ASTM A504-93(1999)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Wrought Carbon Steel Wheels
Standard Specification for Wrought Carbon Steel Wheels
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers one-wear, two-wear, and multiple-wear wrought carbon steel wheels for locomotives and cars, designated Class U, untreated, and Classes L, A, B, and C, heat-treated, wheels.
1.2 The service for which the various classes are intended is as follows:
1.2.1 Class B or C wheels shall be used for freight cars in interchange service.
1.2.2 Class B or C wheels are recommended for use on locomotives.
1.2.3 For passenger car service, the various classes are intended generally as follows:
1.2.3.1 Class L -High speed with more severe braking conditions than other classes and light wheel loads.
1.2.3.2 Class A -High speed with more severe braking conditions, but moderate wheel loads.
1.2.3.3 Class B -High speed service with severe braking conditions and heavier wheel loads.
1.2.3.4 Class C -( ) Service with light braking conditions and heavier wheel loads.
1.2.3.5 Class C -( ) Service with heavier braking conditions where off-tread brakes are employed.
1.2.4 Class U -Wheels may be used in service in which the wheel load and braking are low.
1.3 The use of two-wear wheels is recommended for freight car service.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 504 – 93 (Reapproved 1999)
Standard Specification for
Wrought Carbon Steel Wheels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 504; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This specification covers one-wear, two-wear, and 2.1 ASTM Standards:
multiple-wear wrought carbon steel wheels for locomotives E 59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination
and cars, designated Class U, untreated, and Classes L, A, B, of Chemical Composition
and C, heat-treated, wheels. E 350 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Carbon Steel,
1.2 The service for which the various classes are intended is Low-Alloy Steel, Silicon Electrical Steel, Ingot Iron, and
as follows: Wrought Iron
1.2.1 Class B or C wheels shall be used for freight cars in E 415 Test Method for Optical Emission Vacuum Spectro-
interchange service. metric Analysis of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel
1.2.2 Class B or C wheels are recommended for use on E 1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur,
locomotives. Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel and in Iron, Nickel, and
1.2.3 For passenger car service, the various classes are Cobalt Alloys
intended generally as follows: 2.2 SAE Documents:
1.2.3.1 Class L—High speed with more severe braking SAE J 442 Test Strip, Holder and Gage for Shot Peening
conditions than other classes and light wheel loads. SAE J 443 Recommended Practice for Procedures for
1.2.3.2 Class A—High speed with more severe braking Using Standard Shot Peening Test Strip
conditions, but moderate wheel loads. SAE J 827 Recommended Practice for Cast Steel Shot
1.2.3.3 Class B—High speed service with severe braking 2.3 Military Standard:
conditions and heavier wheel loads. MIL-S-13165B Shot Peening of Metal Parts
1.2.3.4 Class C—(1) Service with light braking conditions 2.4 AAR Standard:
and heavier wheel loads. AAR Wheel and Axle Manual, Section G, M-107
1.2.3.5 Class C—(2) Service with heavier braking condi-
NOTE 1—The tables of tape sizes may be referred to in the AAR Wheel
tions where off-tread brakes are employed.
and Axle Manual, Section G, Part 2.
1.2.4 Class U—Wheels may be used in service in which
the wheel load and braking are low. 3. Ordering Information
1.3 The use of two-wear wheels is recommended for freight
3.1 Orders for wheels under this specification shall include
car service.
the following information as appropriate:
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.1.1 Quantity (number of pieces),
as the standard.
3.1.2 Class (see Table 1),
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.3 Full identification of wheel design, including tread and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
flange contour, and dimensional drawing if required,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.4 Rough bore size,
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.5 Intended service (see Section 1),
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.06.
1 4
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel, Available from the Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc., 400 Commonwealth
Stainless Steel, and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Drive, Warrendale, PA 15096.
A01.06 on Steel Forgings and Billets. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 1993. Published February 1994. Originally Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
published as A 504 – 64 to replace A 57 and A 186. Combined with A 25 in this Available from Association of American Railroads, 50 “F” St., Washington, DC
edition. Last previous edition A 504 – 89. 20001.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 504 – 93 (1999)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
plate area extended approximately one half of the way into the
Composition, % hub and rim fillet radii on the front and on the back of the
wheel.
Carbon:
Class U 0.65–0.77
6.2.4 Arc Height Measurement—Measurements of arc
Class L, max 0.47
height shall be made in accordance with SAE Standard J 442 or
Class A 0.47–0.57
Class B 0.57–0.67 SAE Recommended Practice J 443.
