ASTM D473-07(2017)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Sediment in Crude Oils and Fuel Oils by the Extraction Method
Standard Test Method for Sediment in Crude Oils and Fuel Oils by the Extraction Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 A knowledge of the sediment content of crude oils and fuel oils is important both to the operation of refining and the buying or selling of these commodities.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of sediment in crude oils and fuel oils by extraction with toluene. The precision applies to a range of sediment levels from 0.01 % to 0.40 % mass, although higher levels may be determined.
Note 1: Precision on recycled oils and crankcase oils is unknown and additional testing is required to determine that precision.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 5.1.1.6 and 6.1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D473 − 07 (Reapproved 2017)
Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards (MPMS), Chapter 10.1
Standard Test Method for
Sediment in Crude Oils and Fuel Oils by the Extraction
Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D473; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
ε NOTE—Footnote 1 was corrected editorially in August 2017.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This test method covers the determination of sediment 2.1 ASTM Standards:
in crude oils and fuel oils by extraction with toluene. The D4057Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
precision applies to a range of sediment levels from 0.01% to Petroleum Products (API MPMS Chapter 8.1)
0.40% mass, although higher levels may be determined. D4177Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
Petroleum Products (API MPMS Chapter 8.2)
NOTE 1—Precision on recycled oils and crankcase oils is unknown and
D5854Practice for Mixing and Handling of Liquid Samples
additional testing is required to determine that precision.
of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (API MPMS Chap-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
ter 8.3)
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
E29Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
standard.
Determine Conformance with Specifications
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2.2 API Standards:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Chapter 8.1Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Products (ASTM Practice D4057)
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Chapter 8.2Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petro-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
leum Products (ASTM Practice D4177)
warning statements, see 5.1.1.6 and 6.1.
Chapter 8.3Mixing and Handling of Liquid Samples of
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
Petroleum and Petroleum Products (ASTM Practice
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
D5854)
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
2.3 ISO Standard:
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
5272 Toluene for industrial use—Specifications
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3. Summary of Test Method
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.1 Extract test portion of a representative oil sample,
contained in a refractory thimble, with hot toluene until the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and the API Committee on
Petroleum Measurement, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.02 For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
/COMQ, the joint ASTM-API Committee on Hydrocarbon Measurement for contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Custody Transfer (Joint ASTM-API). This test method has been approved by the Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
sponsoring committees and accepted by the Cooperating Societies in accordance the ASTM website.
with established procedures. Available from American Petroleum Institute (API), 1220 L. St., NW,
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2017.PublishedJuly2017.Originallyapproved Washington, DC 20005-4070, http://api-ec.api.org.
ɛ1 4
in 1938. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D473–07 (2012) . DOI: Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
10.1520/D0473-07R17E01. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
© Jointly copyrighted by ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, USA and the American Petroleum Institute (API), 1220 L Street NW, Washington DC 20005, USA
´1
D473 − 07 (2017)
NOTE 1—Apparatus B shows the water cup in position.
FIG. 1 Extraction Apparatus for Determination of Sediment
rate drops below a pre-set limit has been found suitable to prevent
residue reaches constant mass.The mass of residue, calculated
vaporized toluene from igniting. The use of such a device is recom-
as a percentage, is reported as sediment by extraction.
mended.
4. Significance and Use
5.1.1.3 Extraction Thimble —The extraction thimble shall
be of a refractory porous material, pore size 20.0µm to
4.1 A knowledge of the sediment content of crude oils and
30.0µm (as certified by the manufacturer), 25mm in diameter
fuel oils is important both to the operation of refining and the
by 70mm in height, weighing not less than 15g and not more
buying or selling of these commodities.
than 17g. Suspend the thimble from the condenser coil by
5. Apparatus means of a basket so that it hangs approximately midway
betweenthesurfaceoftheextractingsolventandthebottomof
5.1 Usuallaboratoryapparatusandglassware,togetherwith
the condenser coil.
the following are required for this test method.
