ASTM D6667-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Total Volatile Sulfur in Gaseous Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum Gases by Ultraviolet Fluorescence
Standard Test Method for Determination of Total Volatile Sulfur in Gaseous Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum Gases by Ultraviolet Fluorescence
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The sulfur content of LPG, used for fuel purposes, contributes to SOx emissions and can lead to corrosion in engine and exhaust systems. Some process catalysts used in petroleum and chemical refining can be poisoned by sulfur bearing materials in the feed stocks. This test method can be used to determine sulfur in process feeds, to measure sulfur in finished products, and can also be used for compliance determinations when acceptable to a regulatory authority.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total volatile sulfur in gaseous hydrocarbons and liquefied petroleum (LP) gases. It is applicable to analysis of natural, processed, and final product materials. Precision has been determined for sulfur in gaseous hydrocarbons in the range of 1 mg/kg to 100 mg/kg and for sulfur in LP gases in the range of 1 mg/kg to 196 mg/kg (Note 1).
Note 1: An estimate of pooled limit of quantification (PLOQ), information regarding sample stability and other general information derived from the interlaboratory studies on precision can be referenced in the ASTM research reports.2,3
1.2 This test method may not detect sulfur compounds that do not vaporize under the conditions of the test.
1.3 This test method is applicable for total volatile sulfur determination in LP gases containing less than 0.35 % (mass/mass) halogen(s).
