ASTM A769/A769M-05
(Specification)Standard Specification for Carbon and High-Strength Electric Resistance Forge-Welded Steel Structural Shapes
Standard Specification for Carbon and High-Strength Electric Resistance Forge-Welded Steel Structural Shapes
ABSTRACT
This specification covers carbon and high-strength steel shapes of structural quality manufactured by the electric resistance forge-welding process from coils. The specimens shall be established by the steel supplier, shape manufacturer, and shape purchaser of the materials. Specimens shall conform to the required chemical compositions of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur and silicon. Specimens shall undergo tension tests, peel tests and tee tension tests and shall conform to the required values of tensile strength, yield point, and elongation.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers carbon and high-strength steel shapes of structural quality manufactured by the electric-resistance forge-welding process from coils.
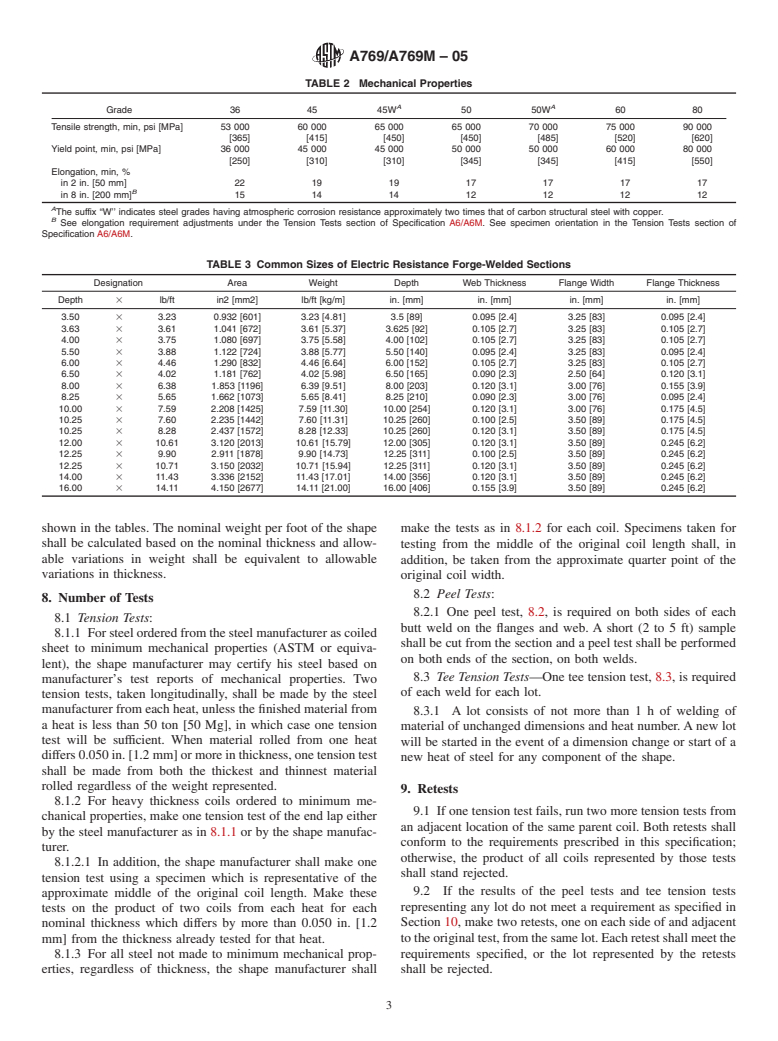
1.2 The size range covered is described in nominal dimensions for columns, beams, and tees.Size Range, in. (mm)Web thickness0.060 to 0.375 [1.5 to 10] Flange thickness0.060 to 0.500 [1.5 to 12.7] Overall depth 2.00 to 24.00 [50 to 600] Flange width 0.50 to 12.00 [12.7 to 300]
1.3 These shapes are intended for two classes of application:
1.3.1 Class 1 General structural use where static loading predominates.
1.3.2 Class 2Structural use where fatigue loading occurs and is a principal design consideration. Note 1Caution-Because of the absence of smooth, integral, large radius fillets at the junctions of the webs and the flanges (see Fig. 1), fatigue limits of resistance forge-welded shapes in torsion, lateral loading, and flexure are usually lower than those for hot-rolled shapes of similar size and material. Users should consult shape manufacturers for recommended values of fatigue limits for each specific use, material, and size in cases where dynamic loading is a principal design consideration.
