ASTM B338-17(2021)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Titanium and Titanium Alloy Tubes for Condensers and Heat Exchangers
Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Titanium and Titanium Alloy Tubes for Condensers and Heat Exchangers
ABSTRACT
This specification covers 28 grades of seamless and welded titanium alloy tubes for surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers. Seamless tube shall be made from hollow billet by any cold reducing or cold drawing process that will yield a product meeting the requirements prescribed. Welded tube shall be made from flat-rolled product by an automatic arc-welding process. The welded tube shall be sufficiently cold worked to final size in order to transform the cast weld microstructure into a typical equiaxed microstructure in the weld upon subsequent heat treatment. The titanium shall conform to the chemical requirements prescribed. The room temperature tensile properties of the tube in the condition normally supplied shall conform to the requirements prescribed. Tubing shall withstand, without cracking, flattening under a load applied gradually at room temperature until the distance between the load platens is not more than the required height. Welded tube shall be subjected to a reverse flattening test in accordance with supplement II of test methods and definitions A 370. Welded tubing shall be tested using both a non-destructive electromagnetic test and an ultrasonic test method. Seamless and welded/cold worked tubing shall be tested using an ultrasonic test method. Welded tubing shall be tested with a hydrostatic or pneumatic test method. Seamless tubing shall be tested with an electromagnetic or hydrostatic or pneumatic test method.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers the requirements for 28 grades of titanium and titanium alloy tubing intended for surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers, as follows:
1.1.1 Grade 1—UNS R50250. Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.2 Grade 2—UNS R50400. Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.2.1 Grade 2H—UNS R50400. Unalloyed titanium (Grade 2 with 58 ksi (400 MPa) minimum UTS),
1.1.3 Grade 3—UNS R50550. Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.4 Grade 7—UNS R52400. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
1.1.4.1 Grade 7H—UNS R52400. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium (Grade 7 with 58 ksi (400 MPa) minimum UTS),
1.1.5 Grade 9—UNS R56320. Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium),
1.1.6 Grade 11—UNS R52250. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
1.1.7 Grade 12—UNS R53400. Titanium alloy (0.3 % molybdenum, 0.8 % nickel),
1.1.8 Grade 13—UNS R53413. Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
1.1.9 Grade 14—UNS R53414. Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
1.1.10 Grade 15—UNS R53415. Titanium alloy (0.5 % nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
1.1.11 Grade 16—UNS R52402. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.11.1 Grade 16H—UNS R52402. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium (Grade 16 with 58 ksi (400 MPa) minimum UTS),
1.1.12 Grade 17—UNS R52252. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.13 Grade 18—UNS R56322. Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium) plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1.14 Grade 26—UNS R52404. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.14.1 Grade 26H—UNS R52404. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium (Grade 26 with 58 ksi (400 MPa) minimum UTS),
1.1.15 Grade 27—UNS R52254. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.16 Grade 28—UNS R56323. Titanium alloy (3 % aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium) plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.17 Grade 30—UNS R53530. Titanium alloy (0.3 % cobalt, 0.05 % palladium),