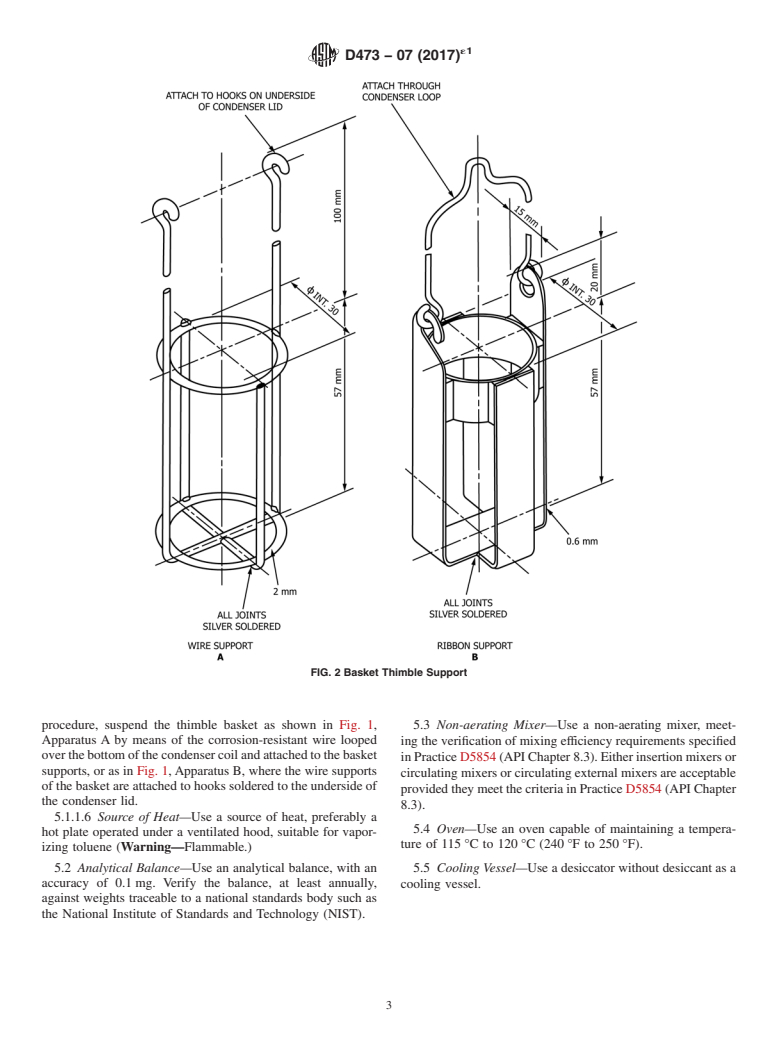
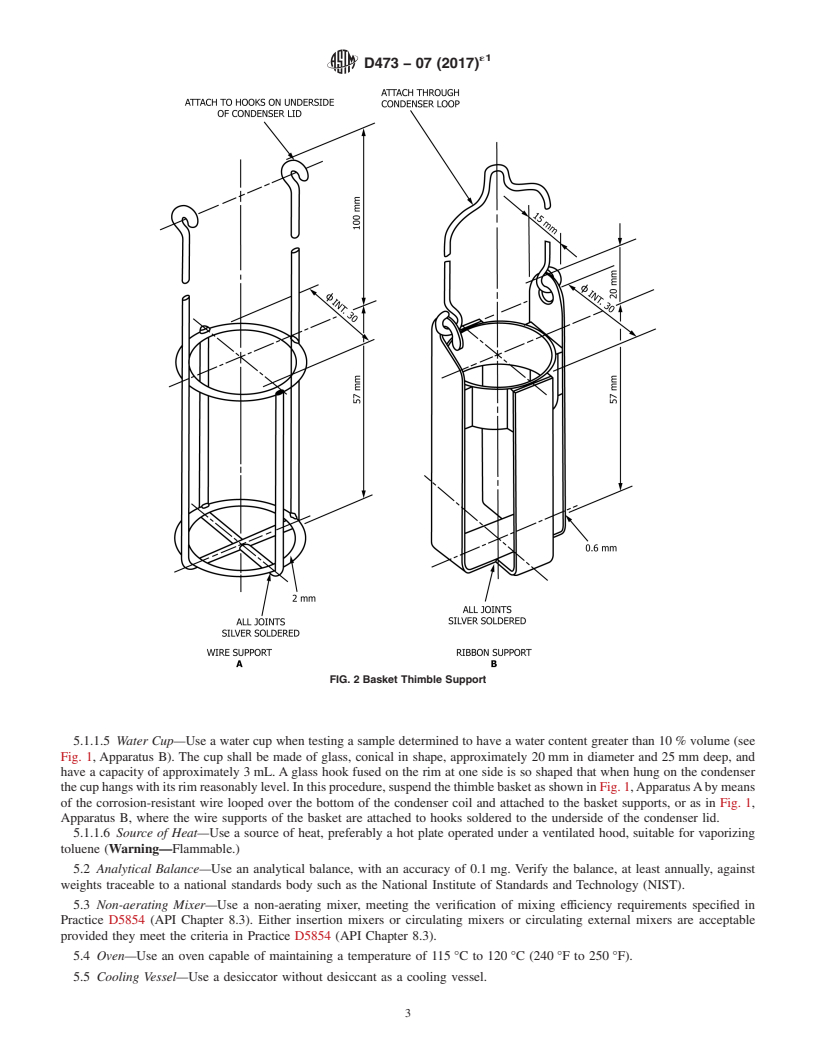
5.1.1.4 Thimble Basket—The thimble basket shall be
5.1.1 Extraction Apparatus—Usetheapparatusillustratedin
corrosion-resistant and shall be made of platinum, stainless
Figs. 1 and 2 and consisting of the elements described in
steel, nickel-chromium alloy, or similar material. Fig. 2 shows
5.1.1.1 – 5.1.1.3.