1.4 When the steel is to be welded, it is presupposed that a welding procedure suitable for the grade of steel and intended use or service will be utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specification A 6/A 6M for information on weldability.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents. Therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this specification.
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section , of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A769/A769M – 05
Standard Specification for
Carbon and High-Strength Electric Resistance Forge-
1
Welded Steel Structural Shapes
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA769/A769M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
test methods portion, Section 10, of this specification: This
1.1 This specification covers carbon and high-strength steel
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
shapes of structural quality manufactured by the electric-
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
resistance forge-welding process from coils.
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
1.2 The size range covered is described in nominal dimen-
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
sions for columns, beams, and tees.
tions prior to use.
Size Range, in. (mm)
Web thickness 0.060 to 0.375 [1.5 to 10]
2. Referenced Documents
Flange thickness 0.060 to 0.500 [1.5 to 12.7]
Overall depth 2.00 to 24.00 [50 to 600] 2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Flange width 0.50 to 12.00 [12.7 to 300]
A6/A6M SpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforRolled
1.3 These shapes are intended for two classes of applica-
Structural Steel Bars, Plates, Shapes, and Sheet Piling
tion:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
1.3.1 Class 1— General structural use where static loading
of Steel Products
predominates.
A568/A568M Specification for Steel, Sheet, Carbon, Struc-
1.3.2 Class 2—Structural use where fatigue loading occurs
tural, and High-Strength, Low-Alloy, Hot-Rolled and
and is a principal design consideration.
Cold-Rolled, General Requirements for
A700 PracticesforPackaging,Marking,andLoadingMeth-
ods for Steel Products for Shipment
NOTE 1—Caution—Because of the absence of smooth, integral, large
radius fillets at the junctions of the webs and the flanges (see Fig. 1), 2.2 American Welding Society Standard:
3
fatigue limits of resistance forge-welded shapes in torsion, lateral loading,
AWS Specification D1.1 Structural Welding Code
and flexure are usually lower than those for hot-rolled shapes of similar
size and material. Users should consult shape manufacturers for recom- 3. Ordering Information
mended values of fatigue limits for each specific use, material, and size in
3.1 Orders for material under this specification should
cases where dynamic loading is a principal design consideration.
include the following, as required, to describe the desired
1.4 When the steel is to be welded, it is presupposed that a
material adequately:
welding procedure suitable for the grade of steel and intended
3.1.1 Quantity (total number of feet (metres) or lengths),
use or service will be utilized. See Appendix X3 of Specifica-
3.2 ASTM designation and year of issue, grade, and class,
tion A6/A6M for information on weldability.
3.3 Shape and size,
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
3.4 Length of each piece,
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
3.5 Information on intended application,
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
3.6 Other special requirements, and
system are not exact equivalents. Therefore, each system must
3.7 Required certification and test reports.
be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in nonconformance with this specifi-
cation.
1 2
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
A01.02 on Structural Steel for Bridges, Buildings, Rolling Stock and Ships. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2005. Published September 2005. Originally the ASTM website.
3
Available fromAmerican Welding Society, 550 N. W. LaJeune Rd., Miami, FL
approved in 1979. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as A769/A769M – 00.
33135.
DOI: 10.1520/A0769_A0769M-05.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A769/A769M – 05
FIG. 1 Appearance of Peel Test Criteria
A
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
4. Materials and Manufacture General Limitations, %
Carbon 0.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.