1.1.18 Grade 31—UNS R53532. Titanium alloy (0.3 % cobalt, 0.05 % palladium),
1.1.19 Grade 33—UNS R53442. Titanium alloy (0.4 % nickel, 0.015 % palladium, 0.025 % ruthenium, 0.15 % chromium),
1.1.20 Grade 34—UNS R53445. Titanium alloy (0.4 % nickel, 0.015 % palladium, 0.025 % ruthenium, 0.15 % chromium),
1.1.21 Grade 35—UNS R56340. Titanium alloy (4.5 % aluminum, 2 % molybdenum, 1.6 % vanadium, 0.5 % iron, 0.3 % silicon),
1.1.22 Grade 36—UNS R58450. Titanium alloy (45 % niobium),
1.1.23 Grade 37—UNS R5281...
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:B338 −17 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Specification for
Seamless and Welded Titanium and Titanium Alloy Tubes
for Condensers and Heat Exchangers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B338; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 1.1.12 Grade 17—UNS R52252. Unalloyed titanium plus
0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for 28
1.1.13 Grade 18—UNS R56322. Titanium alloy (3 %
grades of titanium and titanium alloy tubing intended for
aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium) plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
surface condensers, evaporators, and heat exchangers, as fol-
1.1.14 Grade 26—UNS R52404. Unalloyed titanium plus
lows:
0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.1 Grade 1—UNS R50250. Unalloyed titanium,
1.1.14.1 Grade 26H—UNS R52404. Unalloyed titanium
1.1.2 Grade 2—UNS R50400. Unalloyed titanium,
plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium (Grade 26 with 58 ksi (400
1.1.2.1 Grade 2H—UNS R50400. Unalloyed titanium
MPa) minimum UTS),
(Grade 2 with 58 ksi (400 MPa) minimum UTS),
1.1.15 Grade 27—UNS R52254. Unalloyed titanium plus
1.1.3 Grade 3—UNS R50550. Unalloyed titanium,
0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.4 Grade 7—UNS R52400. Unalloyed titanium plus 0.12
1.1.16 Grade 28—UNS R56323. Titanium alloy (3 %
to 0.25 % palladium,
aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium) plus 0.08 to 0.14 % ruthenium,
1.1.4.1 Grade 7H—UNS R52400. Unalloyed titanium plus
1.1.17 Grade 30—UNS R53530. Titanium alloy (0.3 %
0.12 to 0.25 % palladium (Grade 7 with 58 ksi (400 MPa)
cobalt, 0.05 % palladium),
minimum UTS),
1.1.18 Grade 31—UNS R53532. Titanium alloy (0.3 %
1.1.5 Grade 9—UNS R56320. Titanium alloy (3 %
cobalt, 0.05 % palladium),
aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium),
1.1.19 Grade 33—UNS R53442. Titanium alloy (0.4 %
1.1.6 Grade 11—UNS R52250. Unalloyed titanium plus
nickel, 0.015 % palladium, 0.025 % ruthenium, 0.15 %
0.12 to 0.25 % palladium,
chromium),
1.1.7 Grade 12—UNS R53400. Titanium alloy (0.3 %
1.1.20 Grade 34—UNS R53445. Titanium alloy (0.4 %
molybdenum, 0.8 % nickel),
nickel, 0.015 % palladium, 0.025 % ruthenium, 0.15 %
1.1.8 Grade 13—UNS R53413. Titanium alloy (0.5 %
chromium),
nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
1.1.21 Grade 35—UNS R56340. Titanium alloy (4.5 %
1.1.9 Grade 14—UNS R53414. Titanium alloy (0.5 %
aluminum, 2 % molybdenum, 1.6 % vanadium, 0.5 % iron,
nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
0.3 % silicon),
1.1.10 Grade 15—UNS R53415. Titanium alloy (0.5 %
1.1.22 Grade 36—UNS R58450. Titanium alloy (45 %
nickel, 0.05 % ruthenium),
niobium),
1.1.11 Grade 16—UNS R52402. Unalloyed titanium plus
1.1.23 Grade 37—UNS R52815. Titanium alloy (1.5 %
0.04 to 0.08 % palladium,
aluminum),
1.1.11.1 Grade 16H—UNS R52402. Unalloyed titanium
1.1.24 Grade 38—UNS R54250. Titanium alloy (4 %
plus 0.04 to 0.08 % palladium (Grade 16 with 58 ksi (400
aluminum, 2.5 % vanadium, 1.5 % iron), and
MPa) minimum UTS),
1.1.25 Grade 39—UNS R53390. Titanium alloy (0.25 %
iron, 0.4 % silicon).
NOTE 1—H grade material is identical to the corresponding numeric
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B10 on
grade (that is, Grade 2H = Grade 2) except for the higher guaranteed
Reactive and Refractory Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee B10.01 on Titanium. minimum UTS, and may always be certified as meeting the requirements
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2021. Published December 2021. Originally of its corresponding numeric grade. Grades 2H, 7H, 16H, and 26H are
ɛ1
approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as B338 – 17 . DOI:
intended primarily for pressure vessel use.
