ASTM C919-98
(Practice)Standard Practice for Use of Sealants in Acoustical Applications
Standard Practice for Use of Sealants in Acoustical Applications
SCOPE
1.1 This practice is a guide for the use of sealants to reduce the sound transmission characteristics of interior walls, ceilings, and floors by proper application of sealants to joints, voids, and penetrations normally found in building construction.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 The committee with jurisdiction over this standard is not aware of any comparable standards published by other organizations.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C 919 – 98
Standard Practice for
Use of Sealants in Acoustical Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 919; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Housing, Section 4900.1
HUD Minimum Property Standard for Multi Family Hous-
1.1 This practice is a guide for the use of sealants to reduce
ing, Section 4910.1
the sound transmission characteristics of interior walls, ceil-
HUD Minimum Property Standard for Care Type Housing,
ings, and floors by proper application of sealants to joints,
Section 4920.1
voids, and penetrations normally found in building construc-
tion.
3. Significance and Use
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1 Construction utilizing lightweight walls and floors can
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
have undesirable sound transmission characteristics if care is
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
not taken to seal joints and voids that are common to this type
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
of construction. By sealing these penetrations the transmission
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
of sound can be diminished.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Sound Transmission Class
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1 The construction industry has adopted Sound Transmis-
C 570 Specification for Oil- and Resin-Base Caulking Com-
2 sion Class (STC) units (defined in Definitions C 634) to rate
pound for Building Construction
3 the sound barrier properties of walls, ceilings, and floors. The
C 634 Terminology Relating to Environmental Acoustics
2 STC is determined in accordance with Classification E 413.
C 834 Specification for Latex Sealants
2 The test data are obtained in accordance with Test Methods
C 920 Specification for Elastomeric Joint Sealants
E 90 or E 336.
E 90 Test Method for Laboratory Measurement of Airborne
Sound Transmission Loss of Building Partitions
NOTE 1—For example, The Department of Housing and Urban Devel-
E 336 Test Method for Measurement of Airborne Sound opment (DHUD) has issued the following three standards dealing with the
STC limitation in various housing units:
Insulation in Buildings
HUD Minimum Property Standard for One and Two Family Housing,
E 413 Classification for Rating Sound Insulation
Section 4900.1;
E 497 Practice for Installing Sound-Isolating Lightweight
HUD Minimum Property Standard for Multi Family Housing, Section
Partitions
4910.1; and
2.2 Federal Specifications:
HUD Minimum Property Standard for Care Type Housing, Section
TT-S-1657 (COM-NBS) Interim Federal Specification for
4920.1
Sealing Compound—Single Component, Butyl Rubber
5. Need to Seal Openings
Based, Solvent Release Type (for Buildings and Other
Type of Construction) 5.1 The effect of unsealed openings on the STC of partition
TT-C-598C (COM-NBS) Interim Federal Specification for walls is shown in Fig. 1. This chart also shows the improve-
Caulking Compound, Oil and Resin Base Type (for ment of the STC when openings are sealed. It should be
Building Construction) recognized for slit openings that the STC values may be
2.3 DHUD Standards: different from the STC value for a hole opening.
HUD Minimum Property Standards for One and Two Family 5.2 Fig. 2 shows examples of how sound travels through
openings in walls and how sealing may serve to minimize
sound transmission. Further examples may be found in Practice
E 497.
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-24 on Building
Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.20 on
6. Positioning of Sealants
General Sealant Standards.
Current edition approved Oct. 26, 1984. Published December 1984. Originally
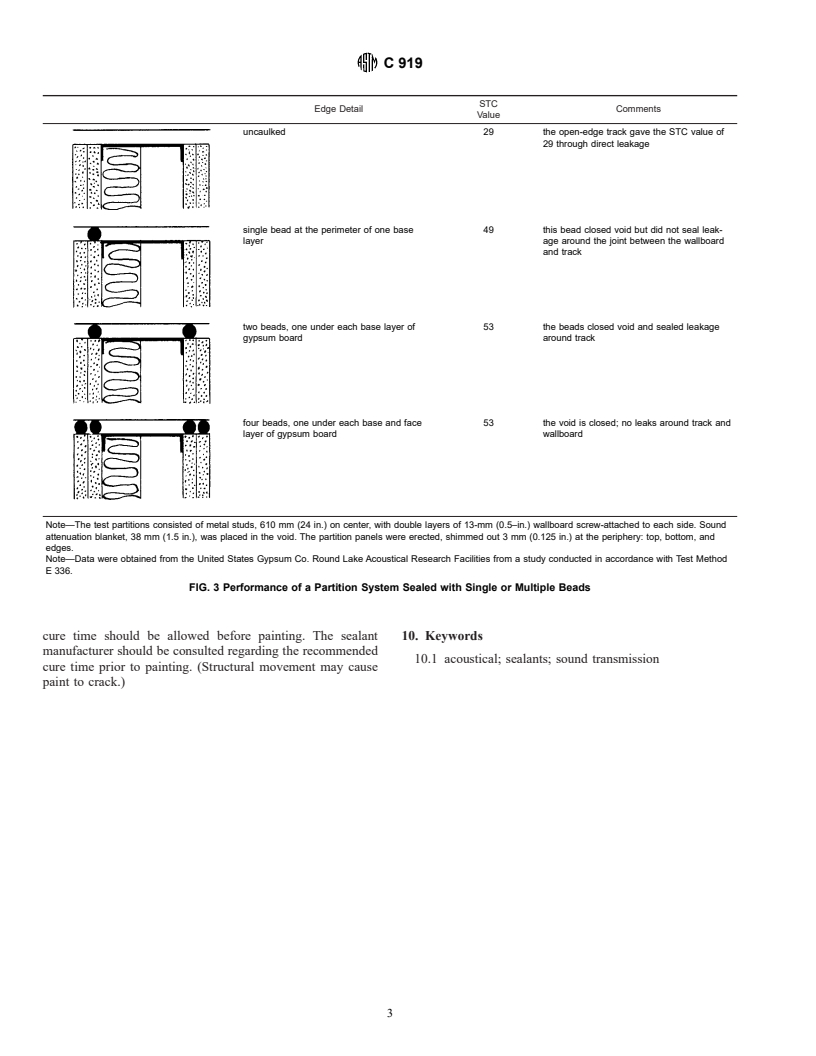
6.1 Fig. 3 illustrates placement of beads of sealant to
published as C 919 – 79. Last previous edition C 919 – 79.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.06.
4 5
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700 Available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing
Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS. Office, Washington, DC 20402.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C 919
that point is unnecessary.
7. Application Method of Gunnable Sealant
7.1 Fig. 4 shows typical sealant applications.
8. Types of Sealant for Acoustical Improvement
8.1 Preformed Sealants—Preformed sealants include gas-
keting, tapes, and preformed foams. Most of these materials are
effective only when the tolerances of the perimeter joints can
be accurately predicted and installed to those tolerances. Joint
sizes vary widely and preformed sealants may have difficulty in
maintaining a proper seal at all points with the constant
compression that is necessary to effect a seal. Preformed
sealants in the form of pads have proved to be effective for
sealing electric, telephone, and television jack boxes.
8.2 Gunnable Sealants—These sealants have the capacity of
conforming to the wide range of joint sizes
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.