the design and dimensions of two typical baskets that have
5.1.1.1 Extraction Flask—Use a wide-neck (Erlenmeyer)
been used successfully in the industry.
flask of 1L capacity, with a minimum external neck diameter
5.1.1.5 Water Cup—Use a water cup when testing a sample
of 50mm, for the procedure.
determined to have a water content greater than 10% volume
5.1.1.2 Condenser—Acondenser in the form of a metal coil
(see Fig. 1, Apparatus B). The cup shall be made of glass,
approximately 25mm in diameter and 50mm in length at-
conicalinshape,approximately20mmindiameterand25mm
tached to, and with the ends projecting through, a lid of
deep,andhaveacapacityofapproximately3mL.Aglasshook
sufficient diameter to cover the neck of the flask as shown in
fusedontherimatonesideissoshapedthatwhenhungonthe
Fig. 1. The coil shall be made from stainless steel, tin,
condenser the cup hangs with its rim reasonably level. In this
tin-plated copper, or tin-plated brass tubing having an outside
diameter of 5mm to 8mm and a wall thickness of 1.5mm. If
constructed of tin-plated copper or brass, the tin coating shall
The sole source of supply of the extraction thimble,AN 485, 25mm × 70mm,
have a minimum thickness of 0.075mm. The exposed surface
coarse porosity, drawing number QA005163, known to the committee at this time
is Saint-Gobain/Norton Industrial Ceramics Corporation of Worcester, MA. If you
of the coil for cooling purposes is about 115cm .
are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM
NOTE 2—The use of a water flowmeter/controller unit that monitors International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a
water flow to the condenser that shuts off the heat source when the flow meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
´1
D473 − 07 (2017)
FIG. 2 Basket Thimble Support
procedure, suspend the thimble basket as shown in Fig. 1, 5.3 Non-aerating Mixer—Use a non-aerating mixer, meet-
Apparatus A by means of the corrosion-resistant wire looped
ingtheverificationofmixingefficiencyrequirementsspecified
overthebottomofthecondensercoilandattachedtothebasket
inPracticeD5854(APIChapter8.3).Eitherinsertionmixersor
supports, or as in Fig. 1,Apparatus B, where the wire supports
circulatingmixersorcirculatingexternalmixersareacceptable
ofthebasketareattachedtohookssolderedtotheundersideof
providedtheymeetthecriteriainPracticeD5854(APIChapter
the condenser lid.
8.3).
5.1.1.6 Source of Heat—Use a source of heat, preferably a
5.4 Oven—Use an oven capable of maintaining a tempera-
hot plate operated under a ventilated hood, suitable for vapor-
ture of 115°C to 120°C (240°F to 250°F).
izing toluene (Warning—Flammable.)
5.2 Analytical Balance—Use an analytical balance, with an 5.5 Cooling Vessel—Useadesiccatorwithoutdesiccantasa
accuracy of 0.1mg. Verify the balance, at least annually,
cooling vessel.
against weights traceable to a national standards body such as
the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
´1
D473 − 07 (2017)
TABLE 1 Typical Characteristics for ACS Reagent Grade Toluene
in temperature during mixing exceeds 10°C (20°F), cool the
Assay 99.5+ % sample,andrepeatthemixingatalowerenergyinput.Arisein
Color (APHA) 10
temperature greater than 10°C (20°F) may result in a decrease
A
Boiling range (initial to dry point) 2.0 °C
in viscosity that is sufficient for the sediment to settle.