10.1520/B0338-17R21.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications, see related Specifi-
cation SB-338 in Section II of that Code. as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
B338−17 (2021)
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only the product of an 8 h period for final continuous anneal, or to
and are not considered standard. a single furnace load for final batch anneal.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.4 sponge, n—a lot shall consist of a single blend
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
produced at one time.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.5 weld fittings, n—definition is to be mutually agreed
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
upon between manufacturer and the purchaser.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4. Ordering Information
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 Orders for material to this specification shall include the
following information, as required:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1.1 Quantity,
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
of Steel Products 4.1.2 Grade number (Section 1),
4.1.3 Diameter and wall thickness (Note 2) (Section 12),
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
[Metric] E0008_E0008M
4.1.4 Length (Section 12),
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
4.1.5 Method of manufacture and finish (Sections5 and 13),
Determine Conformance with Specifications
4.1.6 Restrictive chemistry, if desired (Section 6 and
E213 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of Metal Pipe and
Table 1),
Tubing
4.1.7 Product analysis, if desired (Section 7 and Table 2),
E426 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy Current) Examina-
4.1.8 Special mechanical properties, if desired (Section 8
tion of Seamless and Welded Tubular Products, Titanium,
and Table 3),
Austenitic Stainless Steel and Similar Alloys
4.1.9 Nondestructive tests (Section 11),
E499 Practice for Leaks Using the Mass Spectrometer Leak
4.1.10 Packaging (Section 23),
Detector in the Detector Probe Mode
4.1.11 Inspection (Section 17), and
E1409 Test Method for Determination of Oxygen and Nitro-
gen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by Inert Gas Fusion 4.1.12 Certification (Section 21).
E1447 Test Method for Determination of Hydrogen in Tita-
NOTE 2—Tube is available to specified outside diameter and wall
nium and Titanium Alloys by Inert Gas Fusion Thermal
thickness.Average OD and wall are the standard. Maximum or minimum
Conductivity/Infrared Detection Method
OD or wall should be stated.
E1941 Test Method for Determination of Carbon in Refrac-
4.2 Optional supplementary requirements are provided and,
tory and Reactive Metals andTheirAlloys by Combustion
when one or more of these are desired, each shall be so stated
Analysis
in the order.
E2371 Test Method for Analysis of Titanium and Titanium
Alloys by Direct Current Plasma and Inductively Coupled
5. Materials and Manufacture
Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry (Performance-
Based Test Methodology) 5.1 Seamless tube shall be made from hollow billet by any
E2626 Guide for Spectrometric Analysis of Reactive and cold reducing or cold drawing process that will yield a product
Refractory Metals (Withdrawn 2017) meetingtherequirementsofthisspecification.Seamlesstubeis
produced with a continuous periphery in all stages of manu-
3. Terminology
facturing operations.
3.1 Lot Definitions:
5.2 Welded tube shall be made from annealed, flat-rolled
3.1.1 castings, n—a lot shall consist of all castings produced
product by an automatic arc-welding process or other method
from the same pour.
of welding that will yield a product meeting the tensile
3.1.2 ingot, n—no definition required. requirements found in Table 3 of this specification. Welded
tubing shall be heat treated by at least a stress relief after
3.1.3 rounds, flats, tubes, and wrought powder metallurgical
forming and welding. Use of filler material is not permitted.
products (single definition, common to nuclear and non-
nuclear standards), n—a lot shall consist of a material of the
5.3 Welded/cold worked tube (WCS) shall be made from
same size, shape, condition, and finish produced from the same
welded tube manufactured as specified in 5.2.The welded tube
ingot or powder blend by the same reduction schedule and the
shall be sufficiently cold worked to final size in order to
same heat treatment parameters. Unless otherwise agreed
transform the cast weld microstructure into a typical equiaxed
between manufacturer and purchaser, a lot shall be limited to
microstructure in the weld upon subsequent heat treatment.