Class C 0.67–0.77
6.2.5 Coverage—The minimum peening time shall be suf-
Manganese 0.60–0.85
ficient to ensure that full coverage is attained on the Almen C
Phosphorus, max 0.05
Sulfur, max 0.05
strip as defined in the Alternate Procedure of SAE Recom-
Silicon, min 0.15
mended Practices J 443, or MIL-S-13165B, Paragraph 6.11.
6.2.6 Sequence—Shot peening shall be performed on all
wheels and after any corrective surface preparation in the plate
3.1.6 ASTM designation and date of issue, and
area. Plate area is defined in 6.2.3. Peening may be performed
3.1.7 Supplementary requirements (if any).
prior to inspection.
6.2.7 Portable Peeners—A portable peening device may be
4. Manufacture
used to re-peen small reconditioned areas (no larger than about
4.1 The steel shall be made by any of the following
2 by 3 in. (50.8 by 76.2 mm)) on wheel plate surfaces
processes: open-hearth, electric-furnace, or basic-oxygen pro-
excluding the critical fillet areas (front hub and back rim). The
cess.
portable equipment must be capable of peening an Almen C-2
4.2 Discard—Sufficient discard shall be made from each
Strip to develop the required average arc height of not less than
ingot to ensure freedom from piping and undue segregation.
0.008 in. (0.203 mm) with a reasonable time of peening.
4.3 Temperatures—During the manufacture, necessary care
Peening time of wheel plates must be at least as long as the
in the regulation of temperature gradients shall be exercised to
time required to develop the 0.008-in. arc height. The equip-
obtain the physical properties to be expected from the chemical
ment must be tested on an Almen C Strip each 8-h shift that the
composition and mechanical work and to prevent the develop-
portable peener is used. A record of the Almen C test results
ment of faulty structure. Immediately after the last hot fabri-
shall be maintained.
cating operation (coning or dishing), all wheels shall be
6.3 Quality Assurance Provisions:
allowed to cool to a temperature below the critical range. The
6.3.1 Wheel Surface Condition—The peened appearance of
cooling shall be controlled to prevent injury by too rapid
rim and hub shall not be cause for rejection.
cooling below the critical range.
6.3.2 Frequency of Test—Arc height determinations shall be
5. Heat Treatment
made on Almen strips attached to a test wheel at the beginning
and end of each production run but not less than once in each
5.1 For Classes L, A, B, and C wheels, the heat treatment
shall consist of treatment of the rim only. eight operating hours.
5.2 Rim-Quenching Treatment—The wheels shall be re- 6.3.3 Retest—If a test fails to meet the arc height require-
heated uniformly to the proper temperature to refine the grain
ments of 0.008 Almen C-2, two retests shall be made. These
and then the rims shall be quenched. Following quenching, the retests shall be averaged with the first determination. The
wheels shall be charged into a furnace for tempering to meet
average shall be not less than 0.008 and no more than one value
the requirements of Section 12, and subsequently cooled under of the three shall be less than 0.008.
controlled conditions.
6.3.4 Repeening—When test values fail to meet the provi-
sions of 6.3.3, corrective action shall be initiated and satisfac-
6. Shot Peening
tory test values secured before proceeding with production
6.1 Scope—The plate surfaces of all wheels shall be shot-
peening. If the average Almen value of the unsatisfactory test
peened in accordance with the following requirements:
is 0.006 or 0.007, the last half of the wheels peened prior to the
6.2 Requirements:
unsatisfactory test, but subsequent to a satisfactory test, shall
6.2.1 Shot—The shot shall be SAE No. 550 or larger
be repeened with at least ⁄2 exposure time. If the average
hardened steel as specified in SAE Recommended Practice
Almen value is less than 0.006, all the wheels peened since the
J 827.
last satisfactory test shall be repeened with full exposure.
6.2.2 Shot Size Control—The peening machines shall be
equipped with a separator for continuously removing broken
7. Retreatment
shot. Sufficient new shot shall be added to ensure that a
7.1 Any wheel failing to meet the requirements of Section
minimum of 85 % of No. 550 or larger shot is maintained in the
12 may be retreated and tested in accordance with 12.1 and
machines at all times.
12.2.
6.2.3 Peening Intensity—The peening intensity shall be
sufficient to produce an average arc height of not less than
8. Mating
0.008 Almen C-2 on the front plate near the hub fillet and on
the back plate near the rim fillet of wheels of the standard 8.1 Wheels shall be measured and marked to the lower tape
design, and at back plate hub fillet and front plate rim fillet of number until the next graduation is reached. Wheels shall be
the reverse plate design. The area to be peened is defined as the shipped in pairs of the same measured tape size.
