ASTM B790/B790M-11
(Practice)Standard Practice for Structural Design of Corrugated Aluminum Pipe, Pipe-Arches, and Arches for Culverts, Storm Sewers, and Other Buried Conduits
Standard Practice for Structural Design of Corrugated Aluminum Pipe, Pipe-Arches, and Arches for Culverts, Storm Sewers, and Other Buried Conduits
ABSTRACT
This practice is intended for the structural design of corrugated aluminum pipe and pipe-arches, and aluminum structural plate pipe, pipe-arches, and arches for use as culverts, storm sewers, and other buried conduits. This practice is for pipe installed in a trench or embankment and subjected to highway, railroad, and aircraft loadings. It must be recognized that buried corrugated aluminum pipes are composite structures made up of the aluminum ring and the soil envelope, and both elements play a vital part in the structural design. Corrugated aluminum pipe and pipe-arches shall be of annular fabrication using riveted seams, or of helical fabrication having a continuous lockseam. Structural plate pipe, pipe-arches, and arches shall be fabricated in separate plates that when assembled at the job site by bolting form the required shape. The design load or pressure on a pipe is comprised of earth load, live load, and impact load. Strength requirements for wall strength, buckling strength, and seam strength may be determined by either the allowable stress design (ASD) method (involves calculation of required wall area and critical buckling stress) or the load and resistance factor design (LRFD) method (involves calculation of factored loads, factored thrust, factored resistance, wall resistance, and seam resistance). Requirements for handling and installation rigidity and minimum cover are detailed. Design considerations for deflection, smooth-line pipe, spiral-rib pipe, pipe-arch, pipe materials, soil, minimum spacing, end treatment, abrasive or corrosive conditions, construction and installation, and structural plate arches are provided.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice is intended for the structural design of corrugated aluminum pipe and pipe-arches, and aluminum structural plate pipe, pipe-arches, and arches for use as culverts and storm sewers and other buried conduits. This practice is for pipe installed in a trench or embankment and subjected to highway, railroad, and aircraft loadings. It must be recognized that a buried corrugated aluminum pipe is a composite structure made up of the aluminum ring and the soil envelope, and both elements play a vital part in the structural design of this type of structure.
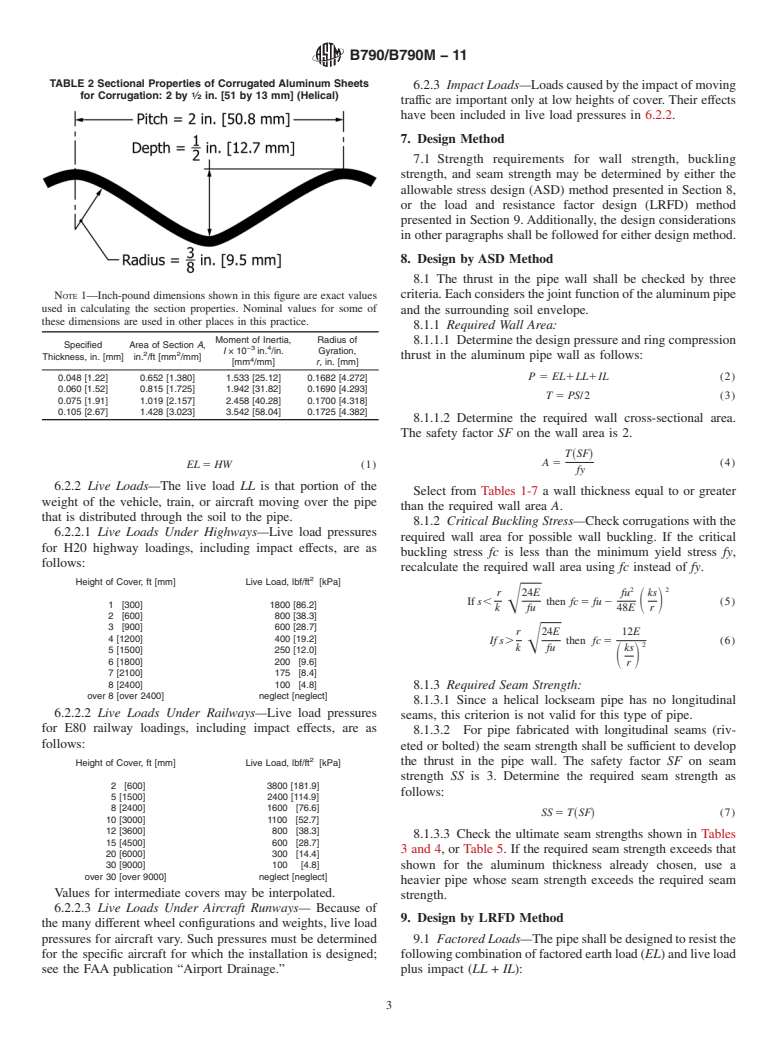
1.2 Corrugated aluminum pipe and pipe-arches shall be of annular fabrication using riveted seams, or of helical fabrication having a continuous lockseam.
