ASTM D3594-93
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Copolymerized Ethyl Acrylate In Ethylene-Ethyl Acrylate Copolymers
Standard Test Method for Copolymerized Ethyl Acrylate In Ethylene-Ethyl Acrylate Copolymers
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers ethylene-ethyl acrylate copolymers containing from 1 to 25% ethyl acrylate comonomer.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. (See Practice E380.)
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1--There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 3594 – 93 An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Copolymerized Ethyl Acrylate In Ethylene-Ethyl Acrylate
Copolymers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3594; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
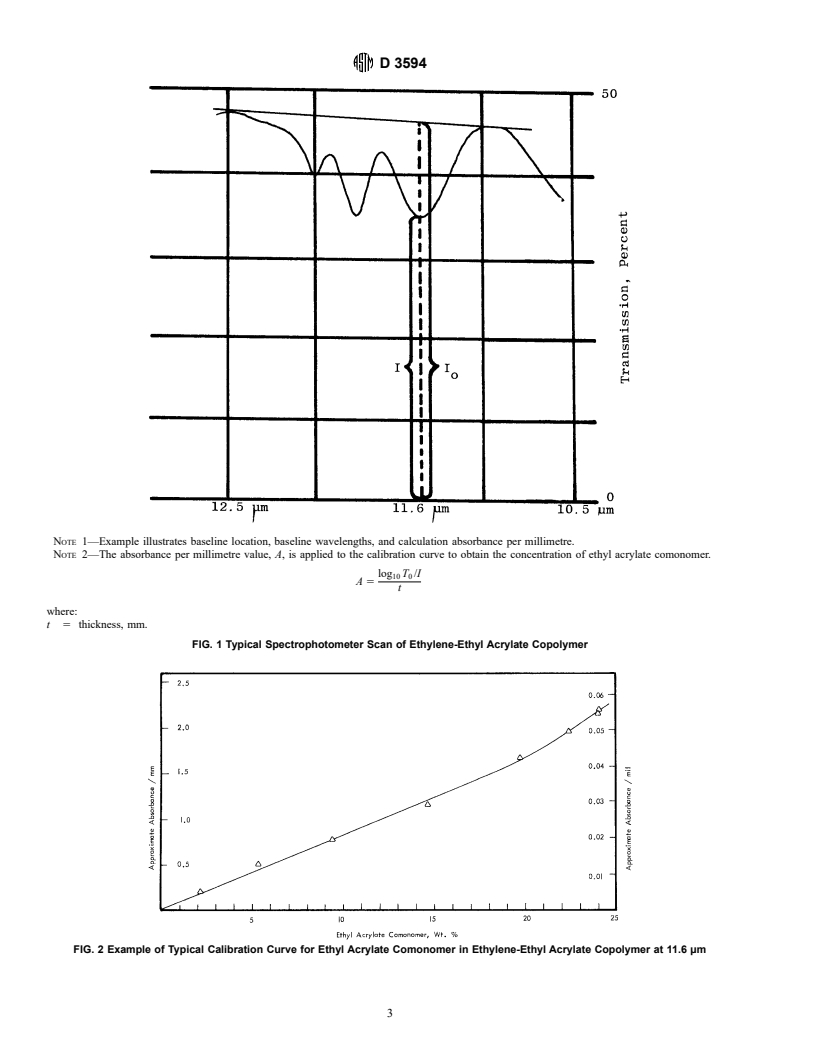
1. Scope interference from the monomer at this wavelength.
4.2 The infrared absorption band at 11.60 μm is of medium
1.1 This test method covers ethylene-ethyl acrylate copoly-
intensity; consequently, fairly thick films are employed. This is
mers containing from 1 to 25 % ethyl acrylate comonomer.
an advantage in that errors in measurements of the thicknesses
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
of films have minimal influence on the analytical result. Film
standard. (See Practice E 380.)
thickness is selected so that not more than 80 % of the infrared
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
energy is absorbed at the analytical wavelength. The approxi-
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
mate thicknesses found to be satisfactory for different concen-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
trations of comonomer are as follows: (1) less than 5 weight %
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ethyl acrylate 5 0.5 mm, (2) 5 to 15 weight % ethyl acry-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
late 5 0.25 mm, and (3) 15 to 25 weight % ethyl acry-
NOTE 1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
late 5 0.18 mm. It is necessary first to press a film approxi-
mately 0.25 mm in thickness and scan it to observe the
2. Referenced Documents
absorption intensity unless the approximate ethyl acrylate
2.1 ASTM Standards:
content is known.