A 504 – 93 (1999)
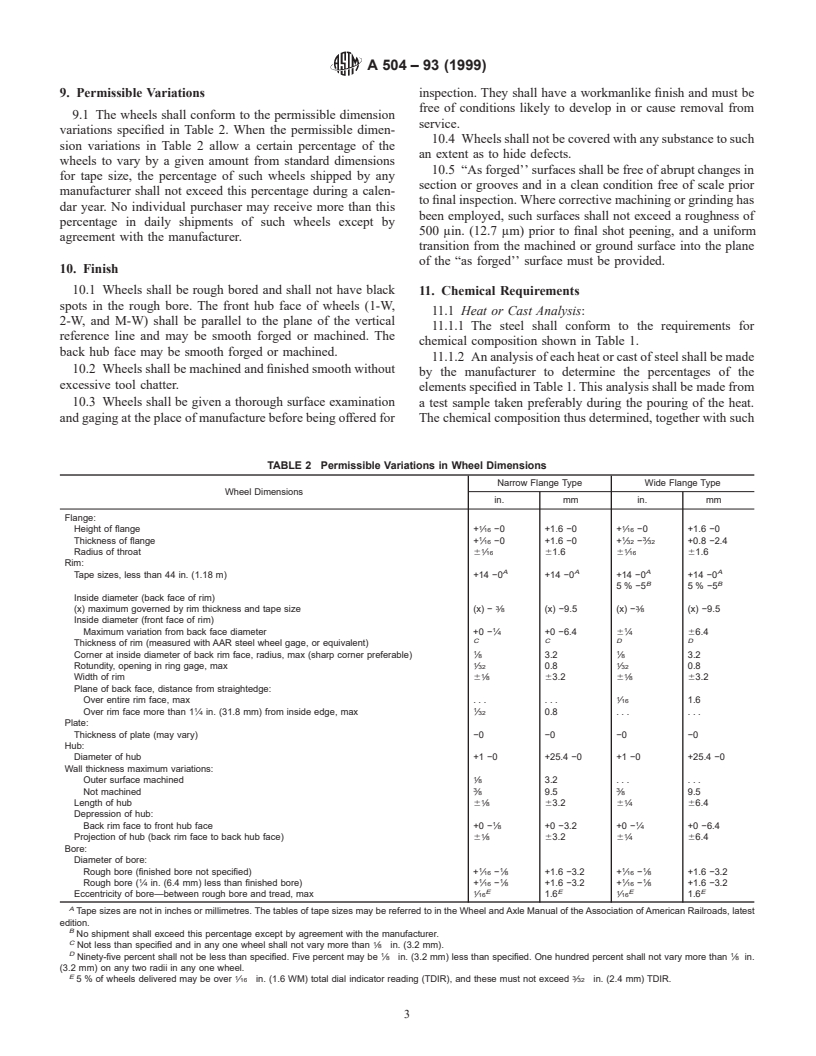
9. Permissible Variations inspection. They shall have a workmanlike finish and must be
free of conditions likely to develop in or cause removal from
9.1 The wheels shall conform to the permissible dimension
service.
variations specified in Table 2. When the permissible dimen-
10.4 Wheels shall not be covered with any substance to such
sion variations in Table 2 allow a certain percentage of the
an extent as to hide defects.
wheels to vary by a given amount from standard dimensions
10.5 “As forged’’ surfaces shall be free of abrupt changes in
for tape size, the percentage of such wheels shipped by any
section or grooves and in a clean condition free of scale prior
manufacturer shall not exceed this percentage during a calen-
to final inspection. Where corrective machining or grinding has
dar year. No individual purchaser may receive more than this
been employed, such surfaces shall not exceed a roughness of
percentage in daily shipments of such wheels except by
500 μin. (12.7 μm) prior to final shot peening, and a uniform
agreement with the manufacturer.
transition from the machined or ground surface into the plane
of the “as forged’’ surface must be provided.
10. Finish
10.1 Wheels shall be rough bored and shall not have black
11. Chemical Requirements
spots in the rough bore. The front hub face of wheels (1-W,
11.1 Heat or Cast Analysis:
2-W, and M-W) shall be parallel to the plane of the vertical
11.1.1 The steel shall conform to the requirements for
reference line and may be smooth forged or machined. The
chemical composition shown in Table 1.
back hub face may be smooth forged or machined.