1.3 Structural plate pipe, pipe-arches, and arches are fabricated in separate plates that when assembled at the job site by bolting form the required shape.
1.4 This specification is applicable to design in inch-pound units as Specification B 790 or in SI units as Specification B 790M. Inch-pound units and SI units are not necessarily equivalent. SI units are shown in brackets in the text for clarity, but they are the applicable values when the design is done in accordance with Specification B 790M.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B790/B790M − 11
Standard Practice for
Structural Design of Corrugated Aluminum Pipe, Pipe-
Arches, and Arches for Culverts, Storm Sewers, and Other
1
Buried Conduits
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B790/B790M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This practice is intended for the structural design of 2.1 ASTM Standards:
corrugated aluminum pipe and pipe-arches, and aluminum B745/B745MSpecification for Corrugated Aluminum Pipe
structuralplatepipe,pipe-arches,andarchesforuseasculverts for Sewers and Drains
andstormsewersandotherburiedconduits.Thispracticeisfor B746/B746MSpecification for CorrugatedAluminumAlloy
pipe installed in a trench or embankment and subjected to Structural Plate for Field-Bolted Pipe, Pipe-Arches, and
highway, railroad, and aircraft loadings. It must be recognized Arches
that a buried corrugated aluminum pipe is a composite struc- B788/B788MPractice for Installing Factory-Made Corru-
ture made up of the aluminum ring and the soil envelope, and gated Aluminum Culverts and Storm Sewer Pipe
both elements play a vital part in the structural design of this B789/B789MPractice for Installing Corrugated Aluminum
type of structure. Structural Plate Pipe for Culverts and Sewers
D698Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Character-
1.2 Corrugated aluminum pipe and pipe-arches shall be of
3
istics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12 400 ft-lbf/ft (600
annular fabrication using riveted seams, or of helical fabrica-
3
kN-m/m ))
tion having a continuous lockseam.
D1556Test Method for Density and Unit Weight of Soil in
1.3 Structural plate pipe, pipe-arches, and arches are fabri-
Place by Sand-Cone Method
cated in separate plates that when assembled at the job site by
D2167Test Method for Density and Unit Weight of Soil in
bolting form the required shape.