B 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
4.3 For the highest precision, the test method requires that
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
the thickness of the sample film be determined accurately.
E 131 Terminology Relating to Molecular Spectroscopy
4.4 The general procedure is to scan the absorption band
E 168 Practices for General Techniques of Infrared Quanti-
from 10.50 to 12.50 μm, although a single-point measurement
tative Analysis
may also be used. This test method describes the use of a scan
E 177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
and employs the base-line method as outlined in 7.2 and the
ASTM Test Methods
figure illustrating the Base-Line Method for Measuring Absor-
E 275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance
bance of Practices E 168. A calibration curve is prepared by
of Ultraviolet, Visible, and Near Infrared Spectrophotom-
plotting absorbance per millimetre values versus weight per-
eters
cent ethyl acrylate for several copolymers which have had
E 380 Practice for Use of the International System of Units
ethyl acrylate contents established by a fast neutron activation
(SI)
analysis of oxygen content. The ethyl acrylate content of an
unknown sample is then obtained by referring the absorbance
3. Terminology
per millimetre value to the calibration curve.
3.1 See Terminology D 883.
5. Significance and Use
4. Summary of Test Method
5.1 Ethyl acrylate is copolymerized with ethylene to pro-
4.1 The infrared absorption band at 11.60 μm responds to
duce film, molding, and wire coating resins with improved
increases in comonomer content. There is no absorption at this
physical properties. Ethyl acrylate comonomer increases flex-
wavelength when there is no comonomer present. It apparently
ibility, stress cracking resistance, toughness, and clarity. A
is unique and characteristic of the copolymer. There is no
rapid quantitative technique is needed for the evaluation of the
amount of ethyl acrylate in a resin for specification purposes
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Plastics
because physical properties change rapidly with increasing
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods
comonomer content.
(Section D20.70.08).
5.2 Infrared spectrophotometric analysis, when suitably
Current edition approved Feb. 15, 1993. Published April 1993. Originally
calibrated, can be used for the measurement of the concentra-
published as D 3594 – 77. Last previous edition D 3594 – 77 (1987).
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
tion of comonomer present. Calibration is performed with
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
samples that have been analyzed for oxygen content by fast
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.01.
neutron activation analysis. Oxygen content is converted to
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
D 3594
100 3 X
ethyl acrylate comonomer content by a simple calculation.
E, wt % 5 (1)
31.5
5.3 A purpose of the infrared method of analysis is to
provide a procedure for use in quality control analysis. It is a
where:
rapid, secondary method of analysis as contrasted with the
X 5 oxygen content of unknown copolymers, weight %.
more expensive and time-consuming fast neutron activation
10.2 Set the controls of the infrared spectrometer for quan-
analysis which is the primary, calibrating method.
titative conditions with a good signal-to-noise ratio and satis-
factory reproducibility. Use a sufficiently expanded chart scale
6. Apparatus
such that line width can be measured accurately. Use a
6.1 Infrared Spectrophotometer, capable of spectral resolu-
scanning speed sufficiently slow to give good reproducibility of
tion equivalent to that defined by Practice E 275 and exhibited
band shape. Set the slit width narrow enough that there is little
in Fig. 7 of that practice. The instrument should be capable of
distortion of the true band shape. Record the instrument
scale expansion along the wavelength (or wave number) axis.
conditions used.
6.1.1 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometer (FT-
−1
NOTE 2—For the Perkin-Elmer Model 221 Spectrophotometer the
IR), with nominal 4 cm resolution.
following settings are satisfactory: Prism NaCl, slits 2X, slit program 927,
6.2 Compression-Molding Press, small, with platens ca-
attenuator speed 600, amplifier gain adjusted to give good response, chart
pable of being heated to 150°C.
scale 0.01 μm/mm, chart speed 0.5 μm/min, electrical balance and
6.3 Metal Plates, two, 150 by 150 mm or larger, of 0.5-mm
suppression adjusted to specifications in instrument manual. Comparable
thickness with smooth surfaces, chromium plated preferably.
operating conditions should be used when other instruments are em-
6.4 Brass Shims, three, approximately 75 by 75 mm and ployed.
thicknesses of 0.50 mm, 0.25 mm, and 0.18 mm, with an
10.3 Scan the films from 10.50 to 12.50 μm.
aperture in the center at least 25 by 38 mm.
NOTE 3—Films having high gloss may exhibit interference fringes i
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.