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 3.1 and Sections 6 and 7 for specific warning statements.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D6667 −21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Total Volatile Sulfur in Gaseous
Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum Gases by Ultraviolet
1
Fluorescence
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6667; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
volatile sulfur in gaseous hydrocarbons and liquefied petro-
leum (LP) gases. It is applicable to analysis of natural,
2. Referenced Documents
processed, and final product materials. Precision has been
4
2.1 ASTM Standards:
determined for sulfur in gaseous hydrocarbons in the range of
D1070 Test Methods for Relative Density of Gaseous Fuels
1 mg⁄kg to 100 mg⁄kg and for sulfur in LP gases in the range
D1265 Practice for Sampling Liquefied Petroleum (LP)
of 1 mg⁄kg to 196 mg⁄kg (Note 1).
Gases, Manual Method
NOTE 1—An estimate of pooled limit of quantification (PLOQ),
D2163 Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbons in
information regarding sample stability and other general information
Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases and Propane/Propene
derived from the interlaboratory studies on precision can be referenced in
2,3
Mixtures by Gas Chromatography
the ASTM research reports.
D2421 Practice for Interconversion of Analysis of C and
5
1.2 This test method may not detect sulfur compounds that
Lighter Hydrocarbons to Gas-Volume, Liquid-Volume, or
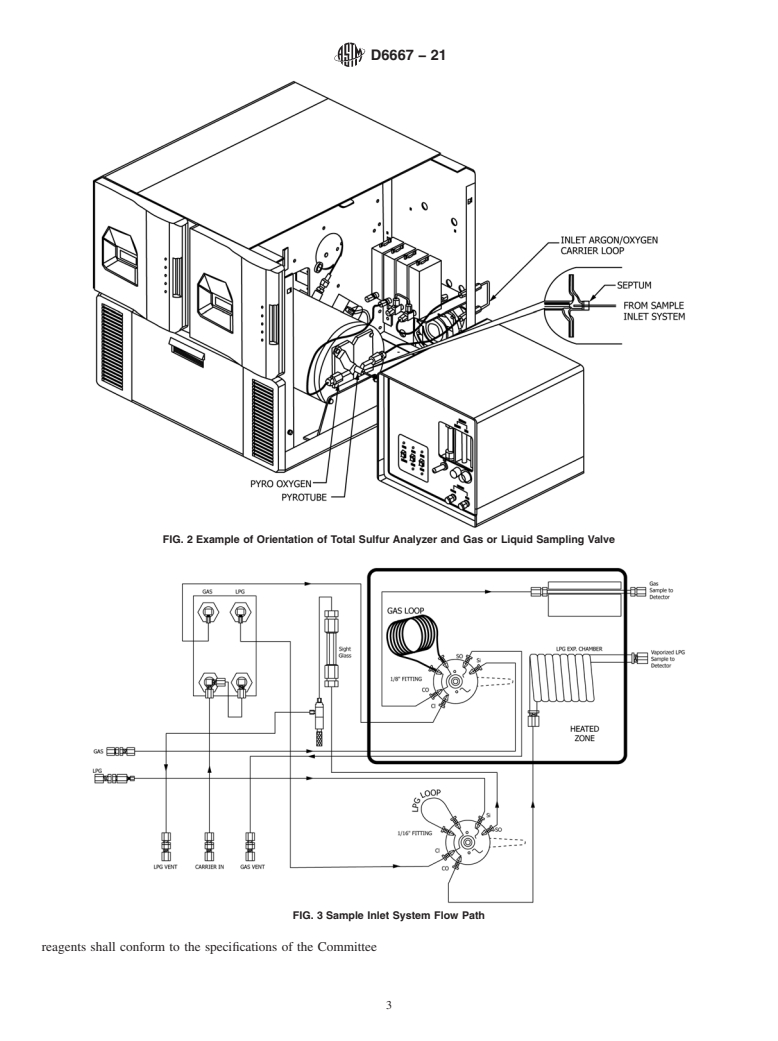
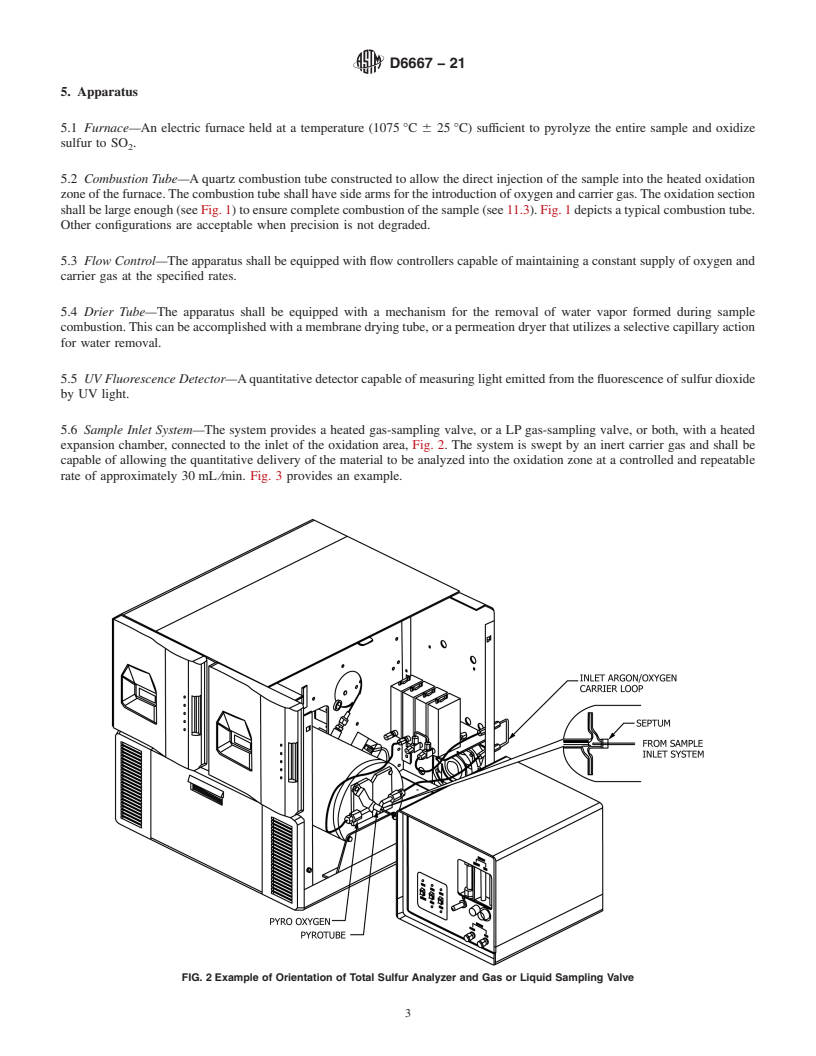
do not vaporize under the conditions of the test.