Place by the Rubber Balloon Method
D2487Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering
1.4 This specification is applicable to design in inch-pound
units as Specification B790 or in SI units as Specification Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System)
D2937Test Method for Density of Soil in Place by the
B790M. Inch-pound units and SI units are not necessarily
equivalent.SIunitsareshowninbracketsinthetextforclarity, Drive-Cylinder Method
D6938Test Method for In-Place Density and Water Content
but they are the applicable values when the design is done in
accordance with Specification B790M. of Soil and Soil-Aggregate by Nuclear Methods (Shallow
Depth)
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3
2.2 FAA Standards:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
AC No. 150/5320-5B, Advisory Circular, “Airport
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Drainage,” Department of Transportation, Federal Avia-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
tion Administration, Publication No. SN-050-007-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
00149-5, 1970
1 2
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B07 on Light For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B07.08 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Corrugated Aluminum Pipe and Corrugated Aluminum Structural Plate. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2011. Published December 2011. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approvedin1990.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2006asB790–00(2006).DOI: Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
10.1520/B0790_B0790M-11. Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B790/B790M − 11
4
2.3 AASHTO Standards:
fy = specified minimum yield strength,
2
LRFD Bridge Design Specifications
= 20 000 lbf/in. [140 MPa] for corrugated alumi-
LRFD Bridge Construction Specifications
num pipe per B745/B745M using Alclad Alloy
3004–H32,
2
3. Terminology
= 24 000 lbf/in. [165 MPa] for all other corrugated
aluminum pipe and structural plate per B745/
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
B745M and B746/B746M,
3.1.1 arch, n—apipeshapethatissupportedonfootingsand
H = depth of fill above top of pipe, ft [m],
does not have a full metal invert.
H
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B790/B790M–00 (Reapproved 2006) Designation: B790/B790M – 11
Standard Practice for
Structural Design of Corrugated Aluminum Pipe, Pipe-
Arches, and Arches for Culverts, Storm Sewers, and Other
1
Buried Conduits
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B790/B790M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This practice is intended for the structural design of corrugated aluminum pipe and pipe-arches, and aluminum structural
platepipe,pipe-arches,andarchesforuseasculvertsandstormsewersandotherburiedconduits.Thispracticeisforpipeinstalled
in a trench or embankment and subjected to highway, railroad, and aircraft loadings. It must be recognized that a buried corrugated
aluminum pipe is a composite structure made up of the aluminum ring and the soil envelope, and both elements play a vital part
in the structural design of this type of structure.
1.2 Corrugated aluminum pipe and pipe-arches shall be of annular fabrication using riveted seams, or of helical fabrication
having a continuous lockseam.
1.3 Structural plate pipe, pipe-arches, and arches are fabricated in separate plates that when assembled at the job site by bolting
form the required shape.
1.4 This specification is applicable to design in inch-pound units as Specification B790 or in SI units as Specification B790M.
Inch-pound units and SI units are not necessarily equivalent. SI units are shown in brackets in the text for clarity, but they are the
applicable values when the design is done in accordance with Specification B790M.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B745/B745M Specification for Corrugated Aluminum Pipe for Sewers and Drains
B746/B746M Specification for Corrugated Aluminum Alloy Structural Plate for Field-Bolted Pipe, Pipe-Arches, and Arches
B788/B788M Practice for Installing Factory-Made Corrugated Aluminum Culverts and Storm Sewer Pipe
B789/B789M Practice for Installing Corrugated Aluminum Structural Plate Pipe for Culverts and Sewers
3 3
D698 Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12 400 ft-lbf/ft (600 kN-m/m ))
D1556 Test Method for Density and Unit Weight of Soil in Place by Sand-Cone Method
D2167 Test Method for Density and Unit Weight of Soil in Place by the Rubber Balloon Method
D2487 Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System) D2922Test Methods
for Density of
Soil and Soil-
Aggregate in
Place by Nuclear
Methods (Shal-
low Depth)
D2937 Test Method for Density of Soil in Place by the Drive-Cylinder Method Test Method for Density of Soil in Place by the
Drive-Cylinder Method
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B07 on Light Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B07.08 on Aluminum
Culvert.
Current edition approved March 1, 2006. Published April 2006. Originally approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as B790–00. DOI:
10.1520/B0790_B0790M-00R06.on Corrugated Aluminum Pipe and Corrugated Aluminum Structural Plate.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2011. Published December 2011. Originally approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as B790–00 (2006). DOI:
10.1520/B0790_B0790M-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B790/B790M – 11
D6938 Test Method for In-Place Density and Water Content of Soil and Soil-Aggregate by Nuclear Methods (Shallow Depth)
3
2.2 FAA Standards:
AC No. 150/5320-5B, Advisory Circular, “Airport Drainage,” Department of Transportation, FederalAviationAdministration,
Publication No. SN-050
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.