ASTM D6395-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Flatwise Flexural Impact Resistance of Rigid Plastics
Standard Test Method for Flatwise Flexural Impact Resistance of Rigid Plastics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The flatwise flexural impact test is a test in which the kinetic energy lost by a moving pendulum during impact is used to determine the energy to break or deform a test specimen.
The standard Izod test apparatus as described in Test Method D256 is retrofitted with clamping jaws, which hold the test specimen such that the flat face of the specimen is struck by the pendulum during a test.
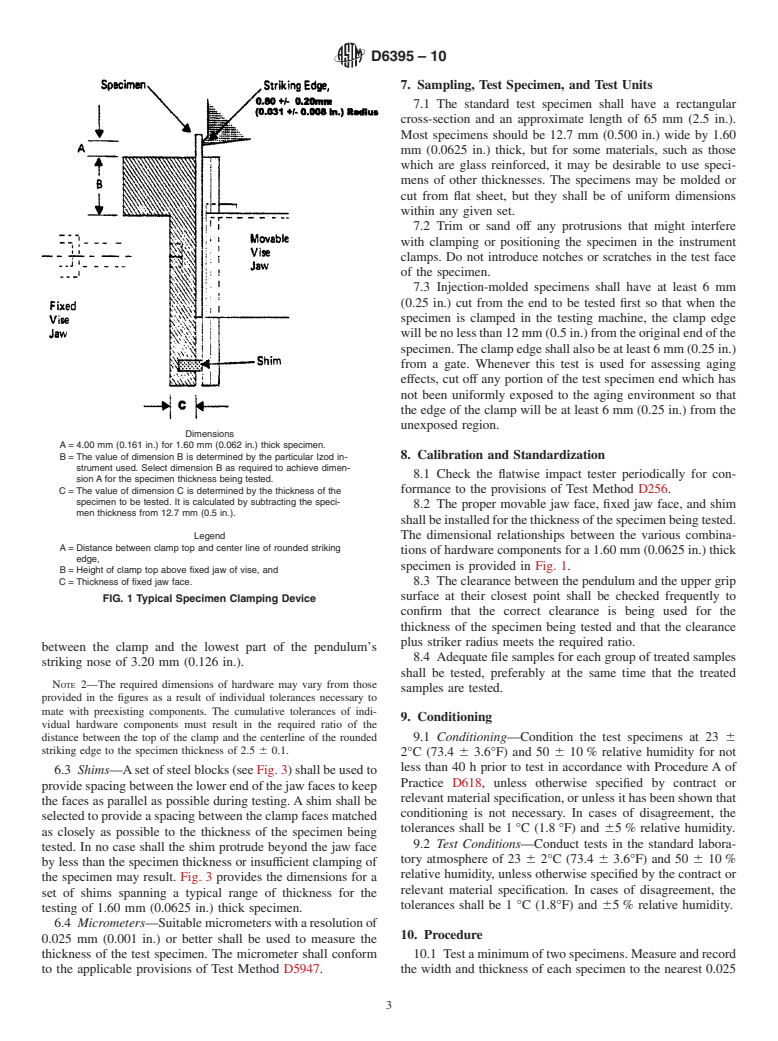
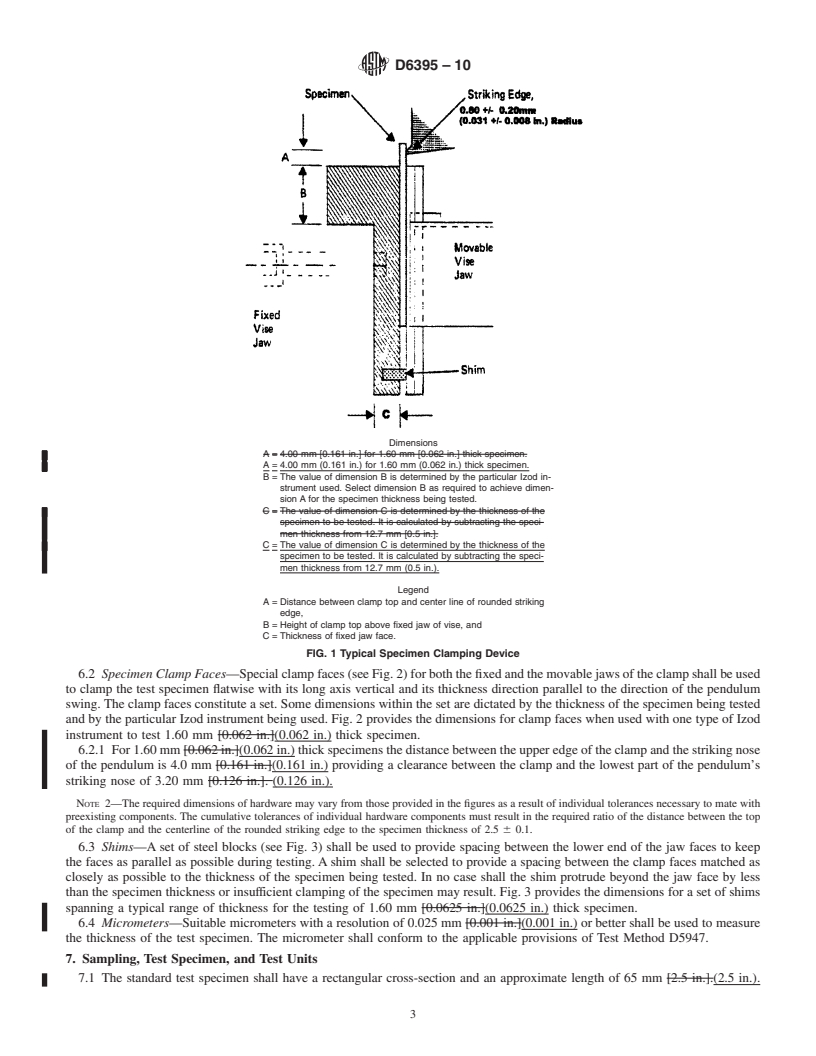
The pendulum shall be a standard Izod pendulum as described in Test Method D256. It shall be capable of delivering an energy of 2.71 ± 0.14 J (2.00 ± 0.10 ft.-lbf). Except as detailed in 10.5, this basic pendulum shall be used with all specimens that extract less than 85 % of the available energy. Higher energy pendulums or a basic pendulum to which weights are added to increase its available energy shall be used with specimens that require more energy to break. A series of energy levels such that each has twice the energy of the next lighter one will be found convenient. The striking nose of the pendulum shall contact one of the flat faces of the specimen at a specified distance above the clamp edge. The ratio of the distance between the top of the clamp and the centerline of the rounded striking edge to the specimen thickness shall be 2.5 ± 0.1.
The type of failure of each specimen tested shall be assigned one of the following categories:
Complete Break (C) A break in which the specimen is separated into two or more pieces.
Hinge Break (H)A nearly complete break in which there is little or no spring back when the free end is bent or displaced.
Partial Break (P)An incomplete break in which fracture extends through at least 50 % of the specimen thickness, and such that the free end can be bent with relatively little effort yet has considerable spring back.
Nonbreak (N)A result where there is no fracture or the fracture extends less than 50 % of the specimen thickness.
The value of this impact test is to determine the change in impact properties that may result from a mat...
SCOPE
