ASTM D2158-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
Standard Test Method for Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the extraneous materials weathering above 38°C that are present in liquefied petroleum gases.
1.2 Liquefied petroleum gases that contain alcohols to enhance their anti-icing behaviour can give erroneous results by this test method.
1.3 The result can be expressed in terms of measured volumes or indices derived from these volumes. In either case, the test method provides an indication of the quantity and nature of materials in the product that are substantially less volatile than the liquefied petroleum gas hydrocarbons.
1.4 Although this test method has been used to verify cleanliness and lack of heavy contaminants in propane for many years, it may not be sensitive enough to protect some equipment from operational problems or increased maintenance. A more sensitive test, able to detect lower levels of dissolved contaminants, may be required for some applications.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see 6.9.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D 2158 – 02
Designation: 317/95
Standard Test Method for
1
Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2158; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 Other Documents:
5
IP Appendix A
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the extra-
neous materials weathering above 38°C that are present in
3. Terminology
liquefied petroleum gases.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 Liquefied petroleum gases that contain alcohols to
3.1.1 residue—the volume, measured to the nearest 0.05
enhance their anti-icing behaviour can give erroneous results
mL, of the residual material boiling above 38°C resulting from
by this test method.
the evaporation of 100 mL of sample under the specified
1.3 The result can be expressed in terms of measured
conditions of this test method.
volumes or indices derived from these volumes. In either case,
3.1.2 R Number —the residue multiplied by 200.
the test method provides an indication of the quantity and
3.1.3 oil stain observation—the volume of solvent-residue
nature of materials in the product that are substantially less
mixture required to yield an oil ring that persists for 2 min
volatile than the liquefied petroleum gas hydrocarbons.
under specified conditions on a prescribed filter paper.
1.4 Although this test method has been used to verify
3.1.4 O Number —10 divided by the oil stain observation.
cleanliness and lack of heavy contaminants in propane for
many years, it may not be sensitive enough to protect some
4. Summary of Test Method
equipment from operational problems or increased mainte-
4.1 A 100-mL sample of liquefied petroleum gas is weath-
nance. A more sensitive test, able to detect lower levels of
ered in a 100-mL centrifuge tube. The volume of residue
dissolved contaminants, may be required for some applica-
remaining at 38°C is measured and recorded as is also the
tions.
appearance of a filter paper to which the residue has been
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
added in measured increments.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Significance and Use
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 Control over the residue content (required by Specifica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
tion D 1835) is of considerable importance in end-use appli-
precautionary statements, see 6.9.
cations. In liquid feed systems residues may lead to trouble-
some deposits and, in vapor offtake systems, residues that are
2. Referenced Documents
carried over can foul regulating equipment. Those that remain
2.1 ASTM Standards:
will accumulate, can be corrosive, and will contaminate
D 96 Test Methods for Water and Sediment in Crude Oil by
following product. Water, particularly if alkaline, can cause
2
Centrifuge Method (Field Procedure)
failure of regulating equipment and corrosion of metals.
D 1796 Test Method for Water and Sediment in Fuel Oils by
3
the Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure)
6. Apparatus
3
D 1835 Specification for Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
4 6.1 Centrifuge Tube, 100-mL graduated, conforming to
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
dimensions given in Fig. 1. The first 0.5 mL shall be graduated
in 0.05-mL increments. The shape of the lower tip of the tube
1
is especially important. The taper shall be uniform and the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
bottom shall be rounded as shown in Fig. 1. Tubes shall be
D02.Hon Liquid Petroleum Gas.
made of thoroughly annealed heat-resistant glass. Volumetric
Current edition approved April 10, 2002. Published June 2002. Originally
e1
published as D 2158 – 63 T. Last previous edition D 2158 – 97 .
2
Discontinued; see 2000 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
4 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03. Available from Institute of Petroleum, 61 Cavendish St., London, NIM 8AR.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 2158
FIG. 1 Cone–Shaped Centrifuge Tube, 203 mm
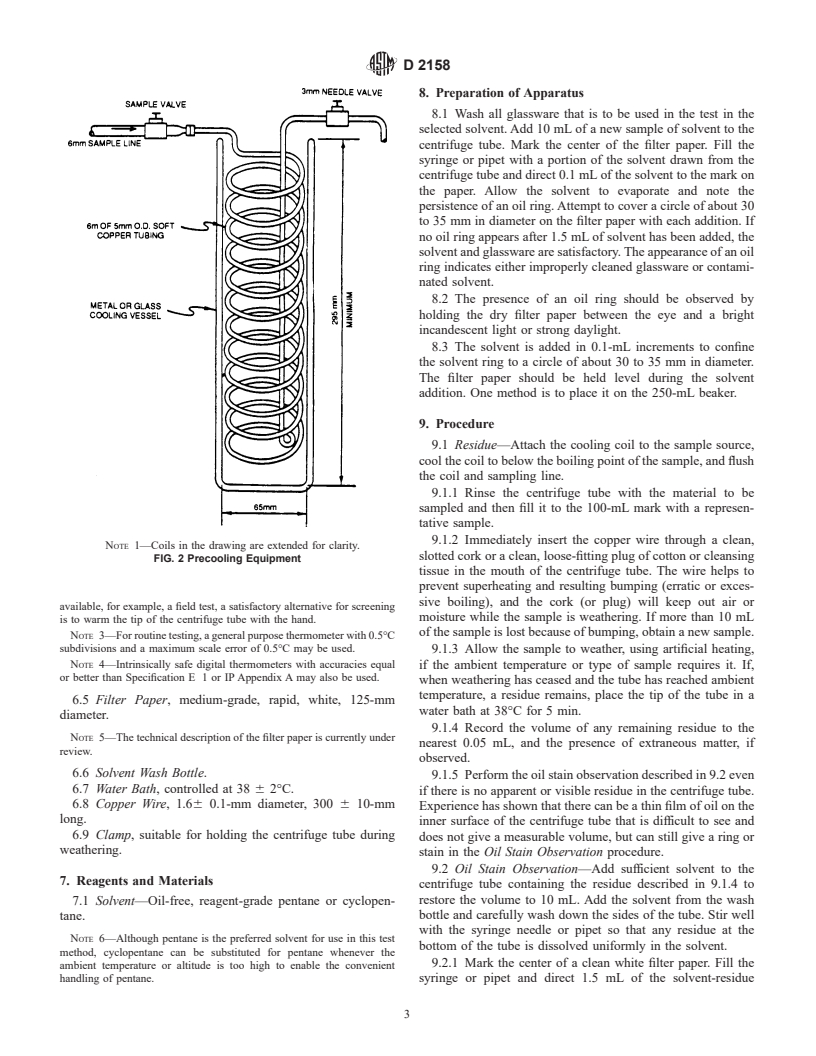
graduation tolerances, based on air-free water at 20°C, are 6.2 Cooling Coil, a minimum length of6mof5to 7-mm
given in Table 1. Detailed requirements for centrifuge tubes outside diameter c
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.