The product shall meet the requirements for seamless tube of
this specification.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.4 Grades 9, 18 and 28, which, at the option of the
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
purchaser, can be furnished in either the annealed or the cold
the ASTM website.
worked and stress relieved condition, defined as at a minimum
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. temperature of 600°F (316°C) for not less than 30 min.
B338−17 (2021)
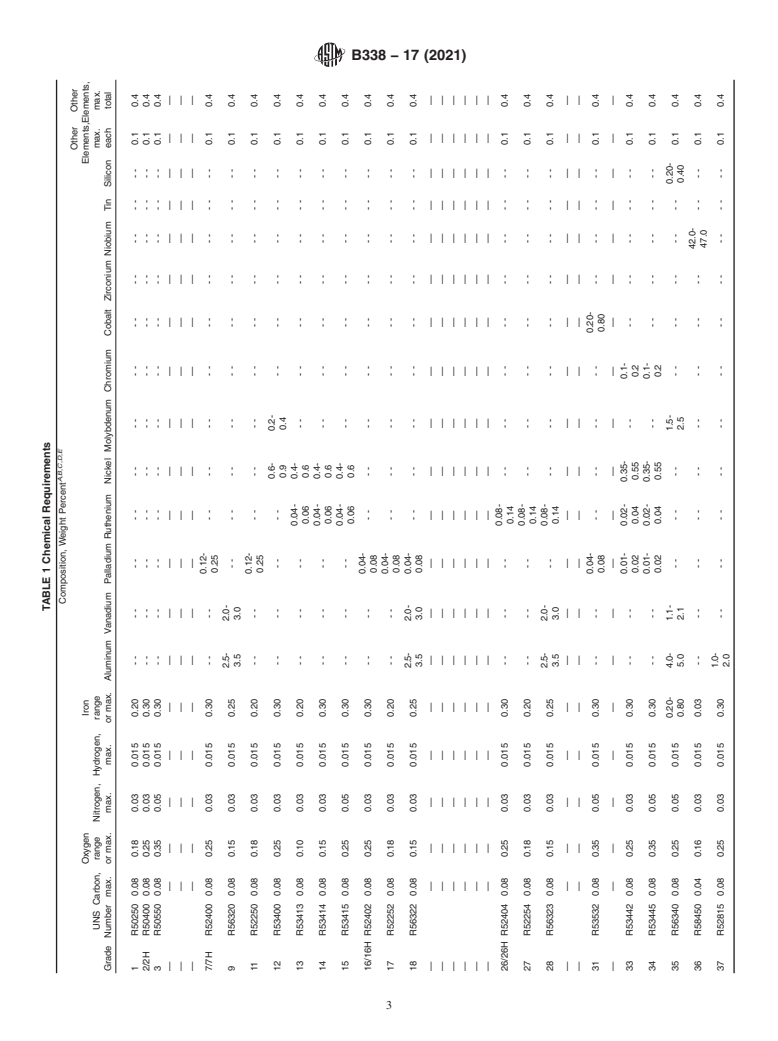
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
A,B,C,D,E
Composition, Weight Percent
Other Other
Oxygen Iron Elements,Elements,
UNS Carbon, range Nitrogen, Hydrogen, range max. max.