1.1 The resistance of plastics to breakage by flexural shock may be determined by test methods such as those contained in Test Method D256. Specimens used in those test methods feature a milled notch to promote brittle fracture. The test specimens are struck by a pendulum with the depth dimension parallel to the direction of pendulum swing. This test method is differentiated from the others by its application to the assessment of the affect on impact resistance of changes in the surface of specimens resulting from weathering or other exposure. In this test method, specimens are struck by a pendulum with the depth dimension perpendicular to the direction of pendulum swing. Test Method D5420 may also be used to conduct testing of weathered or exposed specimens. This test method is differentiated from Gardner Impact by the smaller size of the specimens, which may result in substantially higher productivity of accelerated weathering instruments. Additionally, this test method provides multiple data from a single specimen for characterization of within specimen variability.
1.2 This test method describes the determination of the resistance of rigid plastic strip specimens to breakage or permanent deformation when one end of the specimen is subjected to an impact upon its wide face while the other end of the specimen is firmly clamped.
1.3 This test method is applicable to specimens of 1.60 mm (0.0625 in.) thickness. However, the limits of applicability of the test are not sharply defined, and specimens having other dimensions may frequently be used. For specimens of thicknesses other than 1.60 mm (0.0625 in.) the ratio of the distance between the top of the clamp and the centerline of the rounded striking edge to the specimen thickness must be 2.5 ± 0.1.
1.4 This test method measures the relative impact resistance of samples having approximately the same thickness. Normalization of the impact resistance to unit cross-se...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6395–10
Standard Test Method for
1
Flatwise Flexural Impact Resistance of Rigid Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6395; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* ness, and the importance of these effects in contributing to the
energy absorbed is greater for ductile than for brittle failure.