Residue after evaporation 0.001 %
Substances darkened by H SO passes test
2 4
8. Procedure
Sulfur compounds (as S) 0.003 %
Water (H O) (by Karl Fischer titration) 0.03 %
8.1 For referee tests, use a new extraction thimble (5.1.1.3)
A
Recorded boiling point 110.6 °C.
prepared in accordance with 8.2. For routine tests, thimbles
may be reused. When reusing thimbles, the extraction to
constant mass for one determination should be considered as
the preliminary extraction for the succeeding determination.
5.6 Temperature Measuring Device—Such as a
After several determinations (the accumulated sediment may
thermometer, capable of measuring the temperature of the
be sufficient to interfere with further determinations), follow
sample to the nearest 1°C (2°F).
the procedure described in 8.3 to remove the combustible
6. Solvent portion of the accumulated sediment.Avoid excessive reuse of
thimbles, as over time the pores become c
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D473 − 07 (Reapproved 2017) D473 − 07 (Reapproved 2017)
Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards (MPMS), Chapter 10.1
Standard Test Method for
Sediment in Crude Oils and Fuel Oils by the Extraction
Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D473; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
ε NOTE—Footnote 1 was corrected editorially in August 2017.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of sediment in crude oils and fuel oils by extraction with toluene. The precision
applies to a range of sediment levels from 0.01 % to 0.40 % mass, although higher levels may be determined.
NOTE 1—Precision on recycled oils and crankcase oils is unknown and additional testing is required to determine that precision.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 5.1.1.6 and 6.1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (API MPMS Chapter 8.1)
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (API MPMS Chapter 8.2)
D5854 Practice for Mixing and Handling of Liquid Samples of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (API MPMS Chapter 8.3)
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
2.2 API Standards:
Chapter 8.1 Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (ASTM Practice D4057)
Chapter 8.2 Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (ASTM Practice D4177)
Chapter 8.3 Mixing and Handling of Liquid Samples of Petroleum and Petroleum Products (ASTM Practice D5854)
2.3 ISO Standard:
5272 Toluene for industrial use—Specifications
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Extract test portion of a representative oil sample, contained in a refractory thimble, with hot toluene until the residue
reaches constant mass. The mass of residue, calculated as a percentage, is reported as sediment by extraction.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and the API Committee on Petroleum
Measurement, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.02 /COMQ /COMQ, the joint ASTM-API Committee on Hydrocarbon Measurement for Custody Transfer
(Joint ASTM-API). This test method has been approved by the sponsoring committees and accepted by the Cooperating Societies in accordance with established procedures.
ɛ1
Current edition approved June 1, 2017. Published July 2017. Originally approved in 1938. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D473 – 07 (2012) . DOI:
10.1520/D0473-07R17.10.1520/D0473-07R17E01.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Available from American Petroleum Institute (API), 1220 L. St., NW, Washington, DC 20005-4070, http://api-ec.api.org.
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
© Jointly copyrighted by ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, USA and the American Petroleum Institute (API), 1220 L Street NW, Washington DC 20005, USA
´1
D473 − 07 (2017)
NOTE 1—Apparatus B shows the water cup in position.
FIG. 1 Extraction Apparatus for Determination of Sediment
4. Significance and Use
4.1 A knowledge of the sediment content of crude oils and fuel oils is important both to the operation of refining and the buying
or selling of these commodities.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Usual laboratory apparatus and glassware, together with the following are required for this test method.
5.1.1 Extraction Apparatus—Use the apparatus illustrated in Figs. 1 and 2 and consisting of the elements described in 5.1.1.1
– 5.1.1.3.
5.1.1.1 Extraction Flask—Use a wide-neck (Erlenmeyer) flask of 1 L capacity, with a minimum external neck diameter of
50 mm, for the procedure.
5.1.1.2 Condenser—A condenser in the form of a metal coil approximately 25 mm in diameter and 50 mm in length attached
to, and with the ends projecting through, a lid of sufficient diameter to cover the neck of the flask as shown in Fig. 1. The coil shall
be made from stainless steel, tin, tin-plated copper, or tin-plated brass tubing having an outside diameter of 5 mm to 8 mm and
a wall thickness of 1.5 mm. If constructed of tin-plated copper or brass, the tin coating shall have a minimum thickness of
0.075 mm. The exposed surface of the coil for cooling purposes is about 115 cm .
