ASTM D5007-99
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Wet-to-Dry Hiding Change
Standard Test Method for Wet-to-Dry Hiding Change
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the change in hiding power of an architectural coating during drying, by visual evaluation of the wet and dry film.
1.2 This test method is not recommended for colors other than white and tints.
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D5007–99
Standard Test Method for
Wet-to-Dry Hiding Change
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5007; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope stripes, which is true of the 0.98 (98%) contrast-ratio standard
for most commercial paints. With paints of unusually low
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofthechange
hiding, a lower contrast standard may be required, which can
in hiding power of an architectural coating during drying, by
be simply one of the stripes taken from a drawdown of the test
visual evaluation of the wet and dry film.
paint.
1.2 This test method is not recommended for colors other
3.1.2 hiding power—the spreading rate of a paint applied
than white and tints.
uniformly on a standard black and white hiding power chart to
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
giveastandarddegreeofcontrastjustshortofcompletehiding.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.2.1 Discussion—In reflectometry the standard contrast
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
for hiding power measurements is generally accepted as the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
contrast ratio C 50.98 (98%), which with white and light
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
tinted coatings is equivalent to a visual color difference of
2. Referenced Documents
about 0.75 CIELAB units.That amount of color difference can
reasonably be described as “just-short-of complete-hiding.”
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Since this is a visual method it employs a visual comparator as
D2805 Test Method for Hiding Power of Paints by Reflec-
a standard, which is a hiding power chart with a white coating
tometry
applied at a contrast ratio of 0.98 (98%).
D3924 Specification for Standard Environment for Condi-
3.1.3 logicator—a multi-notch applicator with clearances,
tioning and Testing Paint, Varnish, Lacquer, and Related
and corresponding wet film thicknesses and spreading rates, in
Materials
equal percentage steps.
3. Terminology
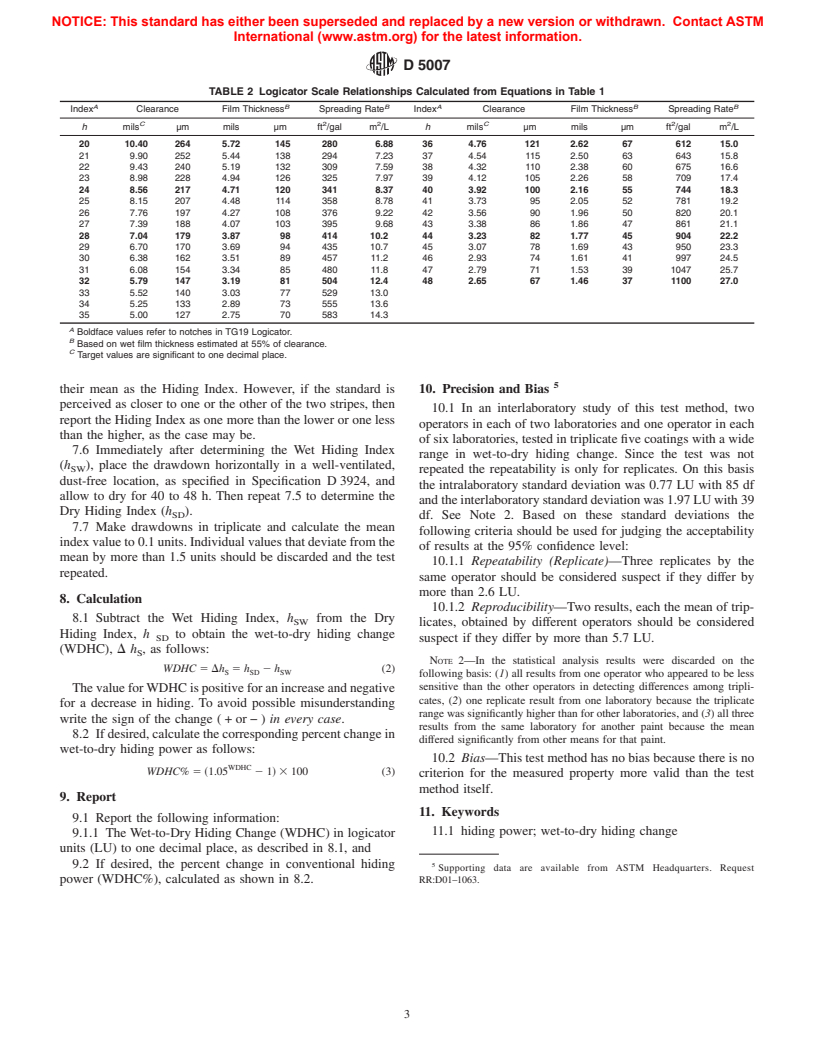
3.1.4 logicator scale—ascalewithvaluesdirectlyrelatedto
the logarithms of corresponding spreading rates. A specified
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
changeinscalevaluerepresentsthesamepercentagechangein
3.1.1 hiding index, h —the Spreading Index at a standard
S
spreading rate over any part of such a scale.
film opacity. In this test method the latter is a visual contrast
3.1.5 spreading index, h—the spreading rate expressed in
standard prepared by applying a semi-opaque white coating on
logicator scale units (LU) as described in 3.1.4 and 3.1.7.
ablackandwhitehiding-powercharttogiveacontrastratioof
3.1.6 spreading rate, H—the area covered per unit quantity
0.98 (98%) which is just short of complete hiding, and is the
of coating. (In this test method the quantity is volumetric).
conventional so-called full hiding end point in photometric
3.1.7 TG19 logicator—a logicator designed for this test
hiding-power methods such as Test Method D2805. Refer to
methodwitheightnotchesnumberedatfour-unitintervalsona
the hiding indices of the wet and dry films as h and h
SW SD
scale from 20 to 48, the notch clearances ranging from 2.65 to
respectively.
