ASTM D1881-97(2002)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Foaming Tendencies of Engine Coolants in Glassware
Standard Test Method for Foaming Tendencies of Engine Coolants in Glassware
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a simple glassware test for evaluating the tendency of engine coolants to foam under laboratory-controlled-conditions of aeration and temperature.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 7.2 and 7.4.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are approximate equivalents provided for information purposes only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
e1
Designation:D1881–97 (Reapproved 2002)
Standard Test Method for
Foaming Tendencies of Engine Coolants in Glassware
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1881; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
e NOTE—The address for Godax Laboratories in footnote 7 was updated editorially in June 2003.
1. Scope 3.1.2 eye, n—the appearance of foam free area on the
surface of the test coolant surrounded by a ring of foam
1.1 This test method covers a simple glassware test for
clinging to the cylinder walls.
evaluating the tendency of engine coolants to foam under
laboratory-controlled-conditions of aeration and temperature.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 Asolution of coolant andASTMType II water is blown
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
with air at a constant rate for 5 min, while maintained at a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
constant temperature of 88 6 1°C (190 6 2°F) by means of a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
suitable temperature bath. The volume of foam, and the time
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
for such foam to break, are measured.
warning statements, see 7.2 and 7.4.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
5. Significance and Use
standard. The values given in parentheses are approximate
5.1 The test method generally will distinguish coolants that
equivalents provided for information purposes only.
have a tendency to foam excessively from those that are
2. Referenced Documents suitable for further evaluation to determine performance in
actual service.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1176 Test Method for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous
NOTE 1—In use, the foaming tendency of a coolant solution may be
Solutions of Engine Coolants or Antirusts for Testing increased by service aging or contamination. A properly functioning
pressure cap will tend to suppress foaming in coolant solutions.
Purposes
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
6. Apparatus
D3585 Specification for ASTM Reference Fluid for Cool-
6.1 Container—A 500-mL graduated container of heat-
ant Tests
resistant glass, having a diameter of 45 to 50 mm and a length
E1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
of 380 mm.
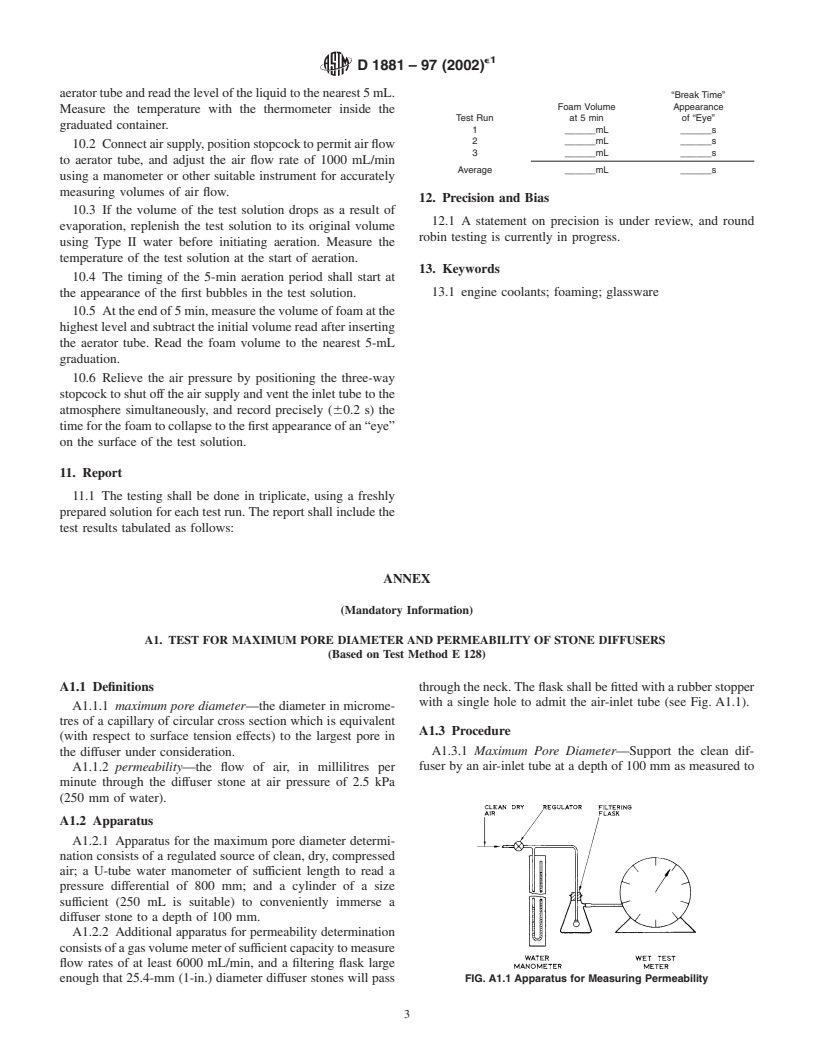
E128 Test Method for Maximum Pore Diameter and Per-
6.2 Temperature Bath—A heat resistant glass container
meability of Rigid Porous Filters for Laboratory Use
largeenoughtopermitimmersionofthegraduatedcontainerat
3. Terminology
least to the 350 mL graduation mark. A 4000-mL beaker is
satisfactory.
