ASTM D6895-03e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Rotational Viscosity of Heavy Duty Diesel Drain Oils at 100°C
Standard Test Method for Rotational Viscosity of Heavy Duty Diesel Drain Oils at 100°C
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the rotational viscosity and the shear thinning properties of heavy duty diesel engine drain oils at 100C, in the shear rate range of approximately 10 to 300 s-1, in the shear stress range of approximately 0.1 to 10 Pa and the viscosity range of approximately 12 to 35 mPas. Rotational viscosity values can be compared at a shear rate of 100 s-1 by this test method.,
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
e1
Designation:D6895–03
Standard Test Method for
Rotational Viscosity of Heavy Duty Diesel Drain Oils at
1
100°C
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6895; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
e NOTE—Added a research report footnote to Section 15 editorially in March 2006.
c
1. Scope
shearstress 5 b~shearrate! (1)
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the rota-
ln~shearstress!5ln b 1 cln~shearrate! (2)
tionalviscosityandtheshearthinningpropertiesofheavyduty
3.1.1.1 Discussion—A rate index of c = 1 signifies Newto-
diesel engine drain oils at 100°C, in the shear rate range of
nian fluid behavior. Values less than one indicate increasing
-1
approximately 10 to 300 s , in the shear stress range of 3
non-Newtonian, shear thinning behavior.
approximately 0.1 to 10 Pa and the viscosity range of approxi-
3.1.2 rotational viscosity—the viscosity obtained by use of
mately 12 to 35 mPa·s. Rotational viscosity values can be
this test method.
-1 ,
23
compared at a shear rate of 100 s by this test method.
3.1.3 VIS100 DEC—rotationalviscosityatshearrateof100
-1
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
s , decreasing shear stress or shear rate sweep.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.4 VIS100 INC—rotational viscosity at shear rate of 100
-1
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
s , increasing shear stress or shear rate sweep.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. 4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The sample is placed in a controlled stress or controlled
2. Referenced Documents
shear rate rheometer/viscometer at 100°C. The sample is
4
-1
2.1 ASTM Standards:
presheared at 10 s for 30 s followed by heating at 100°C for
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and -1
10 min.An increasing shear rate (approximately 10 to 300 s )
Petroleum Products
or shear stress (0.1 to 10 Pa) sweep is run followed by a
D5967 TestMethodforEvaluationofDieselEngineOilsin
decreasing sweep. The rotational viscosity for each step
T-8 Diesel Engine -1
(increasing and decreasing) at 100 s shear rate is interpolated
D6299 Practice forApplying Statistical QualityAssurance
from the viscosity versus shear rate data table. The rate index,
Techniques to Evaluate Analytical Measurement System
as a measure of shear thinning, is calculated from a plot of ln
Performance
(shear stress) versus ln (shear rate).
3. Terminology
5. Significance and Use
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
5.1 Rotationalviscositymeasurementsallowthedetermina-
3.1.1 rate index—the exponent, c, in these expressions
tionofthenon-Newtonian,shearthinningpropertyofdrainoil.
relating shear rate and shear stress:
Rotational viscosity values can be compared at a shear rate of
-1 2,3
100 s by this test method.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
6. Apparatus
PetroleumProductsandLubricantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
6.1 This test method uses rheometers/viscometers of the
D02.07 on Flow Properties.
Current edition approved May 10, 2003. Published July 2003.
controlled stress or controlled rate mode of operation. The test
2
Selby, K., “Rheology of Soot–thickened Diesel Engine Oils,” SAE 981369,
method requires the use of cone and plate or concentric
May 1998.
3 cylinder measuring geometries capable of operating in the
George, H. F., Bardasz, E.A., and Soukup, B., “Understanding SMOTthrough
range of approximately 0.1 to 10 Pa for shear stress and 10 to
Designed Experimentation Part 3: An Improved approach to Drain Oil Viscosity
-1
Measurements—Rotational Rheology,” SAE 97692, May 1997.
300s forshearrate.Instrumentdataloggingorsoftwareshall
4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
be capable of delivering shear stress versus shear rate data and
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
viscosity versus shear rate data in tabular form. Temperature
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. shall be controlled to 100 6 0.2°C at equilibrium. Some
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact ASTM
International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
D6895–03
rheometers ha
...







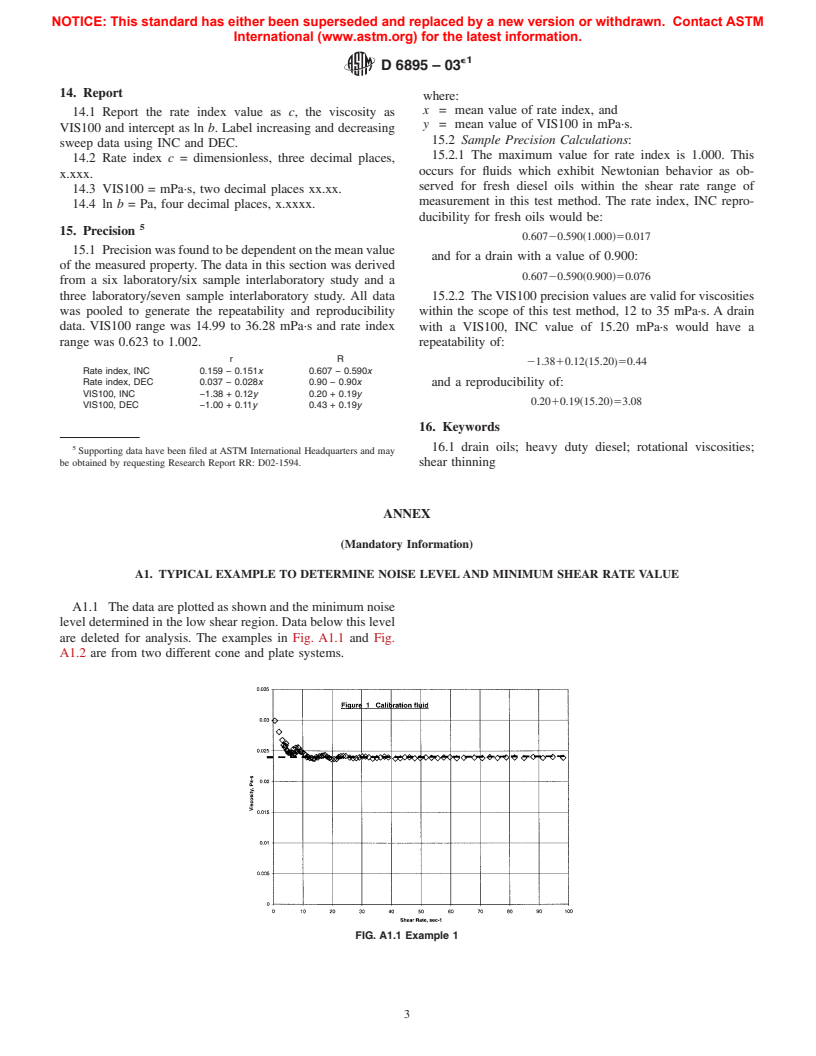
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.