Grade Number max. or max. max. max. or max. Aluminum Vanadium Palladium Ruthenium Nickel Molybdenum Chromium Cobalt Zirconium Niobium Tin Silicon each total
1 R50250 0.08 0.18 0.03 0.015 0.20 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.1 0.4
2/2H R50400 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.015 0.30 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.1 0.4
3 R50550 0.08 0.35 0.05 0.015 0.30 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.1 0.4
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
0.12-
7/7H R52400 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.015 0.30 - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.25
2.5- 2.0-
9 R56320 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.015 0.25 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
3.5 3.0
0.12-
11 R52250 0.08 0.18 0.03 0.015 0.20 - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.25
0.6- 0.2-
12 R53400 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.015 0.30 - - - - - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.9 0.4
0.04- 0.4-
13 R53413 0.08 0.10 0.03 0.015 0.20 - - - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.06 0.6
0.04- 0.4-
14 R53414 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.015 0.30 - - - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.06 0.6
0.04- 0.4-
15 R53415 0.08 0.25 0.05 0.015 0.30 - - - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.06 0.6
0.04-
16/16H R52402 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.015 0.30 - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.08
0.04-
17 R52252 0.08 0.18 0.03 0.015 0.20 - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.08
2.5- 2.0- 0.04-
18 R56322 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.015 0.25 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
3.5 3.0 0.08
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
0.08-
26/26H R52404 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.015 0.30 - - - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.14
0.08-
27 R52254 0.08 0.18 0.03 0.015 0.20 - - - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.14
2.5- 2.0- 0.08-
28 R56323 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.015 0.25 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
3.5 3.0 0.14
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
0.04- 0.20-
31 R53532 0.08 0.35 0.05 0.015 0.30 - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.08 0.80
— — — — ———— — — — — — — — — — — — —
0.01- 0.02- 0.35- 0.1-
33 R53442 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.015 0.30 - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.02 0.04 0.55 0.2
0.01- 0.02- 0.35- 0.1-
34 R53445 0.08 0.35 0.05 0.015 0.30 - - - - -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.02 0.04 0.55 0.2
0.20- 4.0- 1.1- 1.5- 0.20-
35 R56340 0.08 0.25 0.05 0.015 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.80 5.0 2.1 2.5 0.40
42.0-
36 R58450 0.04 0.16 0.03 0.015 0.03 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- -- 0.1 0.4
47.0
1.0-
37 R52815 0.08 0.25 0.03 0.015 0.30 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
2.0
B338−17 (2021)
TABLE1 Continued
A,B,C,D,E
Composition, Weight Percent
Other Other
Oxygen Iron Elements,Elements,
UNS Carbon, range Nitrogen, Hydrogen, range max. max.
Grade Number max. or max. max. max. or max. Aluminum Vanadium Palladium Ruthenium Nickel Molybdenum Chromium Cobalt Zirconium Niobium Tin Silicon each total
0.20- 1.2- 3.5- 2.0-
38 R54250 0.08 0.03 0.015 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 0.1 0.4
0.30 1.8 4.5 3.0
0.15- 0.30-
39 R53390 0.08 0.15 0.03 0.015 —— — — — — — — — — — 0.1 0.4
0.40 0.50
A
At minimum, the analysis of samples from the top and bottom of the ingot shall be completed and reported for all elements listed for the respective grade in this table.
B
Final product hydrogen shall be reported. Ingot hydrogen need not be reported. Lower hydrogen may be obtained by negotiation with the manufacturer.
C
Single values are maximum. The percentage of titanium is determined by difference.
D
Other elements need not be reported unless the concentration level is greater than 0.1 % each, or 0.4 % total. Other elements may not be added intentionally. Other elements may be present in titanium or titanium
alloys in small quantities and are inherent to the manufacturing process. In titanium these elements typically include aluminum, vanadium, tin, chromium, molybdenum, niobium, zirconium, hafnium, bismuth, ruthenium,
palladium, yttrium, copper, silicon, cobalt, tantalum, nickel, boron, manganese, and tungsten.
E
The purchaser may, in the written purchase order, request analysis for specific elements not listed in this specification.
B338−17 (2021)
TABLE 2 Permissible Variations in Product Analysis
8. Tensile Requirements
%
8.1 The room temperature tensile properties of the tube in
Element
Maximum or Permissible Variation
the condition normally supplied shall conform to the require-
Specified Range in Product Analysis
ments prescribed in Table 3. Mechanical properties for condi-
Aluminum 0.5 to 2.5 ±0.20
tions other than those given in this table may be established by
Aluminum 2.5 to 3.5 ±0.40
Carbon 0.10 +0.02
agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser. (See
Chromium 0.1 to 0.2 ±0.02
Test Methods E8.)
Cobalt 0.2 t
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.