-Dichlorobenzene. (Warning—o-Dichlorobenzene is
moderately toxic and should
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5508 − 16 D5508 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Residual Acrylonitrile Monomer in Styrene-
Acrylonitrile Copolymer Resins and Nitrile-Butadiene
Rubber by Headspace-Capillary Gas Chromatography (HS-
1
CGC)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5508; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the residual acrylonitrile (RAN) content in nitrile-butadiene rubbers (NBR),
styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) copolymers, and rubber-modified acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) resins.
1.2 Any components that can generate acrylonitrile in the headspace procedure will constitute an interference. The presence of
3-hydroxypropionitrile in latices limits this procedure to dry rubbers and resins.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and healthsafety, health, and environmental practices and determine
the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in 6.3 and 6.4.
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E2935 Practice for Evaluating Equivalence of Two Testing Processes
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Two dispersions (in o-dichlorobenzene) are prepared and sealed in headspace vials for each polymer; one vial contains the
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods and
Section D20.70.02 on Chromatography.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2016Oct. 1, 2023. Published September 2016October 2023. Originally approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 20092016
ε1
as D5508 - 94aD5508 - 16.(2009) . DOI: 10.1520/D5508-16.10.1520/D5508-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5508 − 23
polymer in solvent while the second vial contains the polymer, solvent, plus a known standard addition of acrylonitrile (AN). Both
vials are agitated for a specified time under ambient conditions. After agitation, the vials are thermally equilibrated in a
constant-temperature bath.
3.2 After completion of the timed equilibration, an aliquot of the heated headspace gas from each vial is injected into a capillary
gas-chromatographic column using an automated injection system. The capillary column will provide the chromatographic
resolution necessary to isolate the AN from other volatiles potentially present. The AN response is measured using a
nitrogen-specific detector (NPD). The raw data signal is converted to a relative RAN concentration through a standard addition
calculation.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 A measurement of the residual acrylonitrile in nitrile rubbers (NBR), styrene-acrylonitrile copolymers or ABS terpolymers will
determine the polymer’s suitability for various applications.
4.2 Under optimum conditions, the minimum level of detection of RAN in NBR, SAN, or ABS terpolymers is approximately 50
ppb.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Gas Chromatograph, equipped with a nitrogen-phosphorus specific detector, backflush valve (s
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.