10.4mils(67to264µm)correspondingtowetfilmthicknesses
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Since this test method is intended to
from 1.46 to 5.7 mils (37 to 145 µm) and spreading rates from
measure hiding-power difference rather than hiding power
2 2
280 to 1100 ft /gal (6.9 to 27 m /L), with one scale unit
itself,a0.98(98%)contrastratiostandardisnotrequired.Itis
representingachangeof5%andthefour-unitintervalbetween
necessary only that the same standard be used for measuring
notches a cumulative change of 21.55% in the clearance and
bothwetanddryfilms.See3.1.8.Forthispurposethestandard
corresponding film thicknesses and spreading rates. Refer to
needs to lie within the contrast range of both the wet and dry
this scale unit as a logicator unit (LU). (See Fig. 1.)
3.1.7.1 Discussion—The percentage difference between
1 4
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-1 on Paint
notches is calculated as (1.05 −1) 3100 521.55. This per-
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications,and is the direct responsibility of
centage is applicable precisely to the notch clearances and
Subcommittee D01.42on Architectural Finishes.
approximatelytotheirrelatedwet-filmthicknessesandspread-
Current edition approved May 10, 1999. Published July 1999. Originally
published as D 5007–89. Last previous edition D 5007–89 (1993). ing rates. The detailed relationships between scalar value and
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.01.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D5007
increase in hiding is sometimes associated with porosity and
poor film integrity with conventionally formulated coatings.A
decreasecanresultinadisappointingpaintjob.Thewet-to-dry
hiding change is therefore a property of great practical impor-
tance.
5.2 This test method can be used in paint specifications and
as a short, simple procedure for evaluation and quality control.
6. Apparatus
6.1 TG19 Logicator —A multi-notch, varied-clearance ap-
plicatordesignedspecificallyforthistestmethod(see3.1.7and
FIG. 1 Diagram of the Leneta TG19 Logicator
Fig. 1).
6.2 Logicator Test Charts —Black and white hiding charts
the notch clearance, wet film thickness, and spreading rate are
with a chevron-stripe pattern and scale numbers printed at the
given in Table 1 and Table 2.
top corresponding to the paint stripes applied by the Logicator
3.1.8 wet-to-dry hiding change (WDHC)—the difference in
(see Fig. 2).
the Hiding Index of a paint between the wet and the dry state,
6.3 Vacuum Plate, for holding the chart flat while the
expressed in logicator units (LU) as follows:
drawdown is made.
6.4 Visual Hiding Standard —A narrow stripe cut from a
WDHC5Dh 5 h 2 h (1)
S SD SW
logicatortestchartonwhichadurableglossywhitecoatinghad
3.1.8.1 Discussion—The WDHC is unchanged if the con-
been applied to obtain a contrast ratio of 0.98. The stripe is
trastlevelofthehidingstandardisvaried,becausetheresultant
mountedonablankcardforconvenienthandling,asillustrated
changes in the two hiding power values are proportional and
in Fig. 3.
their ratio therefore constant.
3.1.8.2 Discussion—The WDHC is unaffected by devia-
7. Procedure
tionsfromtheestimatedfilmthickness/clearanceratio T/N(see
7.1 Prepare a hiding standard as described in 6.4, or use the
Note 1, Table 1), because the ratio of the two recalculated
standard supplied with the logicator test charts.
hiding-power values is unchanged.
NOTE 1—Strong colors were measured according to this test method
4. Summary of Test Method
usingstandardspreparedwiththeself-samecoatings.Somemeasurements
were also made using the regular white standard. Due to poor correlation
4.1 The test paint is applied with a TG19 Logicator on a
inthesetestsitwasdecidedtoexcludestrongcolorsfromthescopeofthe
logicator test chart (see 6.2 and Fig. 2) and the drawdown
test method. However, should measurements with such colors be at-
examined in comparison with an agreed hiding standard
temptedanyway,itisofinteresttonotethatthewhitestandardapparently
immediately after application and again after drying.
servedaswellforthatpurposeasastandardmadewiththeidenticalcolor.
4.2 The scale numbers of the wet and dry stripes that match
7.2 Place a test chart on the vacuum plate. Then place the
the standard in contrast are recorded as the Wet Hiding Index,
logicator at the top of the chart with its arms extending toward
h , and the Dry Hiding Index h .
SW SD
the operator.
4.3 Thedifferencebetweenth
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.