NOTE 2—The use of a water flowmeter/controller unit that monitors water flow to the condenser that shuts off the heat source when the flow rate drops
below a pre-set limit has been found suitable to prevent vaporized toluene from igniting. The use of such a device is recommended.
5.1.1.3 Extraction Thimble —The extraction thimble shall be of a refractory porous material, pore size 20.0 μm to 30.0 μm (as
certified by the manufacturer), 25 mm in diameter by 70 mm in height, weighing not less than 15 g and not more than 17 g.
Suspend the thimble from the condenser coil by means of a basket so that it hangs approximately midway between the surface of
the extracting solvent and the bottom of the condenser coil.
5.1.1.4 Thimble Basket—The thimble basket shall be corrosion-resistant and shall be made of platinum, stainless steel,
nickel-chromium alloy, or similar material. Fig. 2 shows the design and dimensions of two typical baskets that have been used
successfully in the industry.
The sole source of supply of the extraction thimble, AN 485, 25 mm × 70 mm, coarse porosity, drawing number QA 005163, known to the committee at this time is
Saint-Gobain/Norton Industrial Ceramics Corporation of Worcester, MA. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
´1
D473 − 07 (2017)
FIG. 2 Basket Thimble Support
5.1.1.5 Water Cup—Use a water cup when testing a sample determined to have a water content greater than 10 % volume (see
Fig. 1, Apparatus B). The cup shall be made of glass, conical in shape, approximately 20 mm in diameter and 25 mm deep, and
have a capacity of approximately 3 mL. A glass hook fused on the rim at one side is so shaped that when hung on the condenser
the cup hangs with its rim reasonably level. In this procedure, suspend the thimble basket as shown in Fig. 1, Apparatus A by means
of the corrosion-resistant wire looped over the bottom of the condenser coil and attached to the basket supports, or as in Fig. 1,
Apparatus B, where the wire supports of the basket are attached to hooks soldered to the underside of the condenser lid.
5.1.1.6 Source of Heat—Use a source of heat, preferably a hot plate operated under a ventilated hood, suitable for vaporizing
toluene (Warning—Flammable.)
5.2 Analytical Balance—Use an analytical balance, with an accuracy of 0.1 mg. Verify the balance, at least annually, against
weights traceable to a national standards body such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
5.3 Non-aerating Mixer—Use a non-aerating mixer, meeting the verification of mixing efficiency requirements specified in
Practice D5854 (API Chapter 8.3). Either insertion mixers or circulating mixers or circulating external mixers are acceptable
provided they meet the criteria in Practice D5854 (API Chapter 8.3).
5.4 Oven—Use an oven capable of maintaining a temperature of 115 °C to 120 °C (240 °F to 250 °F).
5.5 Cooling Vessel—Use a desiccator without desiccant as a cooling vessel.
´1
D473 − 07 (2017)
TABLE 1 Typical Characteristics for ACS Reagent Grade Toluene
Assay 99.5+ %
Color (APHA) 10
A
Boiling range (initial to dry point) 2.0 °C
Residue after evaporation 0.001 %
Substances darkened by H SO passes test
2 4
Sulfur compounds (as S) 0.003 %
Water (H O) (by Karl Fischer titration) 0.03 %
A
Recorded boiling point 110.6 °C.
5.6 Temperature Measuring Device—Such as a thermometer, capable of measuring the temperature of the sample to the nearest
1 °C (2 °F).
6. Solvent
6.1 Toluene—Reagent grade conforming to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American
Chemical Society (ACS) or to Grade 2 of ISO 5272. (Warning—Flammable. Keep away from heat, sparks and open flame. Vapor
harmful. Toluene is toxic. Particular care shall be taken to avoid breathing the vapors and to protect the eyes. Keep the container
closed. Use with adequate ventilation. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with the skin.)
6.1.1 The typical characteristics for the ACS reagent are shown in Table 1.
7. Sampling
7.1 Sampling shall include all steps required to obtain an aliquot of the contents of any pipe, tank, or other system and to place
the sample into the laboratory test container.
7.2 Only use representative samples obtained a
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.