11.1.2 An analysis of each heat or cast of steel shall be made
10.2 Wheels shall be machined and finished smooth without
by the manufacturer to determine the percentages of the
excessive tool chatter.
elements specified in Table 1. This analysis shall be made from
10.3 Wheels shall be given a thorough surface examination a test sample taken preferably during the pouring of the heat.
and gaging at the place of manufacture before being offered for The chemical composition thus determined, together with such
TABLE 2 Permissible Variations in Wheel Dimensions
Narrow Flange Type Wide Flange Type
Wheel Dimensions
in. mm in. mm
Flange:
1 1
Height of flange + ⁄16 −0 +1.6 −0 + ⁄16 −0 +1.6 −0
1 1 3
Thickness of flange + ⁄16 −0 +1.6 −0 + ⁄32 − ⁄32 +0.8 −2.4
1 1
Radius of throat 6 ⁄16 61.6 6 ⁄16 61.6
Rim:
A A A A
Tape sizes, less than 44 in. (1.18 m) +14 −0 +14 −0 +14 −0 +14 −0
B B
5% −5 5% −5
Inside diameter (back face of rim)
3 3
(x) maximum governed by rim thickness and tape size (x) − ⁄8 (x) −9.5 (x) − ⁄8 (x) −9.5
Inside diameter (front face of rim)
1 1
Maximum variation from back face diameter +0 − ⁄4 +0 −6.4 6 ⁄4 66.4
CCDD
Thickness of rim (measured with AAR steel wheel gage, or equivalent)
1 1
Corner at inside diameter of back rim face, radius, max (sharp corner preferable) ⁄8 3.2 ⁄8 3.2
1 1
Rotundity, opening in ring gage, max ⁄32 0.8 ⁄32 0.8
1 1
Width of rim 6 ⁄8 63.2 6 ⁄8 63.2
Plane of back face, distance from straightedge:
Over entire rim face, max . . . . . . ⁄16 1.6
1 1
Over rim face more than 1 ⁄4 in. (31.8 mm) from inside edge, max ⁄32 0.8 . .
Plate:
Thickness of plate (may vary) −0 −0 −0 −0
Hub:
Diameter of hub +1 −0 +25.4 −0 +1 −0 +25.4 −0
Wall thickness maximum variations:
Outer surface machined ⁄8 3.2 . .
3 3
Not machined ⁄8 9.5 ⁄8 9.5
1 1
Length of hub 6 ⁄8 63.2 6 ⁄4 66.4
Depression of hub:
1 1
Back rim face to front hub face +0 − ⁄8 +0 −3.2 +0 − ⁄4 +0 −6.4
1 1
Projection of hub (back rim face to back hub face) 6 ⁄8 63.2 6 ⁄4 66.4
Bore:
Diameter of bore:
1 1 1 1
Rough bore (finished bore not specified) + ⁄16 − ⁄8 +1.6 −3.2 + ⁄16 − ⁄8 +1.6 −3.2
1 1 1 1 1
Rough bore ( ⁄4 in. (6.4 mm) less than finished bore) + ⁄16 − ⁄8 +1.6 −3.2 + ⁄16 − ⁄8 +1.6 −3.2
E E E E
1 1
Eccentricity of bore—between rough bore and tread, max ⁄16 1.6 ⁄16 1.6
A
Tape sizes are not in inches or millimetres. The tables of tape sizes may be referred to in the Wheel and Axle Manual of the Association of American Railroads, latest
edition.
B
No shipment shall exceed this percentage except by agreement with the manufacturer.
C
Not less than specified and in any one wheel shall not vary more than ⁄8 in. (3.2 mm).
D
1 1
Ninety-five percent shall not be less than specified. Five percent may be ⁄8 in. (3.2 mm) less than specified. One hundred percent shall not vary more than ⁄8 in.
(3.2 mm) on any two radii in any one wheel.
E
1 3
5 % of wheels delivered may be over ⁄16 in. (1.6 WM) total dial indicator reading (TDIR), and these must not exceed ⁄32 in. (2.4 mm) TDIR.
A 504 – 93 (1999)
identifying records as may be desired, shall be reported to the 12.3 Number of Tests:
purchaser or his representative and shall conform to the
12.3.1 Where continuous heat-treating furnaces are used,
requirements specified in Table 1.
Brinell hardness measurements shall be made on 10 % of the
11.2 Chemical Analysis—Chemical analysis of each heat of
wheels from each heat. Where batch-type heat-treating fur-
steel shall be made by one of the following test methods. All
n
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.