ASTM D5173-97(2007)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for On-Line Monitoring of Carbon Compounds in Water by Chemical Oxidation, by UV Light Oxidation, by Both, or by High Temperature Combustion Followed by Gas Phase NDIR or by Electrolytic Conductivity
Standard Test Method for On-Line Monitoring of Carbon Compounds in Water by Chemical Oxidation, by UV Light Oxidation, by Both, or by High Temperature Combustion Followed by Gas Phase NDIR or by Electrolytic Conductivity
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Accurate measurement of organic carbon in water at low and very low levels is of particular interest to the electronic, pharmaceutical, and steam power generation industries.
Elevated levels of organics in raw water tend to degrade ion exchange resin capacity. Elevated levels of organics in high purity water tend to support biological growth and, in some cases, are directly detrimental to the processes that require high purity water.
In the case of steam power generation, naturally occurring organics can become degraded to CO2 and low molecular weight organic acids that, in turn, are corrosive to the process equipment. Their effect on conductivity may also cause water chemistry operating parameters to be exceeded, calling for plant shutdown.
In process water in other industries, organic carbon can signify in-leakage of substances through damaged piping and components, or an unacceptable level of product loss.
In wastewater treatment, organic carbon measurement of influent and in-process water can help adjust optimize treatment schemes. Measurement of organic carbon at discharge may contribute to regulatory compliance.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the selection, establishment, and application of monitoring systems for carbon and carbon compounds by continual sampling or continuous flow-through, automatic analysis, and recording or otherwise signaling of output data. The system chosen will depend on the purpose for which it is intended (for example, regulatory compliance, process monitoring, or to alert the user to adverse trends) and on the type of water to be monitored (low purity or high purity, with or without suspended particulates, purgeable organics, or inorganic carbon). If it is to be used for regulatory compliance, the test method published or referenced in the regulations should be used in conjunction with this test method and other ASTM test methods. The test method covers carbon concentrations of 10 g/L to 5000 mg/L.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 9.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5173 − 97(Reapproved 2007)
Standard Test Method for
On-Line Monitoring of Carbon Compounds in Water by
Chemical Oxidation, by UV Light Oxidation, by Both, or by
High Temperature Combustion Followed by Gas Phase
1
NDIR or by Electrolytic Conductivity
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5173; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
1.1 This test method covers the selection, establishment,
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
and application of monitoring systems for carbon and carbon
D3694 Practices for Preparation of Sample Containers and
compounds by continual sampling or continuous flow-through,
for Preservation of Organic Constituents
automatic analysis, and recording or otherwise signaling of
D3864 Guide for On-Line Monitoring Systems for Water
output data. The system chosen will depend on the purpose for
Analysis
which it is intended (for example, regulatory compliance,
D4453 Practice for Handling of High Purity Water Samples
process monitoring, or to alert the user to adverse trends) and
D4779 Test Method for Total, Organic, and Inorganic Car-
on the type of water to be monitored (low purity or high purity,
bon in High Purity Water by Ultraviolet (UV) or Persul-
with or without suspended particulates, purgeable organics, or
fate Oxidation, or Both, and Infrared Detection (With-
inorganic carbon). If it is to be used for regulatory compliance,
3
drawn 2002)
the test method published or referenced in the regulations
D4839 Test Method forTotal Carbon and Organic Carbon in
should be used in conjunction with this test method and other
WaterbyUltraviolet,orPersulfateOxidation,orBoth,and
ASTM test methods. The test method covers carbon concen-
Infrared Detection
trations of 10 µg/L to 5000 mg/L.
3. Terminology
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the method, refer to Terminology D1129 and Guide D3864.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 4.1 A representative sample of a water stream, or the water
stream itself flows into a reaction chamber where all or some
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
statements, see Section 9. of the dissolved organic carbon is oxidized to carbon dioxide
by either of two means: (1) a chemical oxidant, an energy
2. Referenced Documents source such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, or both, or (2) high
2 temperature combustion. This carbon dioxide is subsequently
2.1 ASTM Standards:
measured in the gas phase by a non-dispersive infrared
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
detector, or is measured in solution by means of electrolytic
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
conductivity. Interference may occur from the latter method if
the water sample has a high conductivity.
1
4.2 If there are suspended solids in the water stream, it is
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.03 on Sampling Water and
advisable to filter them out to prevent accumulation and
Water-Formed Deposits, Analysis of Water for Power Generation and Process Use,
possible blockage in the analyzer. The instrument will then
On-Line Water Analysis, and Surveillance of Water.
measure dissolved carbon plus any particulate carbon that
Current edition approved June 15, 2007. Published July 2007. Originally
approved in 1991. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D5173 – 97 (2001). passes the filter. This parameter is usually called dissolved
DOI: 10.1520/D5173-97R07.
carbon.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5173 − 97 (2007)
4.3 If there is inorganic carbon present in the water (in the 7. Apparatus
form of carbonate, bicarbonate, or carbon dioxide), it wi
...







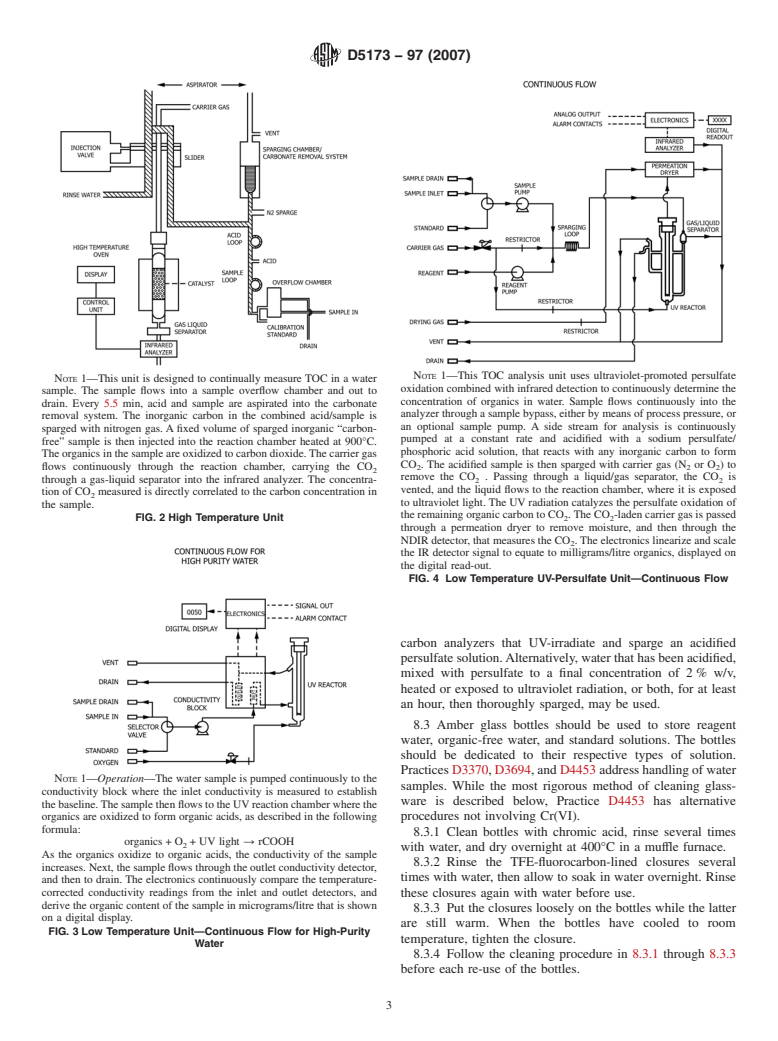
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.