Mass Basis
1.3 This test method is applicable for total volatile sulfur
D2598 Practice for Calculation of Certain Physical Proper-
determination in LP gases containing less than 0.35 % (mass/
ties of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases from Composi-
mass) halogen(s).
tional Analysis
D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Float-
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
ing Piston Cylinder
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
D5287 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Gaseous Fuels
standard.
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Measurement System Performance
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
F307 Practice for Sampling Pressurized Gas for Gas Analy-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
sis
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5
2.2 Gas Processor Association (GPA) Standards:
See 3.1 and Sections 6 and 7 for specific warning statements.
GPA 2166 Obtaining Natural Gas Samples for Analysis by
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
Gas Chromatography
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
GPA 2174 Obtaining Liquid Hydrocarbon Samples for
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Analysis by Gas Chromatography
1
3. Summary of Test Method
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
3.1 Aheatedsamplevalveisusedtoinjectgaseoussamples.
Subcommittee D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) samples are injected by a
Current edition approved April 1, 2021. Published May 2021. Originally
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as D6667 – 14 (2019).
DOI: 10.1520/D6667-21.
2 4
Supporting data have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters and may For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
beobtainedbyrequestingResearchReportRR:D02-1506.ContactASTMCustomer contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Service at service@astm.org. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
3
Supporting data have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters and may the ASTM website.
5
beobtainedbyrequestingResearchReportRR:D02-1784.ContactASTMCustomer Available from Gas ProcessorsAssociation (GPA), 6526 E. 60th St.,Tulsa, OK
Service at service@astm.org. 74145.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6667 − 14 (Reapproved 2019) D6667 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Total Volatile Sulfur in Gaseous
Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum Gases by Ultraviolet
1
Fluorescence
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6667; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total volatile sulfur in gaseous hydrocarbons and liquefied petroleum (LP) gases.
It is applicable to analysis of natural, processed, and final product materials. Precision has been determined for sulfur in gaseous
hydrocarbons in the range of 1 mg ⁄kg to 100 mg ⁄kg and for sulfur in LP gases in the range of 1 mg ⁄kg to 196 mg ⁄kg (Note 1).
NOTE 1—An estimate of pooled limit of quantification (PLOQ), information regarding sample stability and other general information derived from the
2,3
interlaboratory studies on precision can be referenced in the ASTM research reports.
1.2 This test method may not detect sulfur compounds that do not vaporize under the conditions of the test.
1.3 This test method is applicable for total volatile sulfur determination in LP gases containing less than 0.35 % (mass/mass)
halogen(s).
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. See 3.1 and Sections 6 and 7 for specific warning statements.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
4
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1070 Test Methods for Relative Density of Gaseous Fuels
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
Current edition approved May 1, 2019April 1, 2021. Published July 2019May 2021. Originally approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 20142019 as
D6667 – 14.D6667 – 14 (2019). DOI: 10.1520/D6667-14R19.10.1520/D6667-21.
2
Supporting data have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters and may be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:D02-1506. Contact ASTM Customer
Service at service@astm.org.
3
Supporting data have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters and may be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:D02-1784. Contact ASTM Customer
Service at service@astm.org.
4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6667 − 21
D1265 Practice for Sampling Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases, Manual Method
D2163 Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbons in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases and Propane/Propene Mixtures by
Gas Chromatography
D2421 Practice for Interconversion of Analysis of C and Lighter Hydrocarbons to Gas-Volume, Liquid-Volume, or Mass Basis
5
D2598 Practice for Calculation of Certain Physical Properties of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases from Compositional Analysis
D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Floating Piston Cylinder
D5287 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Gaseous Fuels
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical Measure-
ment System Performance
F307 Practice for Sampling Pressurized Gas for Gas Analysis
5
2.2 Gas Processor Association (GPA) Standards:
GPA 2166 Obtaining Natural Gas Samples for Analysis by Gas Chroma
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.