3.1 Definitions:
6.3 Heat Source—Any heating system capable of maintain-
3.1.1 break time, n—the time required for the foam to
ing a uniform bath temperature 61°C (62°F). A750-watt
collapse (after the air supply has been shut off) to the first
electric hot-plate is satisfactory.
appearance of an “eye” on the surface of the test solution.
6.4 Aerator Tube—A 25.4-mm (1-in.) diameter spherical
gas-diffuser stone made of fused crystalline alumina grain
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D15 on Engine
which meets the following specifications when tested in
Coolants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D15.06 on Glassware
accordance with the method given in Annex A1:
Performance Tests.
Current edition approved May 10, 1997. Published June 1998. Originally
Maximum pore diameter, µm Not greater than 80
published as D1881–61T. Last previous edition D1881–96.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.05.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01.
4 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03. For information on aerator supplier and specifications contactASTM Subcom-
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. mittee D15.06 through ASTM International Headquarters.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
e1
D1881–97 (2002)
Nochromix and alcoholic sodium (potassium) hydroxide are
Permeability at a pressure of 2.45 kPa, mL of air/min 3000 to 6400
common acid and base cleaning baths, respectively.
6.5 Thermometer—AnASTMPartialImmersionThermom-
(Warning—The cleaning baths are strong oxidants and strong
eter having a range from −20 to +150°C (0 to 302°F) and
acid and base, respectively.Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and
conforming to the requirements for Thermometer 1F as pre-
clothing. Do not breathe vapor. Handle in a fume hood.)
scribed in Specification E1.
6.6 Air Supply—A clean and dry source, free from grease
8. Test Solution
and other contaminants, capable of maintaining the prescribed
8.1 A33% by volume solution of reference coolant (Speci-
flow rate through the diffuser stone.
fication D3585 test coolant without antifoam) shall be pre-
6.7 Timer—Astopwatchorsuitabletimingdevice,accurate
pared with the proper quantity of Type II water.
to 60.2 s.
8.2 Prepare a 33% by volume solution of the coolant to be
6.8 Vent—Athree-way stopcock inserted in the metered air
tested with Type II water. Use the same glassware used to
supply line immediately ahead of the aerator tube.
preparethereferencecoolanttestsolution.Rinsetheglassware
6.9 Typical Assembly Set-Up—A typical apparatus using a
withTypeIIwaterbetweenpreparations.Additiveconcentrates
hot-plate heat source is shown in Fig. 1.
shall be diluted with Type II water to recommended use
concentration. Preparation of the sample shall be done in
7. Materials and Reagents
accordance with treatment of mixtures described in Test
7.1 Purity of Water—Unlessotherwiseindicated,references
MethodD1176.Thus,anyinsolublematerialswillbeincluded
to water means reagent water as defined by Type II of
in the representative sample.
Specification D1193.
7.2 Acetone, for flushing and drying the test equipment.
9. Test Conditions
(Warning—Acetone is extremely flammable.)
9.1 Test Temperature—Thetemperaturebathshallbekeptat
7.3 Specification D 3585 Test Coolant—Unless otherwise
indicated, references to the reference test coolant means a constant volume (350 to 375 mL mark of the graduated
cylinder) throughout the test. The test solution shall be main-
Specification D3585 coolant prepared without antifoam (Plu-
ronic L-61) as defined in Specification D3585. tained at 88 6 1°C (190 6 2°F) throughout. This temperature
is suitable for both high-boiling and low-boiling coolants.
7.4 Cleaning Bath—Refers to an acid or base cleaning
solution used to clean glassware between tests. The choice of 9.2 Aeration Rate—The aeration rate shall be 1000 6 25
mL/min.
cleaning baths depends on individual needs. For example,
9.3 Number of Tests—The reference coolant shall be tested
to determine if the glassware and testing equipment is con-
taminatedwithresiduedefoamer.Ifthereferencec
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.