1.1 The resistance of plastics to breakage by flexural shock
1.5 This test method is used primarily as a means of
may be determined by test methods such as those contained in
assessing, for a series of samples, changes relative to a control
Test Method D256. Specimens used in those test methods
due to some treatment such as weathering or exposure to active
feature a milled notch to promote brittle fracture. The test
environments. It has been particularly useful as a sensitive
specimens are struck by a pendulum with the depth dimension
indicator of the development of surface cracks or a brittle
parallel to the direction of pendulum swing.This test method is
surface. The existence or formation of cracks in an inherently
differentiated from the others by its application to the assess-
brittle surface produces marked lowering of impact strength
ment of the affect on impact resistance of changes in the
when that surface is the one subjected to tension in the test.
surface of specimens resulting from weathering or other
1.6 This test method is not generally applicable to materials
exposure. In this test method, specimens are struck by a
such as elastomers or nonrigid plastics in which there is no
pendulum with the depth dimension perpendicular to the
fracture, permanent deformation, or other change due to
direction of pendulum swing. Test Method D5420 may also be
yielding in flexure. However, it may be desirable to test such
used to conduct testing of weathered or exposed specimens.
materials as file samples to establish reference points when the
This test method is differentiated from Gardner Impact by the
test is applied as described in 1.5.
smallersizeofthespecimens,whichmayresultinsubstantially
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
higher productivity of accelerated weathering instruments.
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
Additionally, this test method provides multiple data from a
only.
single specimen for characterization of within specimen vari-
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ability.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.2 This test method describes the determination of the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
resistance of rigid plastic strip specimens to breakage or
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
permanent deformation when one end of the specimen is
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
subjected to an impact upon its wide face while the other end
of the specimen is firmly clamped.
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.3 This test method is applicable to specimens of 1.60 mm
2. Referenced Documents
(0.0625 in.) thickness. However, the limits of applicability of
2
the test are not sharply defined, and specimens having other
2.1 ASTM Standards:
dimensions may frequently be used. For specimens of thick-
D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
nesses other than 1.60 mm (0.0625 in.) the ratio of the distance
Impact Resistance of Plastics
between the top of the clamp and the centerline of the rounded
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
striking edge to the specimen thickness must be 2.5 6 0.1.
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
1.4 This test method measures the relative impact resistance
D5420 Test Method for Impact Resistance of Flat, Rigid
of samples having approximately the same thickness. Normal-
Plastic Specimen by Means of a Striker Impacted by a
izationoftheimpactresistancetounitcross-sectionalareaonly
Falling Weight (Gardner Impact)
partly compensates for the effects of specimen thickness
D5947 Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid
variation because, at the fixed cantilever length, the ratio of
Plastics Specimens
shear stress to tensile stress in bending increases with thick-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
2
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published April 2010. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D6395–05 Designation:D6395–10
Standard Test Method for
1
Flatwise Flexural Impact Resistance of Rigid Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6395; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 The resistance of plastics to breakage by flexural shock may be determined by test methods such as those contained in Test
Method D256. Specimens used in those test methods feature a milled notch to promote brittle fracture. The test specimens are
struck by a pendulum with the depth dimension parallel to the direction of pendulum swing.This test method is differentiated from
the others by its application to the assessment of the affect on impact resistance of changes in the surface of specimens resulting
from weathering or other exposure. In this test method, specimens are struck by a pendulum with the depth dimension
perpendiculartothedirectionofpendulumswing.TestMethodD5420mayalsobeusedtoconducttestingofweatheredorexposed
specimens. This test method is differentiated from Gardner Impact by the smaller size of the specimens, which may result in
substantially higher productivity of accelerated weathering instruments.Additionally, this test method provides multiple data from
a single specimen for characterization of within specimen variability.
1.2 This test method describes the determination of the resistance of rigid plastic strip specimens to breakage or permanent
deformation when one end of the specimen is subjected to an impact upon its wide face while the other end of the specimen is
firmly clamped.
1.3 This test method is applicable to specimens of 1.60 mm [0.0625 in.](0.0625 in.) thickness. However, the limits of
applicability of the test are not sharply defined, and specimens having other dimensions may frequently be used. For specimens
of thicknesses other than 1.60 mm [0.0625 in.](0.0625 in.) the ratio of the distance between the top of the clamp and the centerline
of the rounded striking edge to the specimen thickness must be 2.5 6 0.1.
1.4 This test method measures the relative impact resistance of samples having approximately the same thickness.
Normalization of the impact resistance to unit cross-sectional area only partly compensates for the effects of specimen thickness
variation because, at the fixed cantilever length, the ratio of shear stress to tensile stress in bending increases with thickness, and
the importance of these effects in contributing to the energy absorbed is greater for ductile than for brittle failure.
1.5 This test method is used primarily as a means of assessing, for a series of samples, changes relative to a control due to some
treatment such as weathering or exposure to active environments. It has been particularly useful as a sensitive indicator of the
development of surface cracks or a brittle surface. The existence or formation of cracks in an inherently brittle surface produces
marked lowering of impact strength when that surface is the one subjected to tension in the test.
1.6 This test method is not generally applicable to materials such as elastomers or nonrigid plastics in which there is no fracture,
permanent deformation, or other change due to yielding in flexure. However, it may be desirable to test such materials as file
samples to establish reference points when the test is applied as described in 1.5.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in bracketsparentheses are for information
only.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE1—There is no equivalent or similar ISO standard. 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties.
Current edition approved Nov.April 1, 2005.2010.
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.